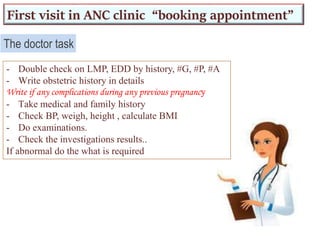
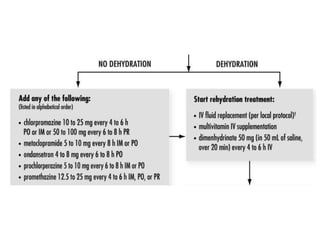
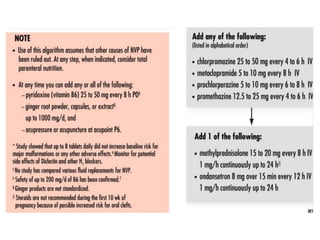
The document provides guidance on evaluating and managing pregnancy. Key points include:
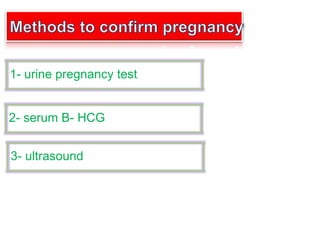
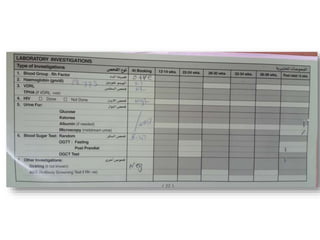
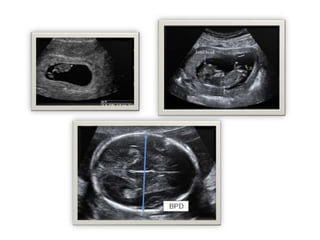
1) Urine pregnancy tests can detect hCG hormone and have 99% accuracy when used correctly. Ultrasound is needed to confirm pregnancy location.
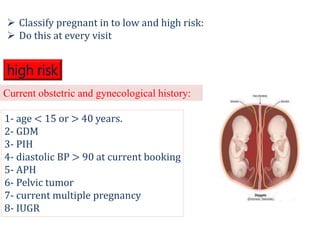
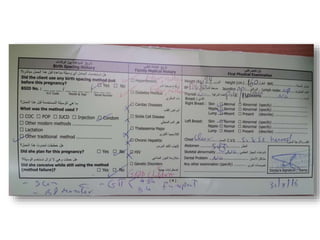
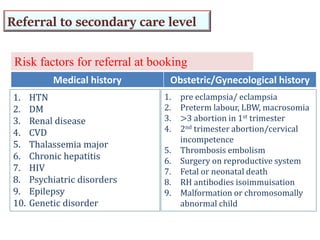
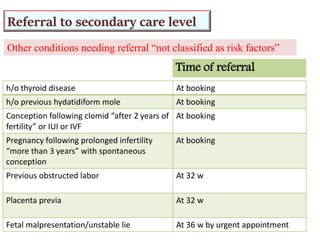
2) Risk factors like medical history, obstetric history, and current symptoms determine if a pregnancy is high or low risk. High risk pregnancies require specialized care.
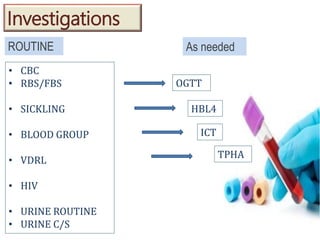
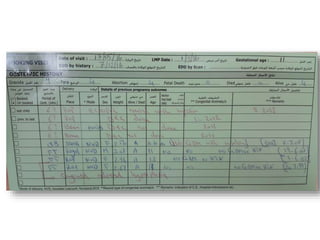
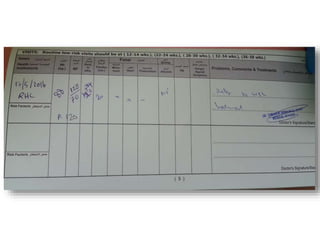
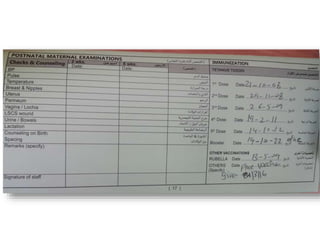
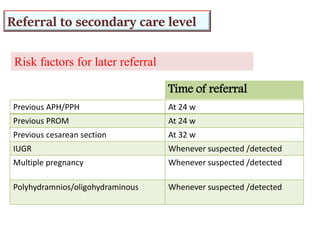
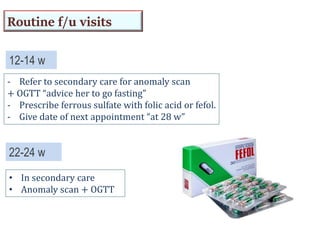
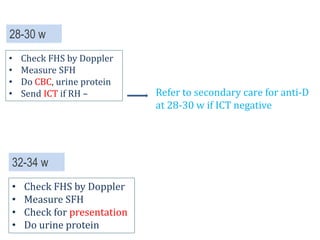
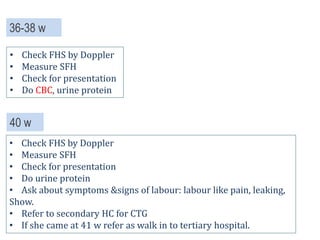
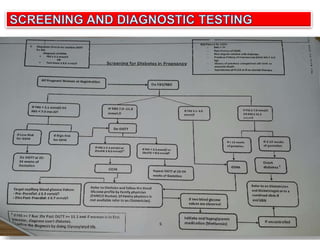
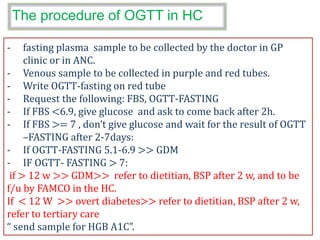
3) Routine prenatal visits include checking vitals, fetal heart rate, size, and position. Labs and tests are interpreted to monitor mother and baby's health. Referrals are made for concerning issues or late pregnancy.