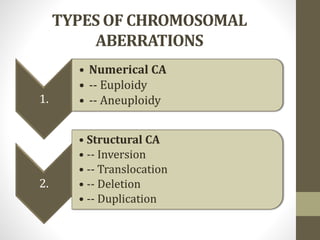
This document discusses chromosomal aberrations, which are abnormalities in human chromosomes that can cause genetic disorders and developmental issues. It defines two main types: numerical aberrations such as aneuploidy where the wrong number of chromosomes are present, and structural aberrations like deletions, duplications, inversions, and translocations that change the structure of chromosomes. Some specific chromosomal disorders are described like Cri-du-chat syndrome caused by deletions on chromosome 5. The causes of aberrations include radiation, spontaneous DNA breaks, and chemicals. Methods to detect aberrations include cytogenetic testing and karyotyping. Clinical effects can include birth defects, intellectual disabilities, growth issues, and some cancers.