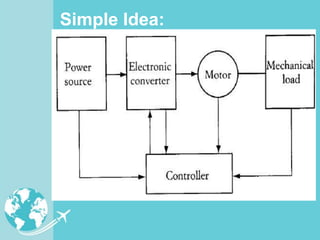
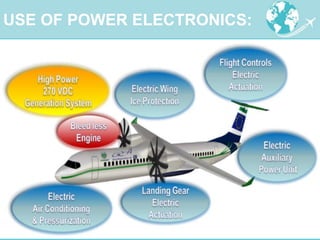
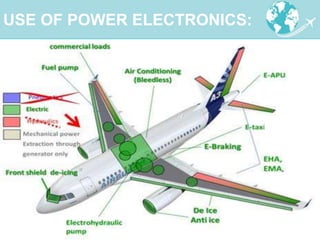
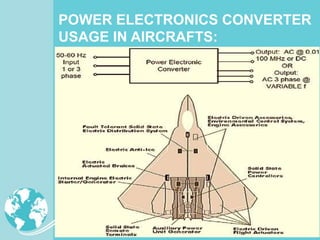
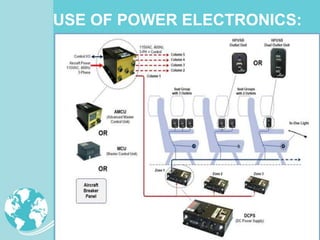
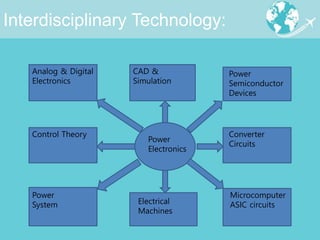
Power electronics technologies are increasingly being used in aircraft to reduce operating costs and fuel usage. This trend toward "More Electric Aircraft" uses electric power instead of hydraulic or mechanical systems to control aircraft subsystems. Power electronics converters are used to manage electrical power on aircraft, providing benefits like improved efficiency, reduced weight, and lower maintenance costs. As aircraft systems require more electric power, power electronics will continue to play an important role in enabling advances in aircraft design and performance.