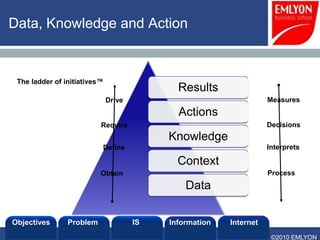
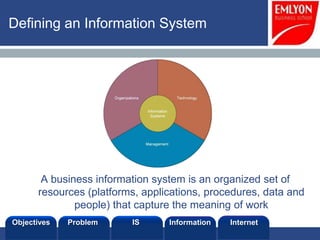
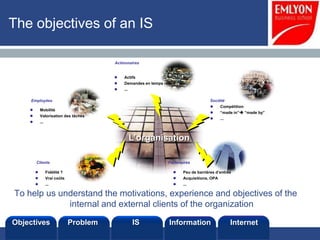
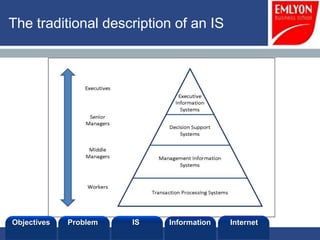
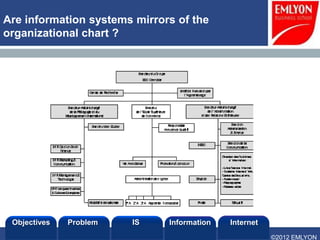
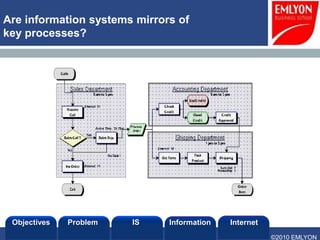
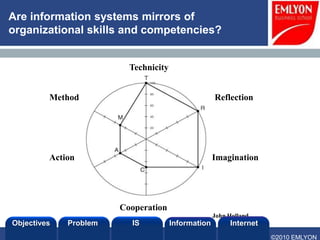
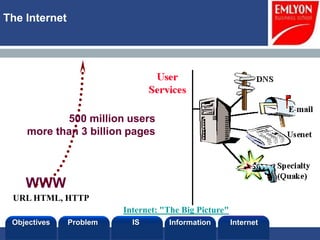
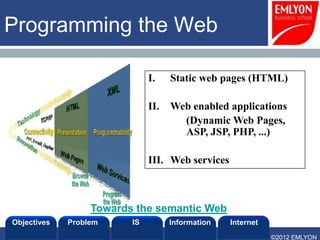
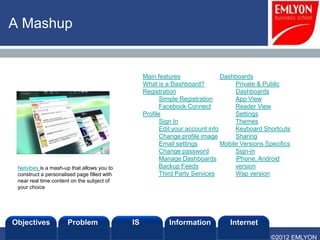
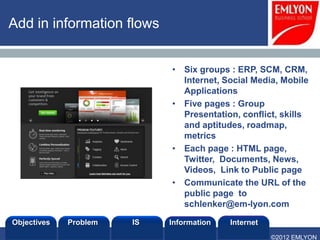
The document provides an introduction to managing information systems. It includes sections on defining an information system, the objectives of an IS, different perspectives of an IS including the financial, logistics, client, and community. It also discusses the role of IT in innovation, the definition of information, structured vs unstructured data, and the objectives of studying information systems. Facilitators of the course are also listed.