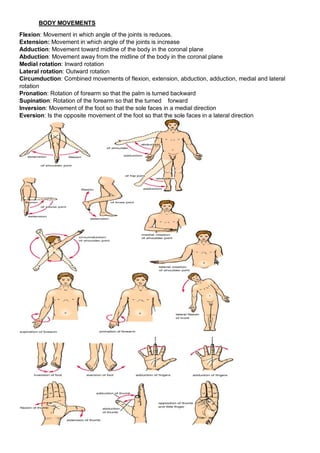
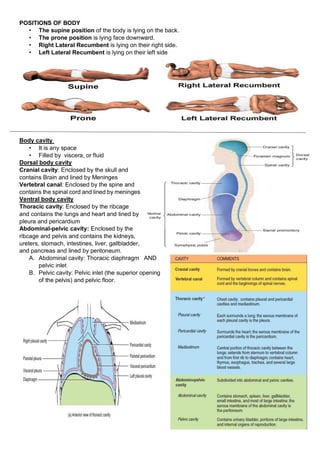
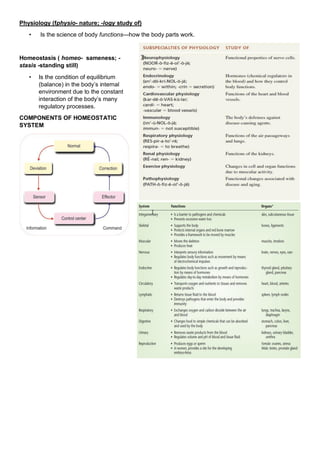
Anatomy is the study of the structure and relationship between body parts, while physiology is the study of how body parts function. The human body maintains homeostasis through various regulatory mechanisms that ensure conditions stay balanced despite internal or external changes. Homeostatic control systems involve stimuli that are detected by receptors and transmitted to control centers which trigger responses through effectors to counteract the original change. Examples of homeostatically regulated variables include body temperature, fluid balance, blood sugar, and blood pressure.