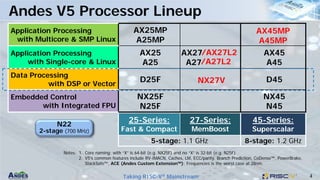
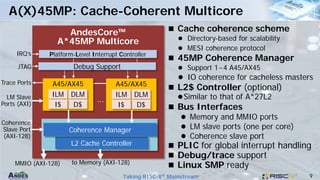
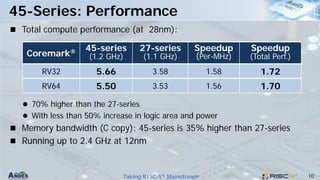
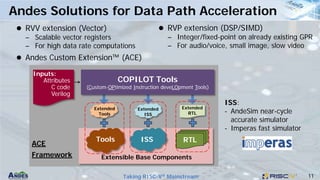
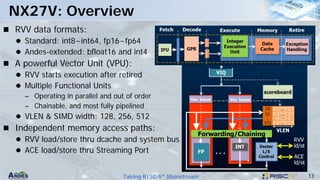
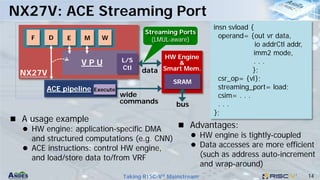
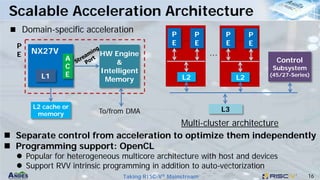
This document discusses Andes Technology Corporation's RISC-V processor IP solutions. It summarizes that Andes is a leading RISC-V CPU IP vendor that provides a portfolio of RISC-V processor cores ranging from embedded control to application processing. It also develops tools like the AndeSight IDE and provides customization services through its AndeSentry security framework and scalable acceleration architecture.