The document discusses various nitrogen mustard compounds and their roles as antineoplastic agents, highlighting their mechanisms of action, chemical properties, and therapeutic uses. It details key drugs like mechlorethamine, cyclophosphamide, melphalan, chlorambucil, and carmustine, emphasizing their DNA alkylation activity and applications in treating cancers. The information encompasses their solubility, stability, and clinical implications in oncology.







![chlorombucil
• 4-[4-[bis(2-chloroethyl)amino]phenyl]butanoic acid
• Chlorambucil appears as white to pale beige crystalline or granular powder with a
slight odor. Melting point 65-69°C.
• Insoluble in water .The sodium salt is soluble in water.
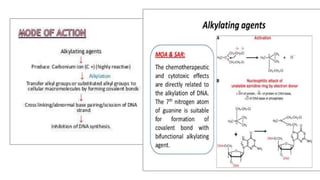
MOA:
• Chlorambucil is an orally-active antineoplastic aromatic nitrogen mustard.
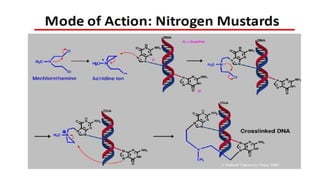
Chlorambucil alkylates and cross-links DNA during all phases of the cell cycle,
resulting in disruption of DNA function, cell cycle arrest, and apoptosis.
USES
• the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. It has a role as an alkylating agent, a
carcinogenic agent, an antineoplastic agent, an immunosuppressive agent and a
drug allergen.Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphomas, and rarely in severe
autoimmune conditions including rheumatoid arthritis, uveitis and nephrotic
syndrome](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/antineoplasticagent-221111093524-b56bf24b/85/Anti-Neoplastic-Agent-ppt-12-320.jpg)

