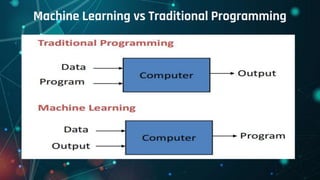
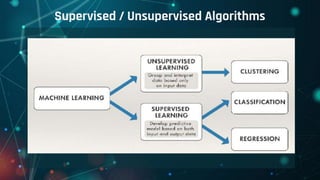
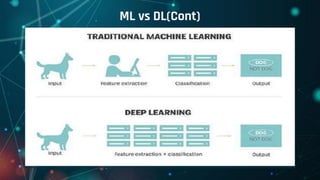
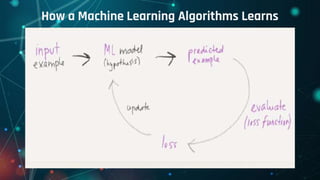
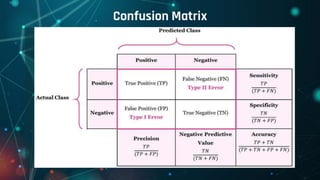
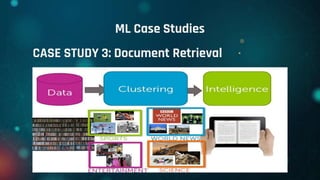
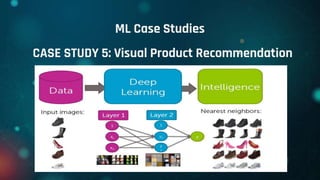
This document provides an overview of machine learning. It defines machine learning as allowing computers to learn from experience without being explicitly programmed. It discusses the differences between machine learning and traditional programming, and describes the main types of machine learning: supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning. Several common algorithms used in supervised and unsupervised learning are also outlined. The document then explains how machine learning algorithms learn and their basic working procedure. It concludes by discussing model evaluation, providing some case studies of machine learning applications, and addressing requirements for math/programming background and platforms for developing machine learning code.