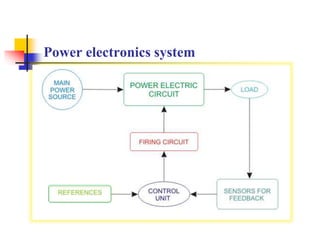
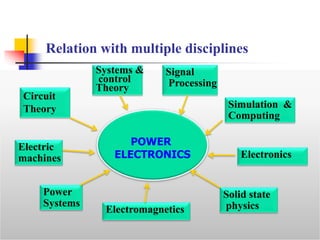
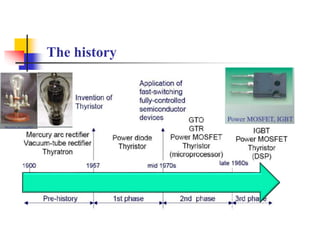
This document provides an introduction to the course "Power Electronics". It defines power electronics as the field that processes and controls the flow of electric power through conversion and control. The document outlines the 5 units that will be covered: power semiconductor devices, AC to DC conversion, DC to DC conversion, DC to AC conversion, and AC to AC conversion and control circuits. It also discusses the history and wide range of applications of power electronics in industrial systems, transportation, utilities, electronics equipment, and other areas. The advantages of power electronics converters include fast response, high efficiency, compact size, and increased flexibility through digital control. Drawbacks include potential for harmonics production and higher initial cost compared to simple conversion equipment.