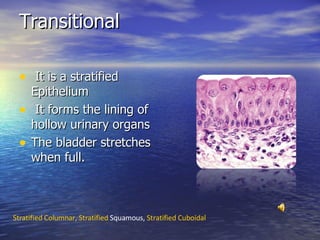
The document discusses the four primary types of tissues in the human body - epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nerve tissue. Epithelial tissue covers organs and forms glands. Connective tissue comprises connective tissue proper, cartilage, bone, and blood. Muscle tissue includes three main types - cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscle. Nerve tissue is composed mainly of neurons and forms the nervous system.