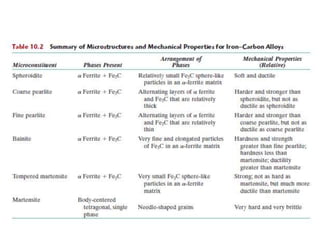
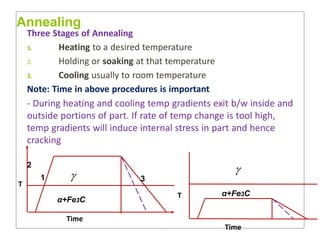
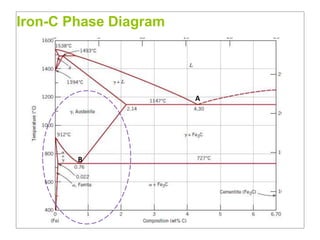
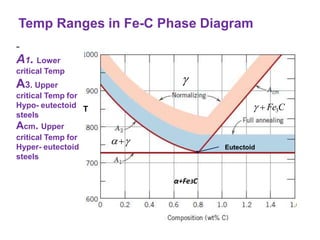
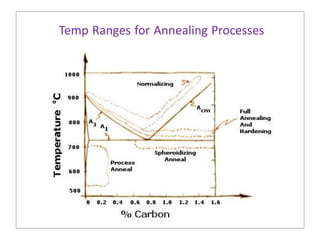
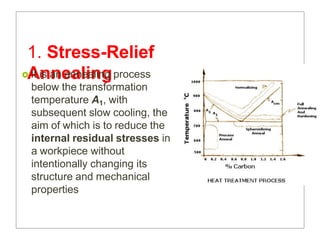
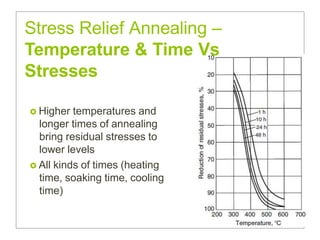
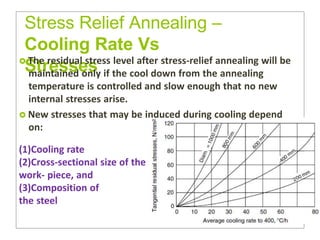
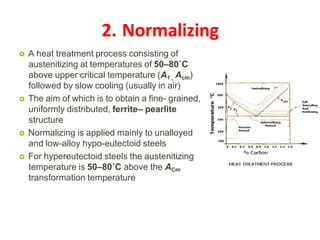
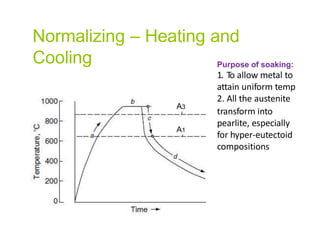
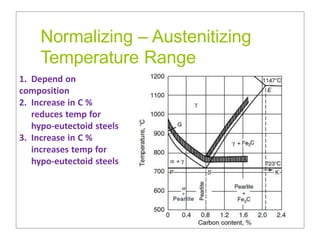
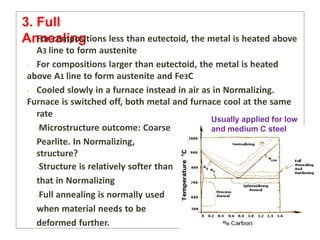
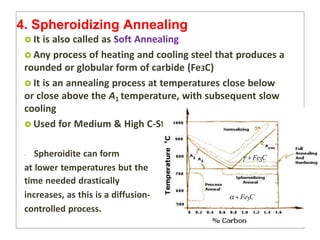
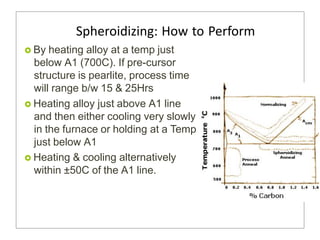
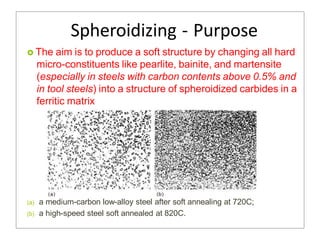
Heat treatment involves heating and cooling metals to alter their physical and chemical properties. There are several types of heat treatments for steel, including annealing, tempering, quenching, and case hardening. Annealing involves heating steel to relieve stresses from cold working and make the metal softer and more ductile. The goal of normalizing is to produce a fine-grained, uniformly distributed ferrite-pearlite microstructure through austenitizing and air cooling. Spheroidizing annealing produces a rounded carbide morphology in steel for improved machinability.