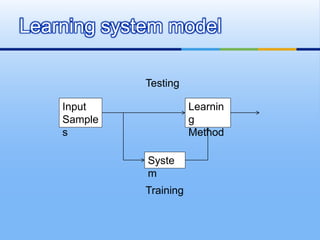
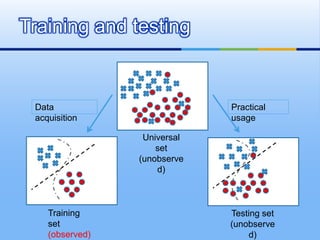
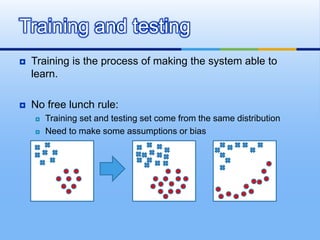
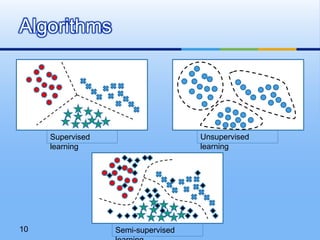
This document provides an overview of machine learning. It defines machine learning as using algorithms to allow computers to learn from empirical data. The document outlines different machine learning models, algorithms, and techniques including supervised learning, unsupervised learning, performance factors, and applications. It concludes that machine learning will become increasingly important and be applied to more solutions.







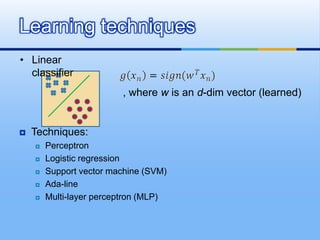
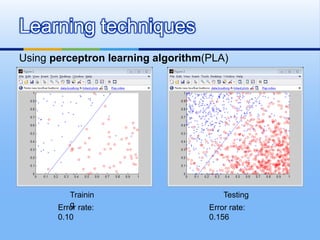
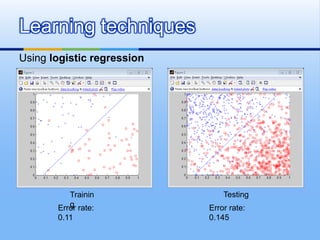
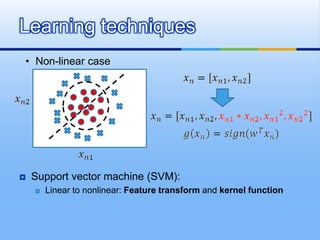



![[1] W. L. Chao, J. J. Ding, “Integrated
Machine Learning Algorithms for Human
Age Estimation”, NTU, 2011.
Reference](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/anoverviewofmachinelearning1-170212052852/85/An-overview-of-machine-learning-1-23-320.jpg)