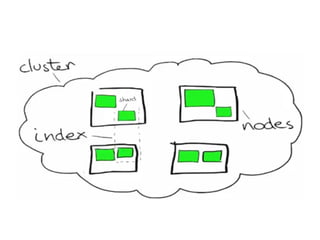
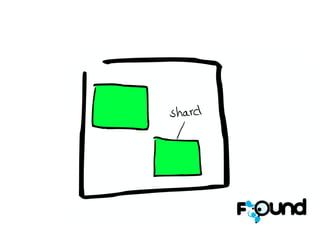
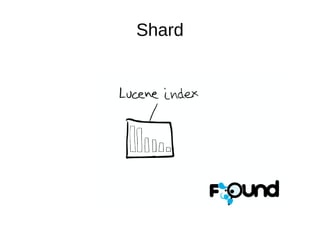
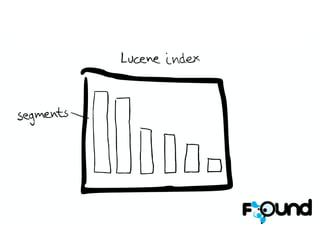
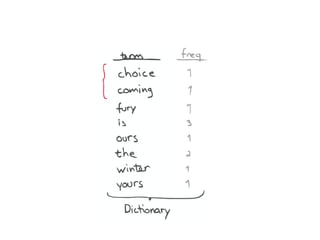
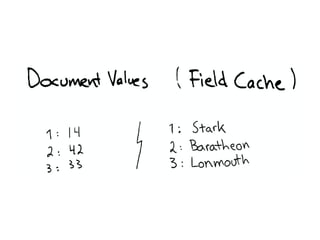
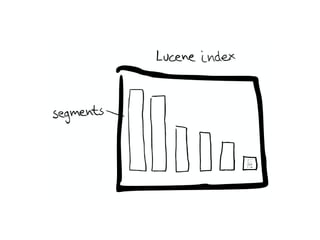
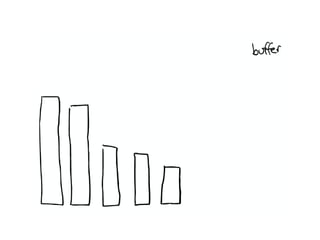
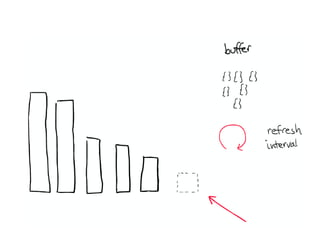
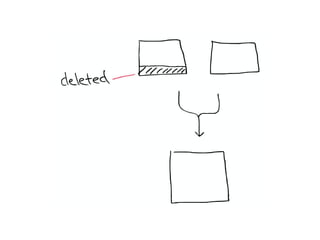
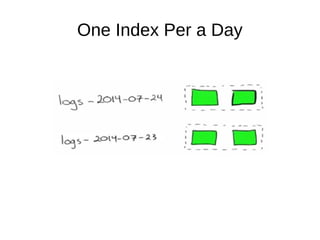
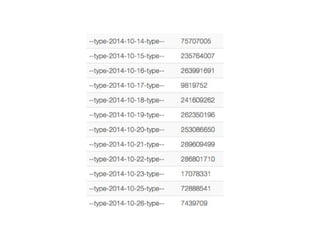
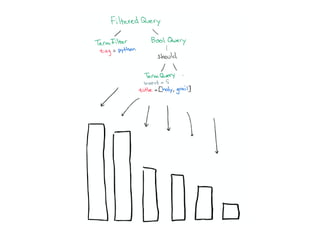
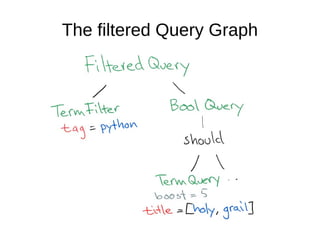
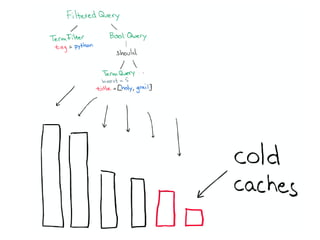
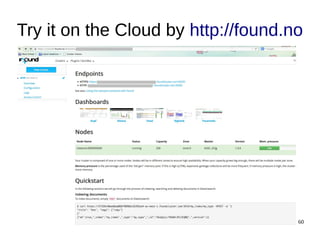
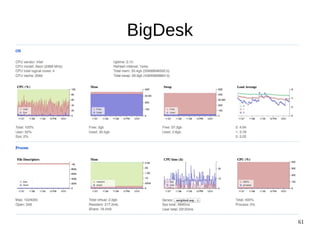
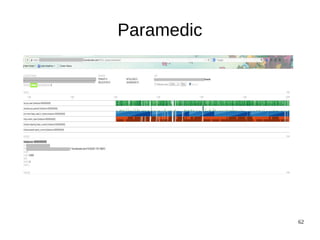
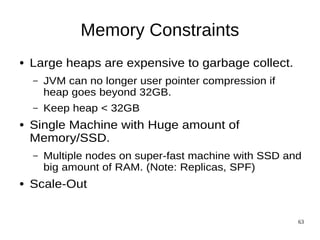
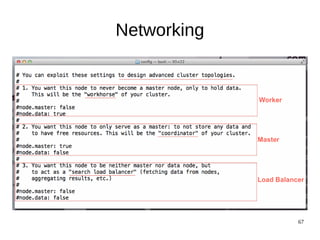
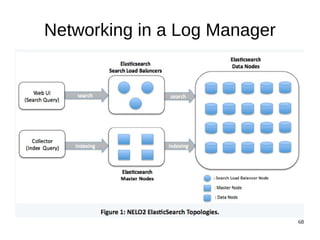
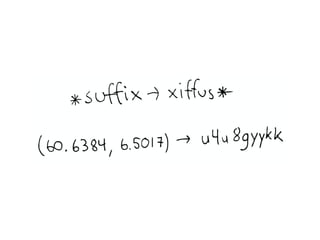The document discusses Elasticsearch, an open-source, full-text search and analytics engine, focusing on its features, performance, and deployment best practices. Key topics include memory management, security, and networking considerations to maintain high reliability and speed in production environments. It emphasizes the importance of having sufficient memory and monitoring tools to avoid performance issues and encourages implementing filters over heavy queries.