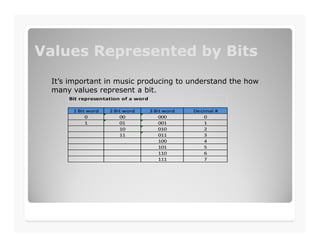
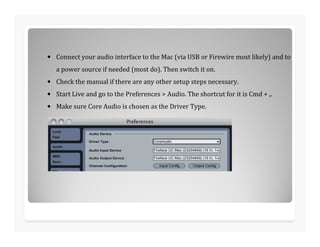
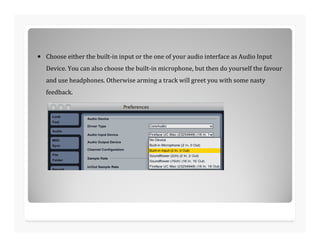
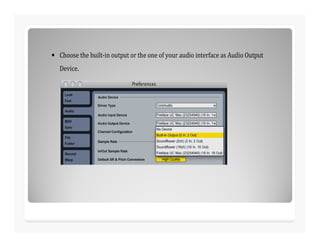
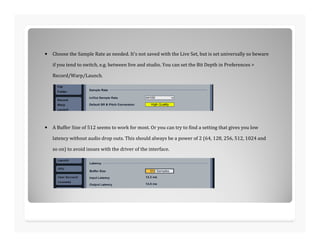
This document discusses analog to digital conversion of sound. It explains that sound is captured through a microphone as changing electrical voltages representing amplitude and frequency. In analog recording, this is recorded continuously on tape. In digital recording, the voltage is sampled at regular time intervals and converted to binary digits representing amplitude and frequency values. Higher bit depths and sample rates allow for more accurate representation of sound. The document provides examples of how binary values represent decimal numbers and discusses setting up an audio interface and DAW for digital audio recording.