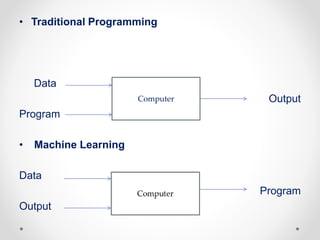
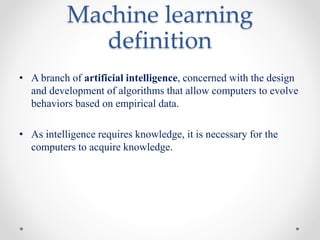
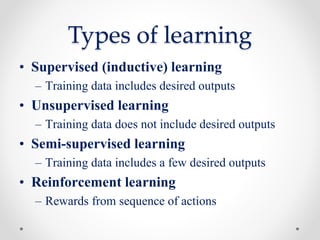
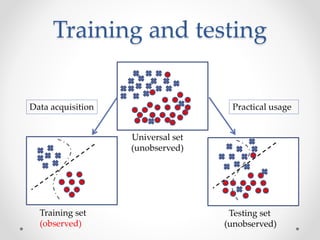
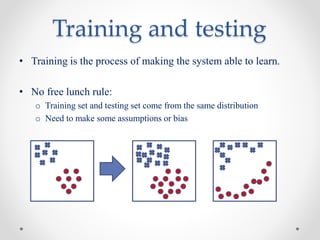
Machine learning is a branch of artificial intelligence focused on developing algorithms that enable computers to learn from empirical data. It encompasses various types of learning, including supervised, unsupervised, semi-supervised, and reinforcement learning, and relies on algorithms to extract useful information from training data. Practical applications range from face and object detection to spam filtering and web advertising.