1) This document discusses the basics of Android development including the Android architecture, tools, and software required.
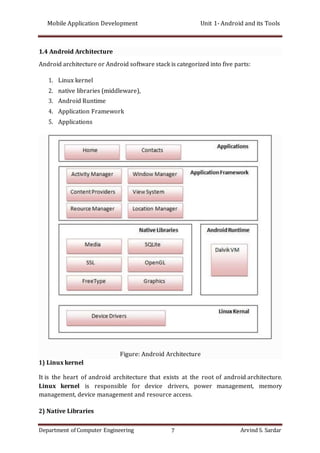
2) The Android architecture consists of the Linux kernel at the bottom layer, with native libraries and the Android runtime in between. At the top are the application framework and applications.
3) Key tools for Android development include Android Studio, the Android SDK, Android emulator, and DDMS for debugging. The SDK includes tools like adb, SQLite, and platform-specific tools.