Alveolar Osteitis-DRY SOCKET .pdf
- 1. Alveolar Osteitis (Dry Socket) PROF ABBAS AY TAHER
- 4. Dry socket (alveolar osteitis) Dry socket (alveolar osteitis) is a painful dental condition that sometimes happens after you have a permanent adult tooth extracted. Dry socket is when the blood clot at the site of the tooth extraction fails to develop, or it dislodges or dissolves before the wound has healed. One of the most common postoperative complications following the extraction of permanent teeth is a condition known as dry socket. This term has been used in the literature since 1896, when it was first described by ‘’CRAWFORD’’. BIRN labeled the complication ‘fibrinolytic alveolitis’ . which is probably the most accurate of all the terms, but is also the least used in the literature. In most cases, the more generic lay term ‘dry socket’ tends to be used or alveolar osteitis(AO).
- 5. Dry socket It can rises in severity at any time between the first and fifth days after the tooth extraction, accompanied by a partial or complete disintegration blood clot within the alveolar socket and with or without halitosis. It occurs in 0.5–5% of routine dental extractions and 25–30% following the extraction of impacted mandibular wisdom tooth. Females are more frequently affected than males, but this appears to be related to oral contraceptive use rather than any underlying gender predilection . Dry socket is unlike other forms of wound infection, alveolar osteitis occurs frequently in the young age group, although wound infection, in general, is more likely to occur with increasing age. Even, in this era of cell and molecular biology, the specific etiology of the dry socket has not yet been defined. Anumerous local and systemic elements make contributions towards it . Some of the risk factors are difficult surgical extraction, trauma, microbiological origin, smoking, age, and contraceptive pill use. The presence of periodontal disease, acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis, local bone disease, or previous history of developing a dry socket has also been implicated.
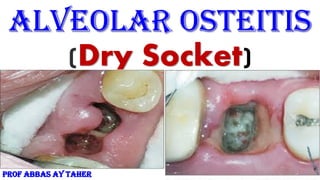
- 6. Clinical and experimental research studies have described an elevated fibrinolytic activity as a major factor for the etiology of the dry socket Synonyms: alveolar osteitis (AO), localized osteitis, postoperative alveolitis, alveolalgia, alveolitis sicca dolorosa, septic socket, necrotic socket, localized osteomyelitis, fibrinolytic alveolitis Sign & symptoms: 1-An empty socket, which is partially or totally devoid of blood clot. Initially, blood clot appears dirty gray and disintegrates,grayish-yellow bony socket bare of granulation tissue 2-Exposed bone may be visible which is extremely painful and sensitive to touch . 3. Some patients may also complain of intense continuous pain irradiating to the ipsilateral ear, temporal region or the eye. 3- Remaining food debris inside the socket that may hide the exposed bone
- 7. 4- Inflammation of the soft tissues around the socket. 5- Delayed Healing of the socket 3. Regional lymphadenopathy (occasionally). True AO, must be distinguished from: conditions in which pre-existing alveolar bone hypervascularity, such as: 1. Vascular or hematological disorders, 2. Radiotherapy-induced osteonecrosis, 3. Osteopetrosis, 4. Paget’s disease 5. Cemento-osseous dysplasia prevent the initial formation of a coagulum. Any other cause of pain on the same side of the face. This becomes costly to the patient as well as to the surgeon, as 45% of patients who develop AO typically require At least four additional postoperative visits in the process of managing this condition.
- 8. Causes of dry socket : Multifactorial origin have been implicated most commonly as etiological, aggravating, and precipitating factors: 1. Oral micro-organisms 2. Difficulty and trauma during surgery 3. Roots or bone fragments remaining in the wound 4. Excessive irrigation or curettage of the alveolus after extraction, spitting alot or drinking through a straw 5. Physical dislodgement of the clot 6. Local blood perfusion & anesthesia 7. Oral contraceptives 8. Smoking 9-Pre-existing infection in the mouth such as necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis or Chronic periodontitis 10-Teeth with pericoronitis are more likely to cause a dry socket after extraction
- 9. Pathogenesis of dry socket Partial or complete lysis and destruction of the blood clot were caused by tissue kinases liberated during inflammation by direct or indirect activation of plasminogen in the blood. Fibrinolytic alveolitis results when fibrinolysis or another proteolytic activity in and around the alveolus was capable of destroying the blood clot The surrounding bone of the alveolus contains,among other components, stable tissue activators that may explain the local fibrinolytic activity in AO Factors influencing the healing: 1. Infection 2. Size of wound 3. Blood supply 4. Resting of part 5. Foreign bodies 6. General condition of the patient
- 10. Prophylactic management of dry socket Prevention of AO can be divided into 1. Non-pharmacological and 2. Pharmacological preventive measures. Non-pharmacological Include a comprehensive history of the patient with identification, and if possible, elimination of risk factors. Risk factors associated with trueAO 1. Previous experience of AO . 2. Deeply impacted mandibular third molar (risk factor is directly proportional to increasing severity of impaction) . 3. Poor oral hygiene of patient . 4. Active or recent history of acute ulcerative gingivitis or pericoronitis . 5. Associated with the tooth to be extracted . 6. Smoking (especially >20 cigarettes per day) . 7. Use of oral contraceptives. 8. Immunocompromised individuals.
- 11. Non-pharmacological measures: 1. Use of good quality current preoperative radiographs 2. Careful planning of the surgery 3. Use of good surgical principles 4. Extractions should be performed with a minimum amount of trauma and maximum amount of care 5. Confirm the presence of blood clot subsequent to extraction (if absent, scrape alveolar walls gently) 6. Wherever possible preoperative oral hygiene measures to reduce plaque levels to a minimum should be instituted 7. Encourage the patient (again) to stop or limit smoking in the immediate postoperative period . 8. Advise patient to avoid vigorous mouth rinsing for the first 24 h post extraction and to use gentle toothbrushing in the immediate postoperative period . 9. For patients taking oral contraceptives extractions should ideally be performed during days 23 through 28 of the menstrual cycle . 10. Comprehensive pre- and postoperative verbal instructions should be supplemented with written advice to ensure maximum compliance.
- 12. Pharmacological measures 1. Antibacterial agents 2. Antiseptic agents and lavage 3. Antifibrinolytic agents 4. Steroid anti-inflammatory agents 5. Obtundent dressings 6. Clot supporting agents Different methods in the management of dry socket: Being an old surgical puzzle, many different methods have been advocated to treat alveolar osteitis (dry socket) , such as the application of local turmeric ,zinc oxide eugenol, alvogyl, honey or vitamin C , and socket irrigation with hydrogen peroxide . However, these conventional treatment approaches merely solve the symptoms but do not target the key etiology. Furthermore, most of these approaches do not completely alleviate the pain and other symptoms.
- 14. More recent approaches come into play based on experience of wound healing management in other surgical specialty areas, and these include the use of low intensity pulsed ultrasound therapy (LIPUS) , low level laser therapy (LLLT) ,Ozone therapy , and the use of plasma rich in growth Factors (PRGF) in general and oral wound healing. As the knowledge on the biology of wound healing advances, the role of cytokines and growth factors in the healing of alveolar osteitis becomes more significant. Understanding the molecular aspects of wound healing plays an important role in dry socket healing. Over the past two decades, plasma rich in growth Factors (PRGF) has been used in many surgical fields as an additional remedy for supporting wound healing. Using Growth Factor in the Healing of Dry Socket Growth factors are the driving force for tissue regeneration by regulating many aspects of cellular behavior, the function of which has been widely accepted.For example, transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) and insulin- like growth factor promote cell proliferation; TGF-β and vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGF) enhance cell migration; bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) and fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) stimulate osteogenic differentiation; VEGF and platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) are essential in the process of angiogenesis. Native growth factors are embedded within the extracellular matrix (ECM). However, exogenous growth factors applied alone in tissue engineering have a short life due to rapid proteolysis
- 15. Concentrated growth factor (CGF): Is the third generation of autologous plasma extract prepared by a special centrifugal program. CGF scaffolds possess unique three-dimensional (3D),fibrin networks, which may establish a conducive microenvironment for newly,formed tissue growing inwards. Particularly, the optimized manufacturing, process endows CGF with a higher level of growth factors, platelets, and cytokines than the traditional platelet concentrates such as platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) . CGF has been suggested as a potentially ideal scaffold for bone defect repair due to its osteogenic promotion effect on bone marrow stem cells (BMSCs). Moreover, recent studies investigated that CGF promoted the proliferation and migration activity of periodontal ligament stem cells (PDLSCs) and Schwann cells (SCs) in vitro, and CGF treatment led to functional nerve recovery in the sciatic nerve injury rat model.
- 16. Concentrated growth factors are ideal for clotting as it contains essential growth factor: Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), Transforming growth factor (TGF), Platelet factor interleukin (IL), Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), Epidermal growth factor (EGF), Insulin-like growth factor IGF, and Fibronectin. Together, this cocktail of growth factors speeds up the development of the delicate fibrovascular granulation tissue. Platelet-Rich Plasma ( PRP ) PRP is a patient’s blood enriched with extra platelets from another sample of the same patient’s blood. Dry socket can be dramatically decreased with the use of PRP. What is the average healing time for dry socket? • Average healing time is 7 to 10 days, as this is the amount of time it takes for new tissue to grow to cover the exposed socket. What is the prognosis for dry socket? • Prognosis is good as there usually are no long-term consequences. Once the tissue is able to cover the bone, the healing will progress normally.
- 17. Complications: The number of secondary complications to the placement of dressings in the treatment of an established dry socket is ignored; most of the complications previously reported, myospherulosis, neuritis, and foreign body reaction, are related to intra-alveolar medication as a preventive methods and not as a treatment Painful, dry socket rarely results in infection or serious complications. However, potential complications may include delayed healing of or infection in the socket or progression to chronic bone infection (osteomyelitis) (a) Maxillary occlusal X-ray. (b) Periapical X-ray. Notice the closure of the foreign body to the right maxillary sinus, and also a nonhealed 3 alveolus
- 18. THANK YOU