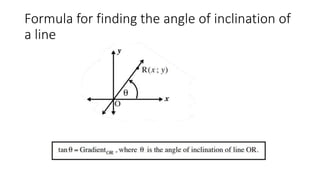
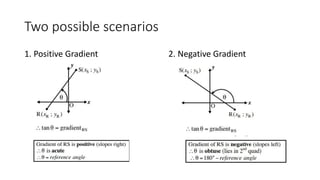
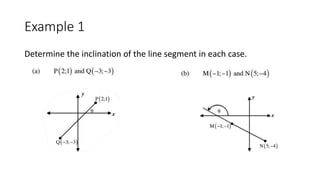
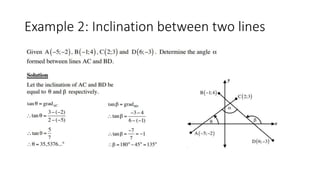
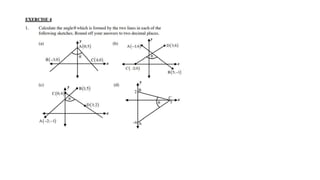
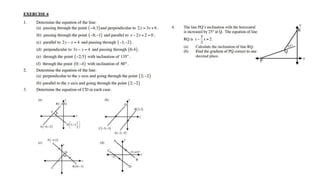
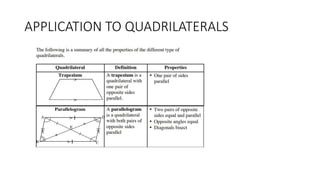
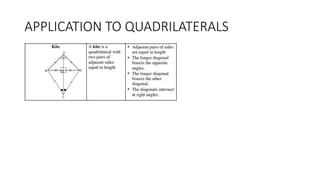
This document provides an introduction to analytical geometry for grade 11 students, focusing on concepts such as the distance between points, midpoints, gradients, and the inclination of lines. It revises key grade 10 topics and introduces equations of straight lines along with applications involving quadrilaterals. The chapter includes examples and scenarios that illustrate how to calculate angles and relationships between lines.