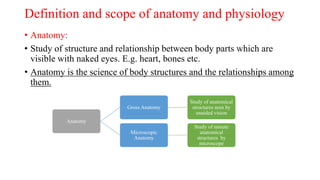
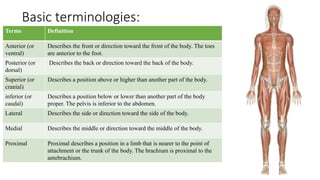
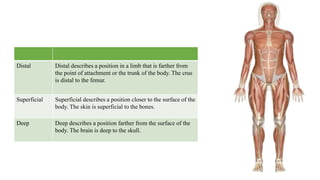
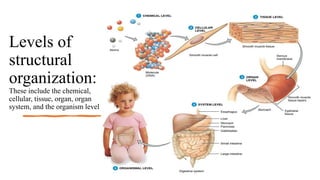
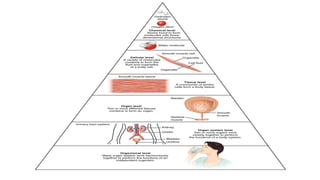
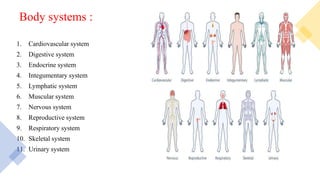
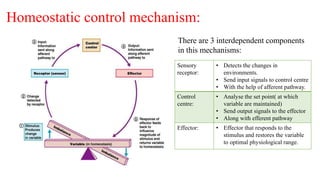
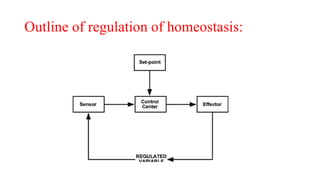
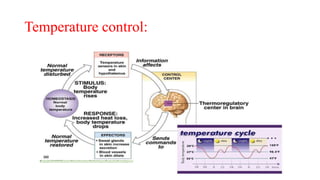
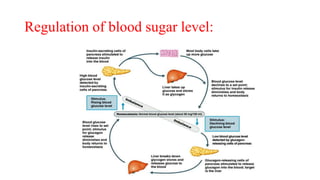
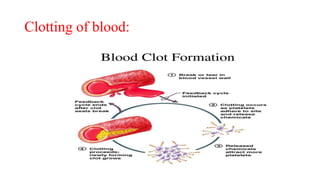
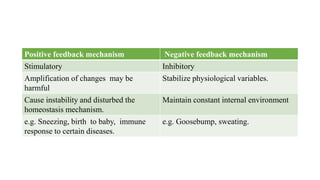
This document provides an introduction to human anatomy and physiology. It defines anatomy as the study of body structures and physiology as the study of body functions. It outlines the basic anatomical terminology used to describe body positions. It also describes the different levels of structural organization in the human body from the chemical and cellular levels up to the organ and organ system levels. The document lists the 11 body systems and 7 basic life processes required to sustain human life. It explains homeostasis as the body's ability to maintain stable internal conditions and outlines some variables that are homeostatically regulated like body temperature, blood pressure, and acid-base balance. It provides examples of positive and negative feedback mechanisms that help control homeostasis.