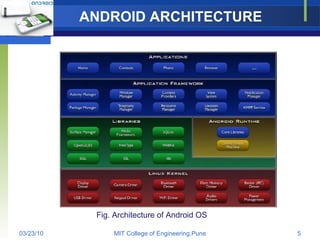
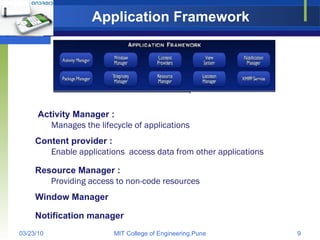
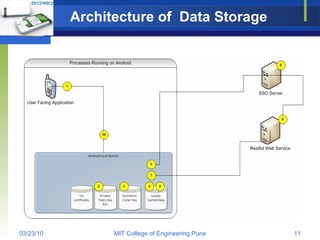
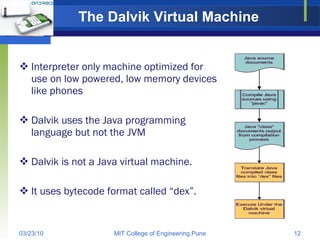
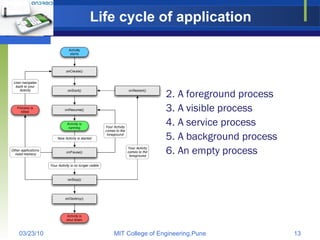
Android is an open source software stack and operating system developed by Google and the Open Handset Alliance. It uses a Linux kernel with middleware, libraries and APIs written in C/C++ and application software running on an application framework and virtual machine. The Android architecture includes secure data storage using SQLite databases and files, as well as an application execution environment using the Dalvik virtual machine to run dex-format files efficiently across multiple processes with an activity-based lifecycle.