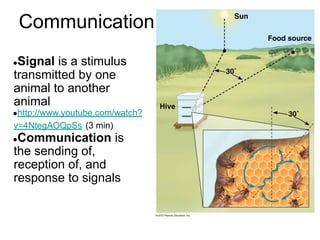
The document discusses various aspects of animal behavior, defining it as actions driven by muscles or glands in response to environmental cues. It categorizes behaviors into innate and learned, explores the influence of genetics and environment, and outlines different learning types, including habituation, imprinting, and social learning. Additionally, it touches on survival mechanisms, communication methods, social interactions, and emotional aspects of animals.