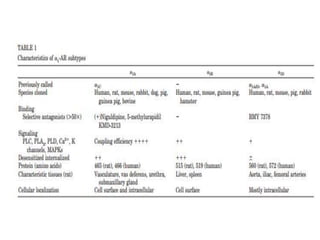
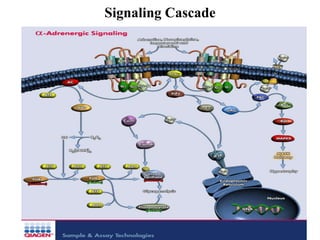
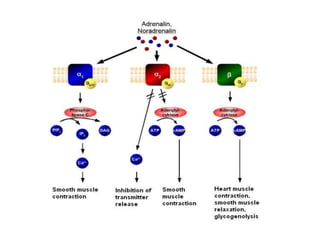
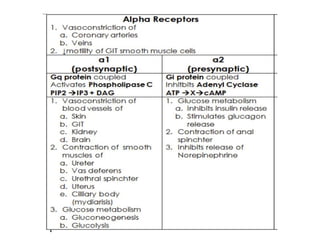
The alpha-1 adrenergic receptor is a G protein-coupled receptor primarily responsive to norepinephrine, found mostly postsynaptically in the central and peripheral nervous systems, and is divided into subtypes α1a, α1b, and α1d. These receptors are located in various tissues including vascular smooth muscle and play roles in functions such as vasoconstriction, mediating heart contraction, and relaxation of gastrointestinal smooth muscle. Agonists like phenylephrine are used for vasoconstriction, while antagonists like prazosin treat hypertension by inducing vasodilation.