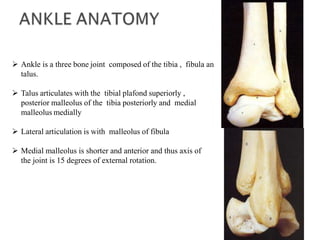
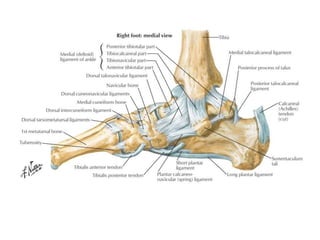
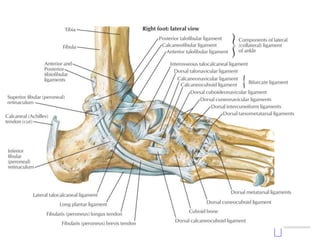
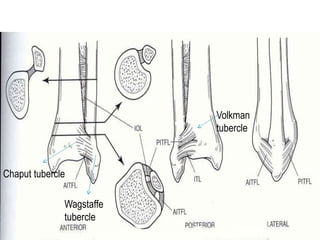
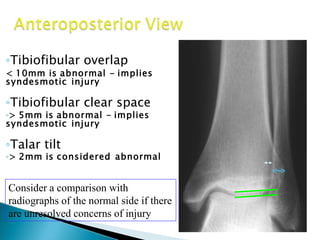
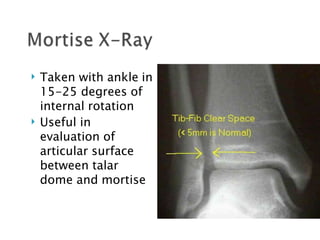
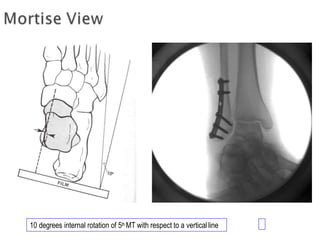
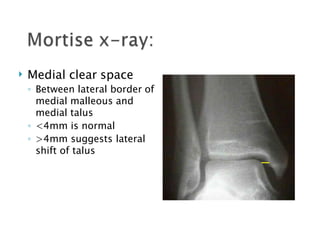
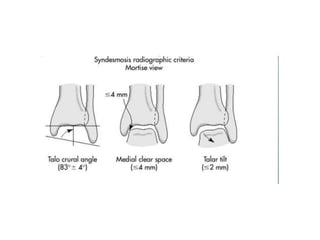
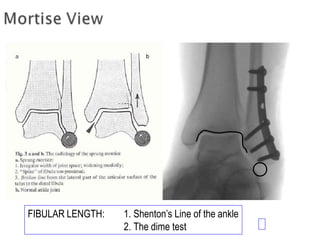
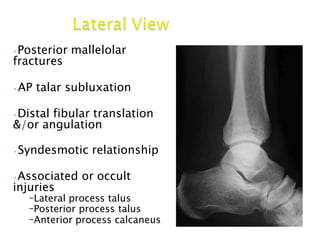
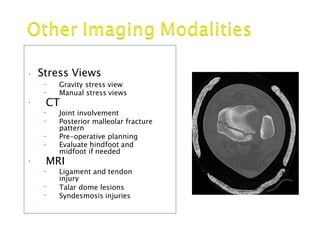
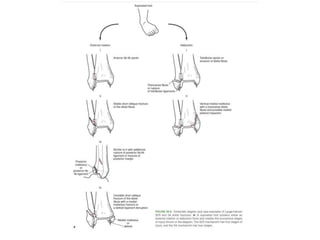
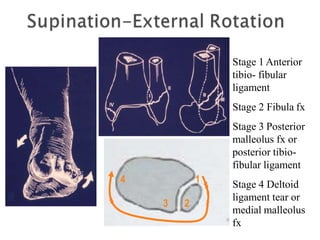
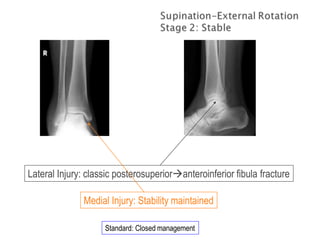
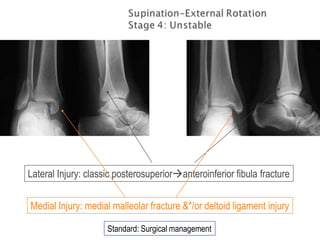
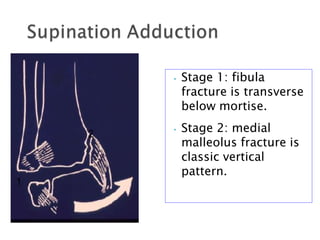
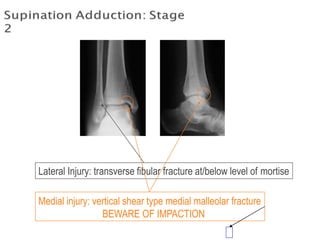
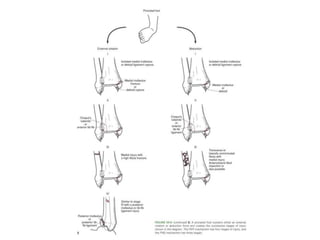
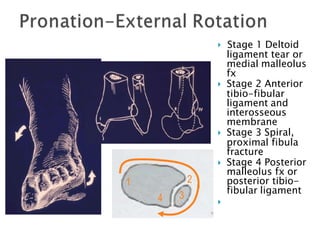
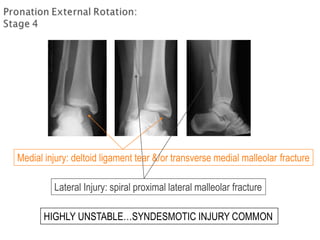
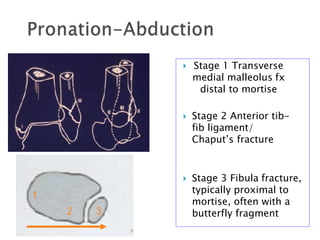
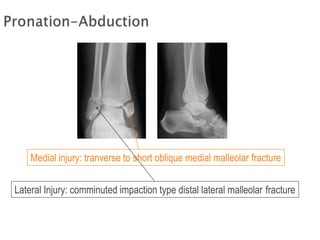
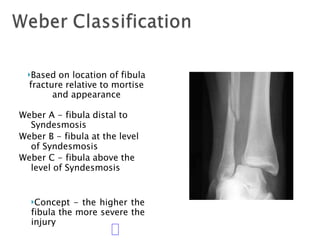
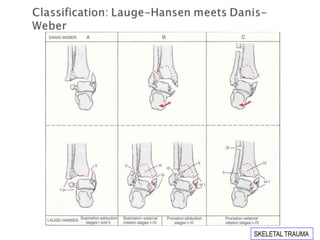
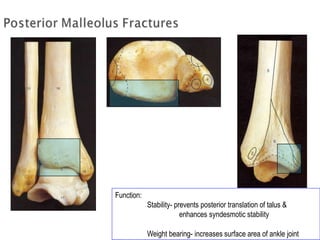
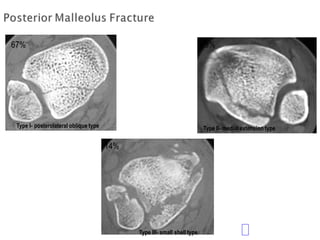
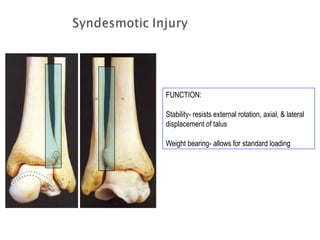
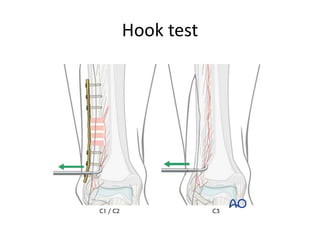
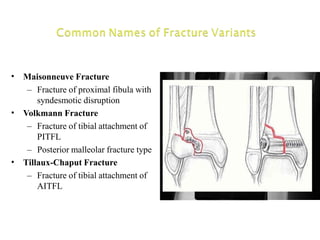
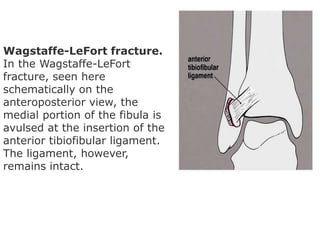
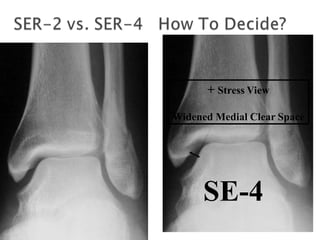
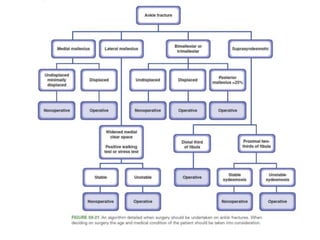
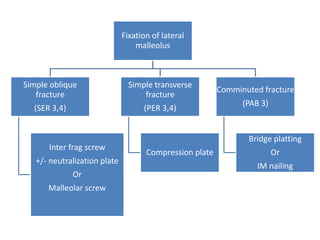
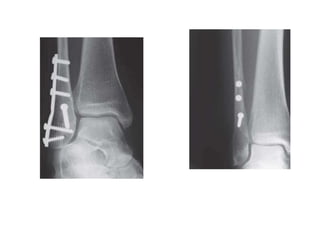
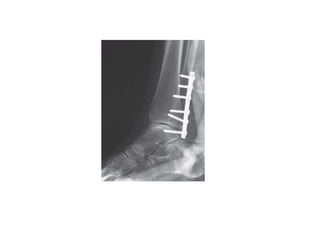
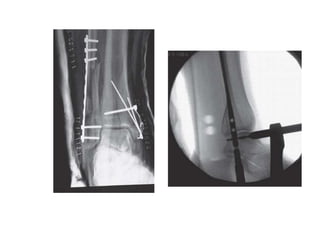
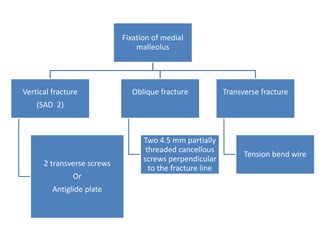
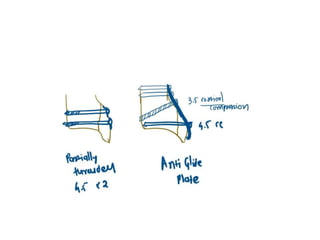
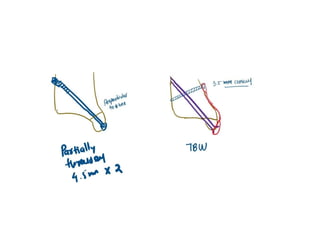
Ankle fractures are common orthopedic injuries that require careful evaluation and management. The ankle is a three-bone joint formed by the tibia, fibula, and talus. Stability is provided by static ligaments like the deltoid ligament and syndesmosis, as well as dynamic stabilizers like muscle forces. Evaluation involves a thorough history, exam, and imaging including plain films and stress views to classify the injury. Classification systems like Lauge-Hansen describe the mechanism of injury. Treatment depends on the fracture pattern and stability, ranging from casting to open reduction and internal fixation. Complications can include malunion, nonunion, infection, and post-traumatic arthritis if anatomy is not restored.