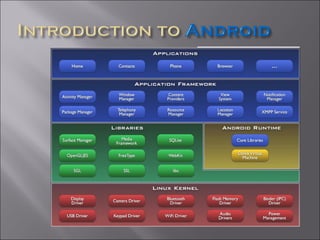
Android is an open source software platform for mobile devices based on the Linux kernel. It includes APIs for app development, core applications like email and maps, and services like notifications and activity management. At its core are the Dalvik virtual machine, C/C++ libraries, and underlying Linux system functionality that allow Android to run efficiently on various hardware configurations and platforms.