This document provides an overview of analgesic models used to study pain and the effects of pain medications. It begins with definitions of pain, nociception, and classifications of acute and chronic pain. It then discusses various types of analgesics and how they are classified. The remainder of the document outlines several experimental animal models used to test analgesics, including thermal, mechanical, electrical, and chemical stimulus models. It also discusses in vitro assays and models of chronic pain conditions. In conclusion, the document provides an in-depth review of the major experimental models employed in analgesic research using animal subjects.






![Concept of Pain in Ayurveda
===tByf;+|;e|
+;Jof;;Ëe]b;fbxif{tif{sDkjt{rfntf]bJoy
fr]i6fbLlgtyfv/k'?ifljzb;'lif/f?
0fj0f{siffolj/;d'vTjzf]ifz"n;'lKt;Íf]rg:tD
egv~htfbLlg r jfof]M sdf{l0f t}/lGjt+
jftljsf/d]jfWoj:o]t ..
r=;"=@).!@](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clusterppt-160519104843/85/ANALGESIC-MODELS-8-320.jpg)




![Analgesics in Ayurveda
• ljbf/LuGwfk[lZgk0fL{a[xtLs06sfl/s}/08sfsf]nL
rGbgf]zL/}nfdw'sfgLlt bz]dfGoËdb{k|
zdgflg ejlGt . -r=;"=$÷$$_
• lkKknLlkKknLd"nrJolrqs>[Ëj]/dl/rfhdf]bfhuG
wfhfhLu08L/f0fLlt bz]dflg z"nk|zdgflg
ejlGt . -r=;"=$÷$%_
• zfns6kmnsbDakBst'Dadf]r/;lz/Lifj~h'n}njfn'
sfzf]sf Olt bz]dflg j]bgf:yfkgflg ejlGt .
-r=;"=$÷$&_](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clusterppt-160519104843/85/ANALGESIC-MODELS-14-320.jpg)




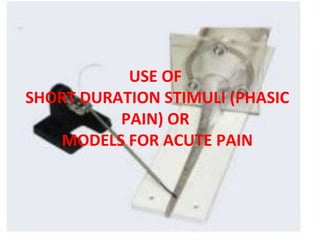



































![; ;DoS;DkGgdGg+ ;'k/LlIft+ ljz'¢dUGoflbif'
k|fu'kgLt+ lzlvgf b[i6dlek|f]lIft+ k|f]If0f}M
k'/M l:ytf] /fhg+ x:ta¢f}iflw/Tg+ ef]ho]t c=;
+=;"= *.$
How the Vaidya examines and certifies
the King’s food:
First, he should test it by fire, then, by
feeding it to a peacock to determine whether
it is poisonous or not. Then, he should chant
holy hymns and chants to ward of evil, and
should ensure that the king has donned and
sacred stones and medicaments as](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clusterppt-160519104843/85/ANALGESIC-MODELS-58-320.jpg)
![rt'ikfbf+ :ofRrt'lj{wM klIf0ff+ lqljwM ..@!..
;LbTofB] e|ldt r, rt'ikbf] j]kt], ttM z"Go ..
dGbfxf/f] ld|ot] Zjf;]g lx rt'y{ j]u] t' ..@@..
Wofolt ljbuM k|yd] j]u] k|efDolt låtLo] t' .
;|:tfËZr t[tLo] ljifj]u] oflt k~rTjd .. –- r=lr=@#÷@!—
@@_
There are four stages in the case of quadrupeds, and
three stages in that of birds. In the animal, in the first
stage, there will be asthenia and whirling; in the
second stage the animal quivers, and in the third,
passes into stupor and takes no food. In the fourth
stage respiration becomes hard and it dies. The bird in
the first stage of poisoning feels depression and in the
second stage whirling in the third stage its limbs get
paralysed and death ensues.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clusterppt-160519104843/85/ANALGESIC-MODELS-59-320.jpg)