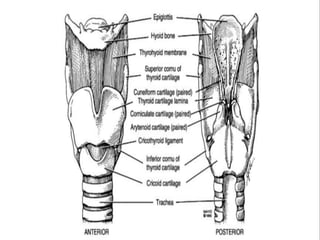
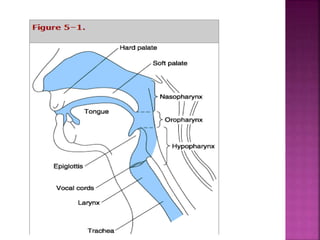
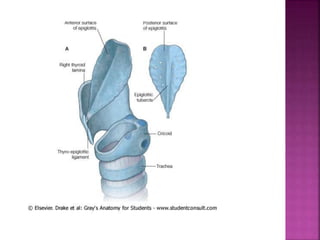
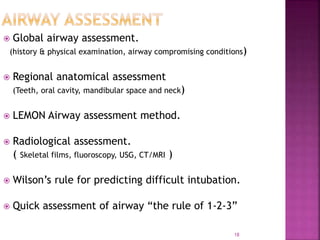
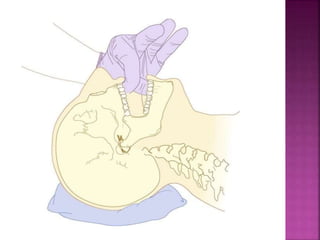
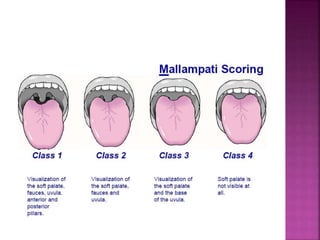
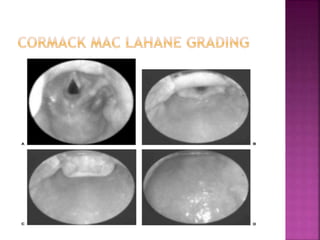
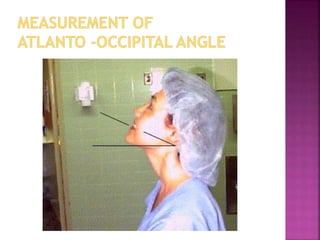
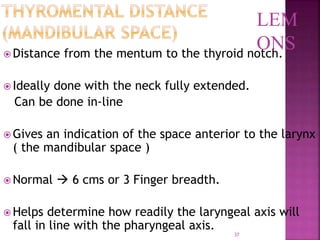
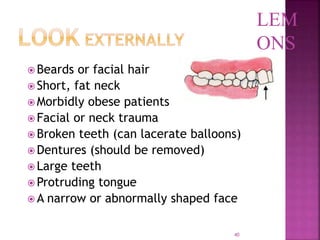
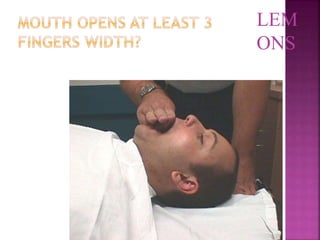
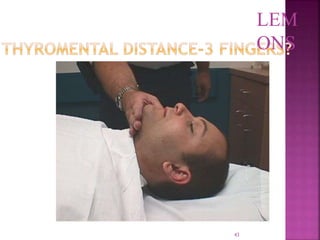
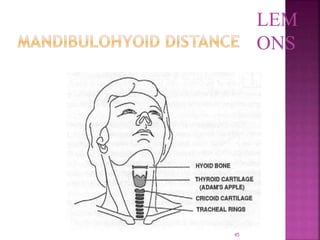
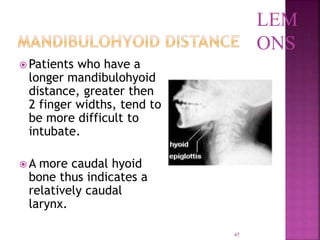
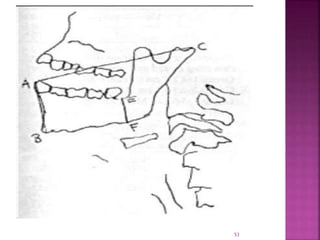
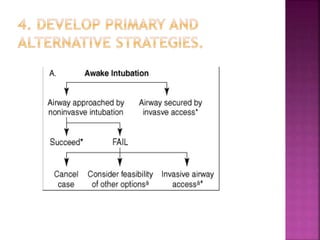
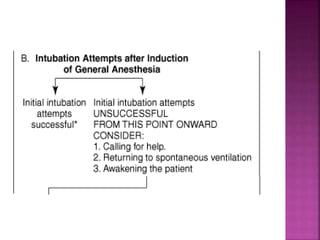
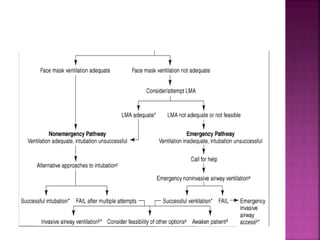
This document discusses airway assessment techniques for predicting difficult intubation. It describes several tests used during airway examination including mouth opening, jaw protrusion, neck mobility, Mallampati score, thyromental distance, and laryngeal palpation. Limitations of airway tests are noted. Proper airway assessment is important for planning management of potential difficult airway scenarios, but cannot predict all difficulties, so preparation for unanticipated problems is key.