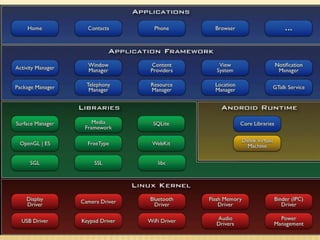
The document provides an overview of Android development, detailing its architecture, core components, and features. It explains that Android is a software stack for mobile devices, based on the Linux kernel, with applications primarily developed in Java using the Dalvik virtual machine. Key topics include the application framework, multimedia capabilities, and the rich set of development tools provided by the Android SDK.