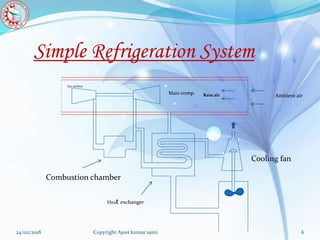
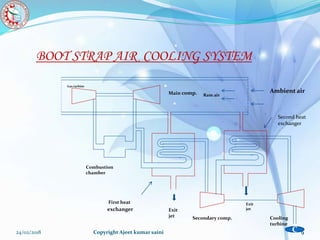
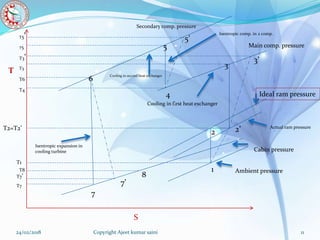
The document presents a presentation on a boot-strap air cooling system by Ajeet Kumar Saini. It discusses the basic concepts of refrigeration, simple air cooling systems, and boot-strap air cooling systems. The boot-strap system uses two compressors and two heat exchangers to raise the pressure and cool air that is then expanded through a turbine to provide cabin cooling. Diagrams of the system and calculations of required air mass and power are included. Advantages are that air is freely available and disadvantages are that ram air is needed for heat exchange, limiting its use to aircraft in flight.