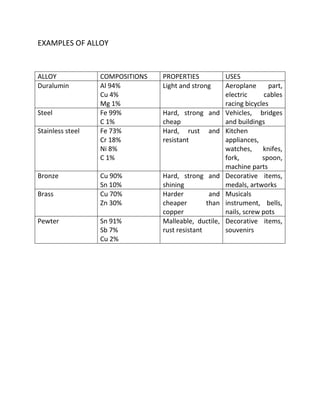
This document discusses alloys and their properties. It defines an alloy as a mixture of two or more metals or a metal and non-metal. Common alloys include steel, duralumin, stainless steel, bronze, and brass. Alloys have improved properties compared to pure metals, such as increased strength, improved corrosion resistance, and better appearance. The document provides examples of common alloys, their compositions, properties, and uses.