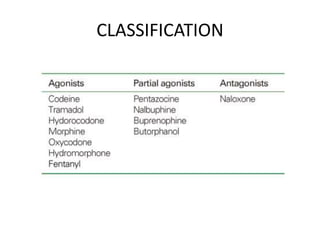
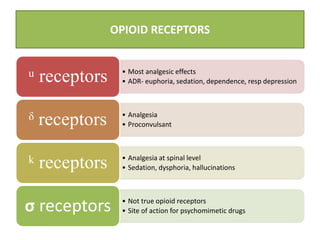
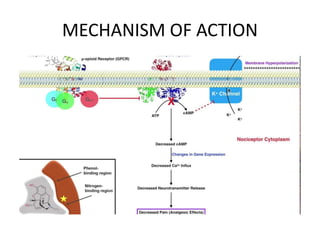
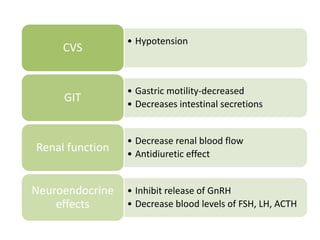
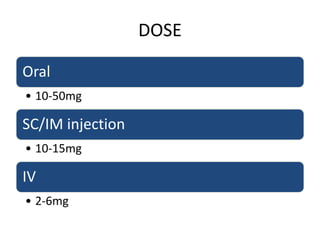
The document discusses various classes of opioid analgesics, including their classifications, mechanisms of action, pharmacologic effects, and therapeutic uses. It highlights key opioids such as morphine, codeine, fentanyl, and methadone, along with partial agonists like buprenorphine and pentazocine, and antagonists including naloxone and naltrexone. Additionally, it briefly mentions other centrally acting analgesics like tapentadol and tramadol for pain management.