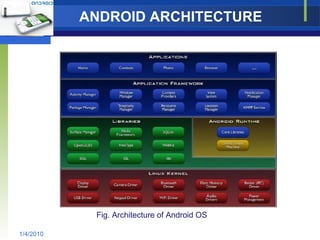
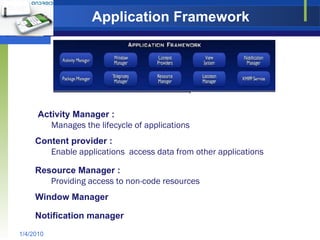
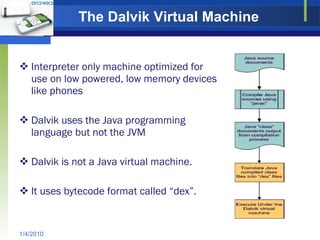
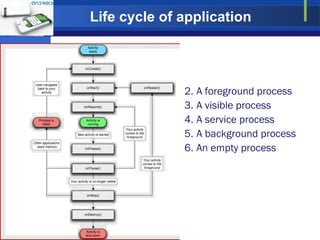
The document provides an overview of the Android operating system, including its architecture, development tools, and application lifecycle. It describes Android's core components like the Linux kernel, libraries, Dalvik virtual machine, and application framework. It also covers the anatomy of application development using the Android SDK, emulator, and debugging tools like DDMS. In conclusion, it discusses Android's potential beyond mobile devices.