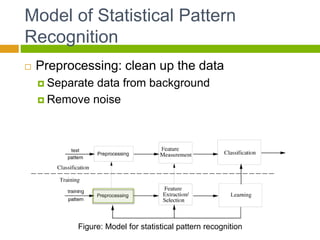
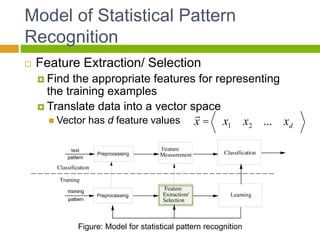
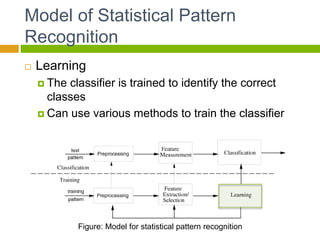
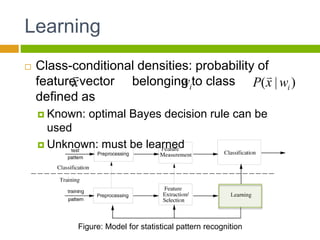
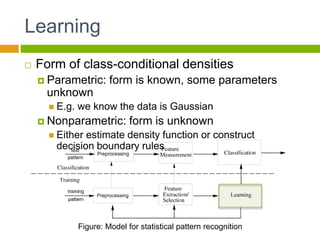
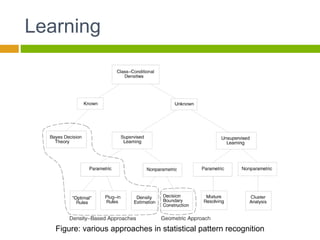
This document provides an introduction to machine learning. It begins with definitions of machine learning and discusses applications such as facial recognition, personalized recommendations, and speech recognition. It also outlines different types of machine learning algorithms including supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning. The document then describes the basic process of statistical pattern recognition, including preprocessing data, extracting features, and performing learning. It provides an overview of the machine learning process and references sources for further information.