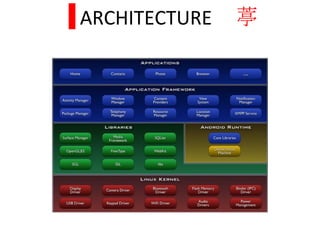
Android is a mobile operating system based on a modified Linux kernel. It is an open source software stack that includes an operating system, middleware, and applications. Android was created to enable software development for small electronic devices and to provide a full phone software stack including applications. It uses architectures like a proven driver model, security and memory management, and efficient computing resource management to function as a stable mobile operating system.