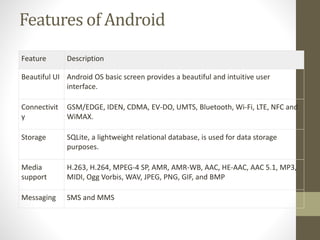
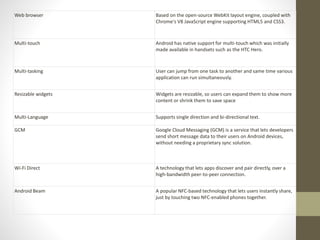
Android is an open source operating system developed by Google and the Open Handset Alliance for use in mobile devices. Key features of Android include a beautiful user interface, support for connectivity technologies, storage using SQLite, media support for common formats, and a web browser based on WebKit. Android applications are typically developed in Java and can be distributed through stores like Google Play.