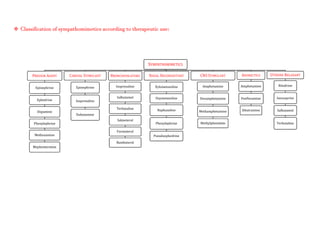
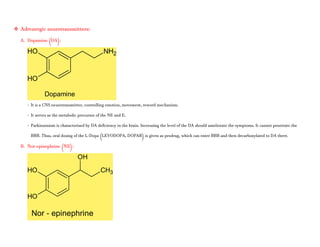
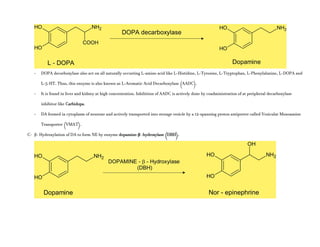
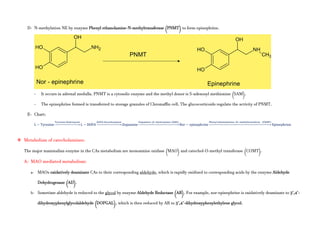
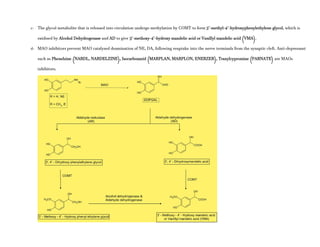
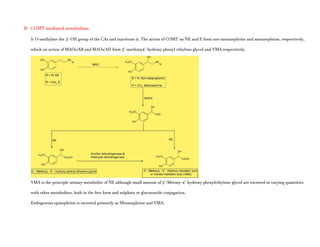
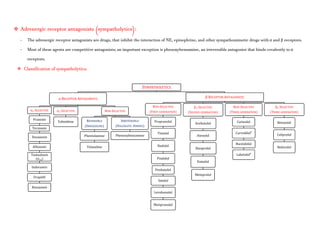
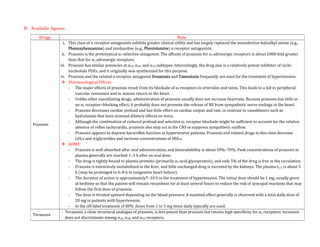
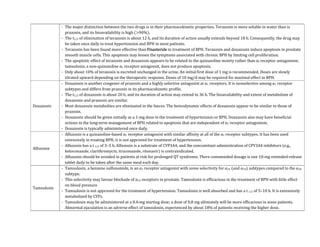
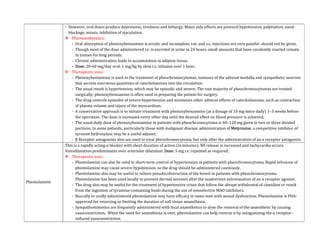
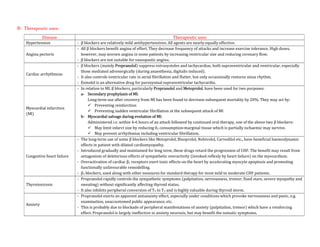
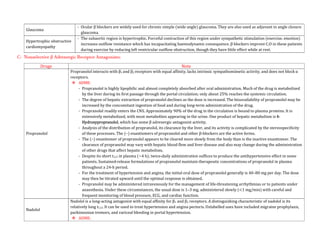
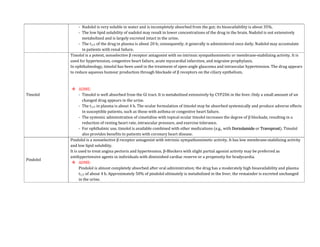
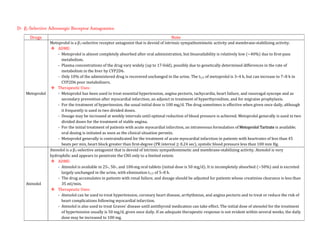
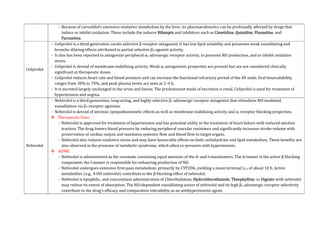
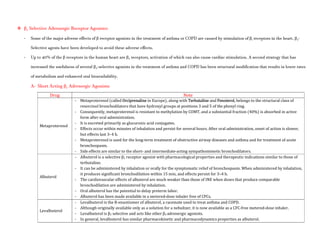
Adrenergic receptors are G protein-coupled receptors that are divided into alpha and beta types with multiple subtypes. Alpha receptors activate either Gq/11 (alpha1) or Gi (alpha2) proteins, while beta receptors activate Gs proteins. Activation of these receptors leads to changes in secondary messengers that mediate various physiological effects. Sympathomimetic drugs can directly or indirectly activate these receptors to produce effects similar to sympathetic nervous system stimulation such as increased heart rate and bronchodilation. These drugs find clinical use in conditions like asthma and hypertension.









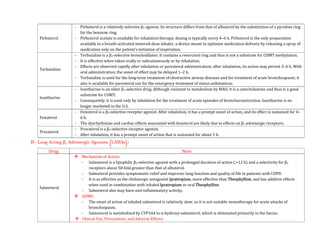
![- Patients with a history of hypertension may exhibit an exaggerated pressor response more frequently. Because dobutamine
facilitates AV conduction, patients with atrial fibrillation are at risk of increases in ventricular response rates; digoxin or other
measures may be required to prevent this from occurring.
- Some patients may develop ventricular ectopic activity. Dobutamine may increase the size of a myocardial infarct by increasing
myocardial O2 demand, a property common to inotropic agents.
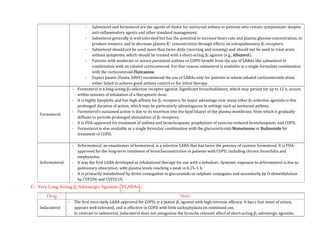
Isoproterenol
- Isoproterenol (INE, isopropyl norepinephrine, isoprenaline, isopropylarterenol, isopropyl noradrenaline, d, l-β-[3,4-
dihydroxyphenyl]-α- isopropylaminoethanol) is a potent, nonselective β receptor agonist with very low affinity for α receptors.
Pharmacological Actions:
- Intravenous infusion of INE lowers peripheral vascular resistance, primarily in skeletal muscle but also in renal and mesenteric
vascular beds. Diastolic pressure falls.
- Systolic blood pressure may remain unchanged or rise, although mean arterial pressure typically falls. Cardiac output is
increased because of the positive inotropic and chronotropic effects of the drug in the face of diminished peripheral vascular
resistance.
- The cardiac effects of INE may lead to palpitations, sinus tachycardia, and more serious arrhythmias; large doses of INE cause
myocardial necrosis in experimental animals.
- Isoproterenol relaxes almost all varieties of smooth muscle when the tone is high, an action that is most pronounced on
bronchial and GI smooth muscle.
- INE prevents or relieves bronchoconstriction. Its effect in asthma may be due in part to an additional action to inhibit antigen
induced release of histamine and other mediators of inflammation, an action shared by β2-selective stimulants.
ADME:
- Isoproterenol is readily absorbed when given parenterally or as an aerosol.
- It is metabolized by COMT, primarily in the liver but also by other tissues.
- INE is a relatively poor substrate for MAO and NET (SLC6A2) and is not taken up by sympathetic neurons to the same extent as
are EPI and NE.
- The duration of action of INE therefore may be longer than that of EPI, but it still is relatively brief.
Therapeutic Uses:
- Isoproterenol may be used in emergencies to stimulate heart rate in patients with bradycardia or heart block, particularly in
anticipation of inserting an artificial cardiac pacemaker or in patients with the ventricular arrhythmia torsades de pointes.
Adverse Effects:
- Palpitations, tachycardia, headache, and flushing are common.
- Cardiac ischemia and arrhythmias may occur, particularly in patients with underlying coronary artery disease.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-adrenergictransmission-210511053241/85/Adrenergic-transmission-17-320.jpg)
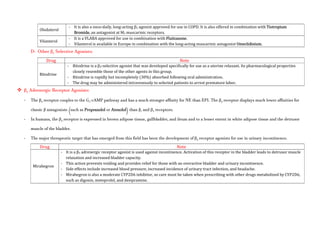


![- The use of EPI generally is contraindicated in patients who are receiving nonselective β receptor antagonists because its unopposed actions on
vascular α1 receptors may lead to severe hypertension and cerebral haemorrhage.
Therapeutic Uses:
- A major use of EPI is to provide rapid, emergency relief of hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, to drugs and other allergens.
- EPI also is used to prolong the action of local anaesthetics, presumably by decreasing local blood flow and reducing systemic absorption.
- It also is used as a topical hemostatic agent on bleeding surfaces, such as in the mouth or in bleeding peptic ulcers during endoscopy of the stomach
and duodenum.
- Systemic absorption of the drug can occur with dental application.
Norepinephrine:
- Norepinephrine (levarterenol, l-noradrenaline, l-β-[3,4-dihydroxyphenyl]- α-aminoethanol) is a major chemical mediator liberated by mammalian
postganglionic sympathetic nerves. It differs from EPI only by lacking the methyl substitution in the amino group.
- NE constitutes 10%–20% of the catecholamine content of human adrenal medulla and as much as 97% in some pheochromocytomas, which may not
express the enzyme phenyl ethanolamine-N-methyltransferase.
Pharmacological Properties:
- Both EPI & NE are direct agonists on effector cells, and their actions differ mainly in the ratio of their effectiveness in stimulating α and β2
receptors. They are approximately equipotent in stimulating β1 receptors.
- NE is a potent α agonist and has relatively little action on β2 receptors; however, it is somewhat less potent than EPI on the α receptors of most
organs.
Cardiovascular Effects:
- In response to intravenous infusion of NE in humans, systolic and diastolic pressures, and usually pulse pressure, are increased.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-adrenergictransmission-210511053241/85/Adrenergic-transmission-27-320.jpg)