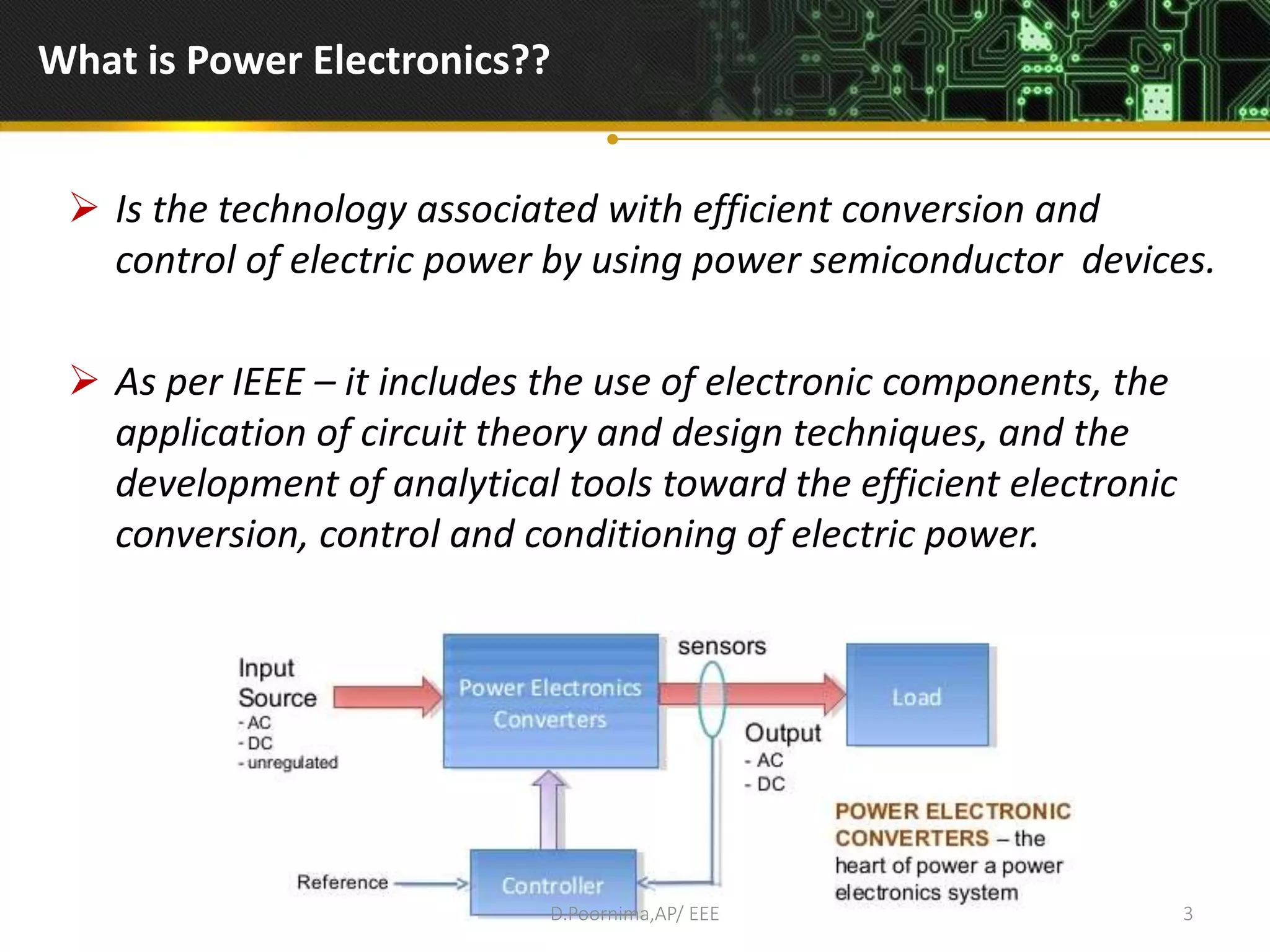
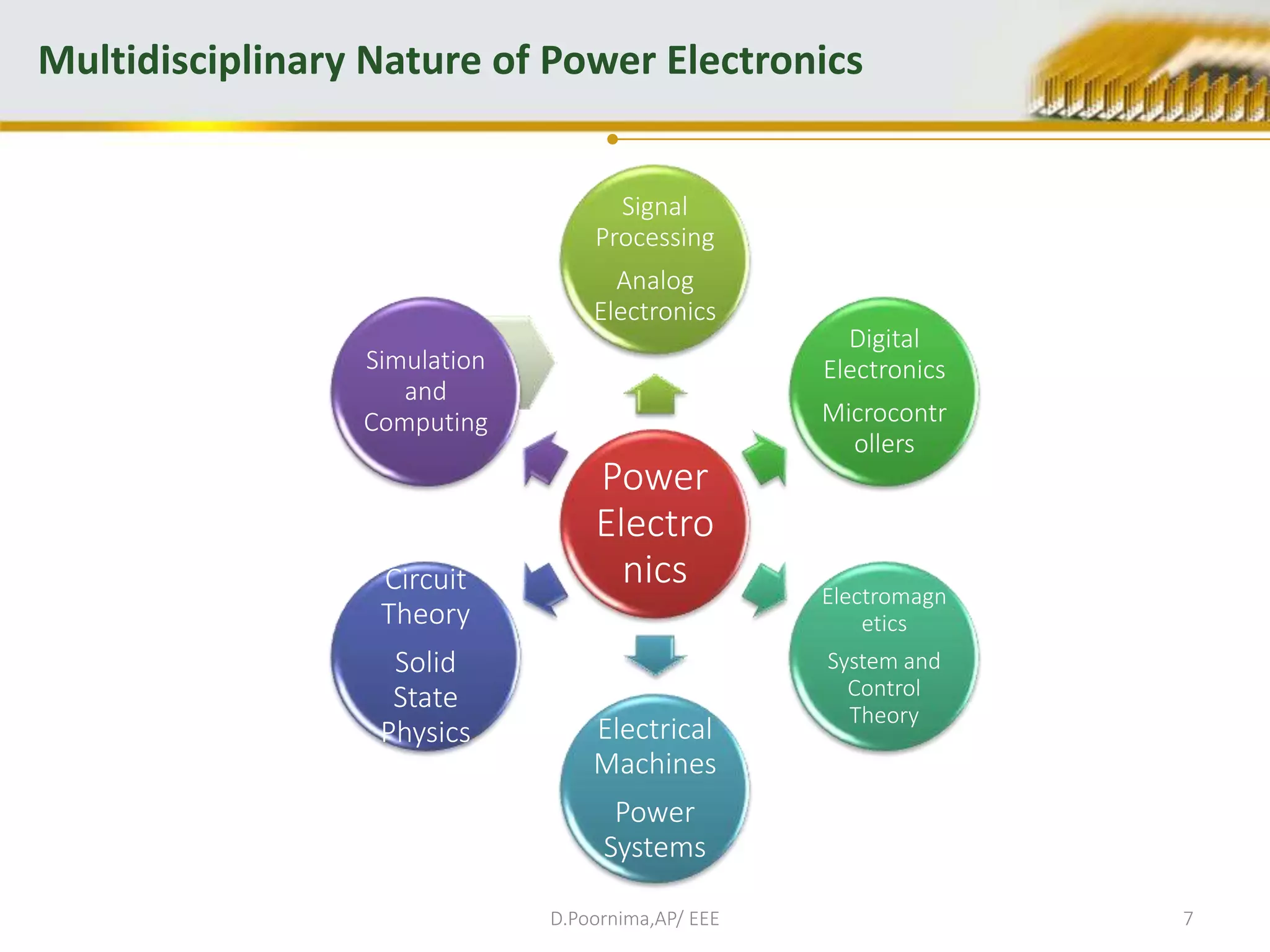
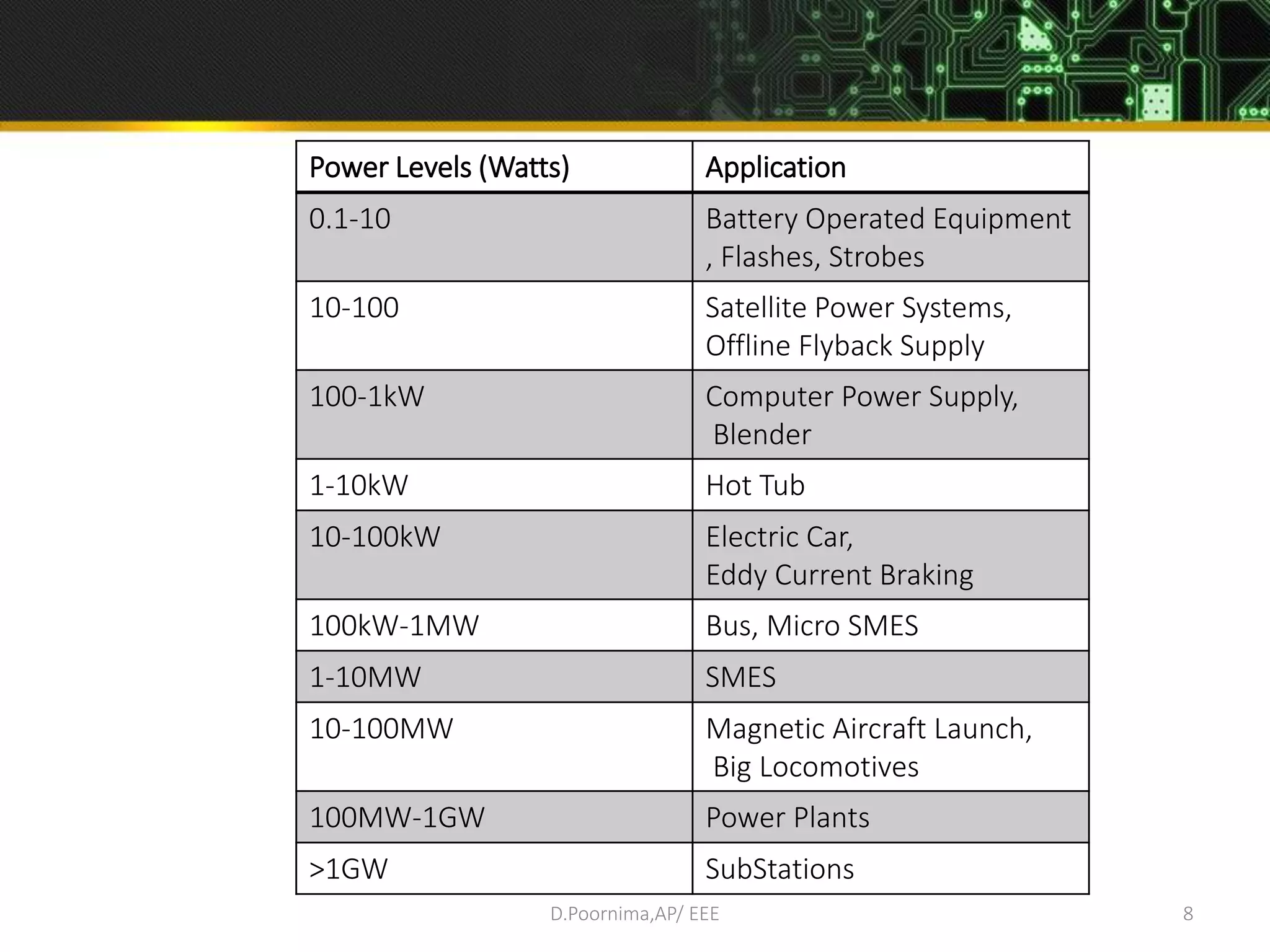
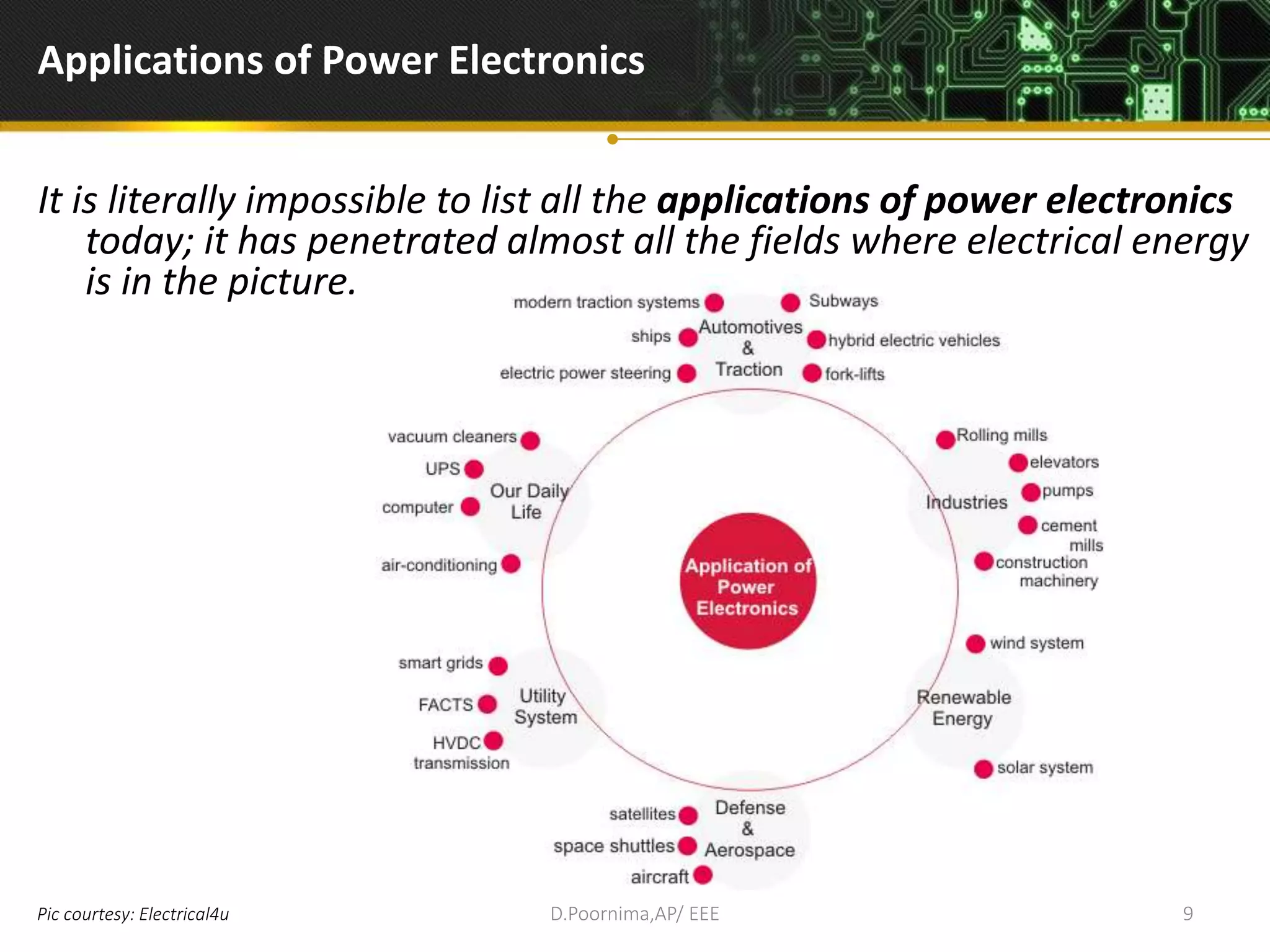
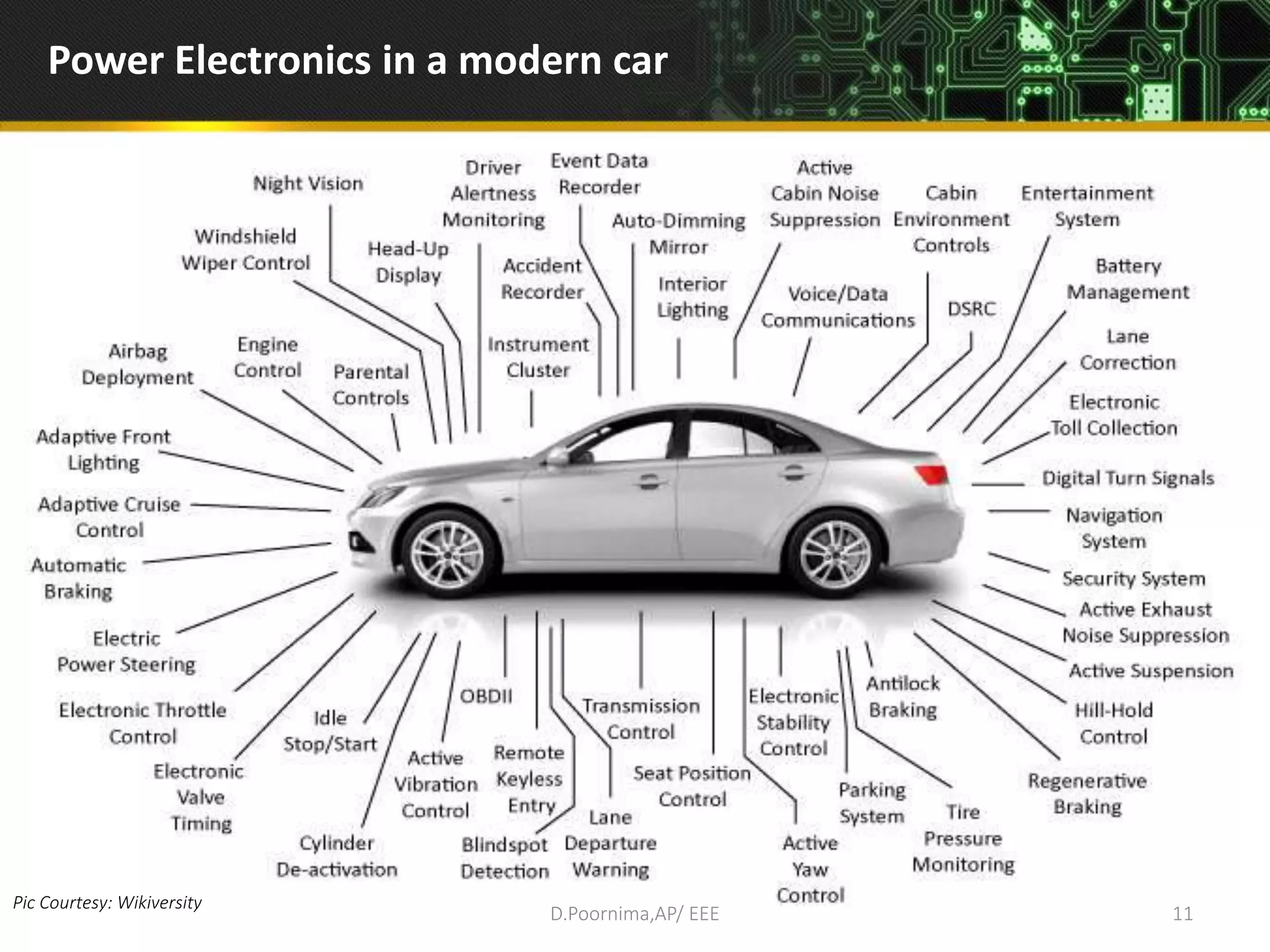
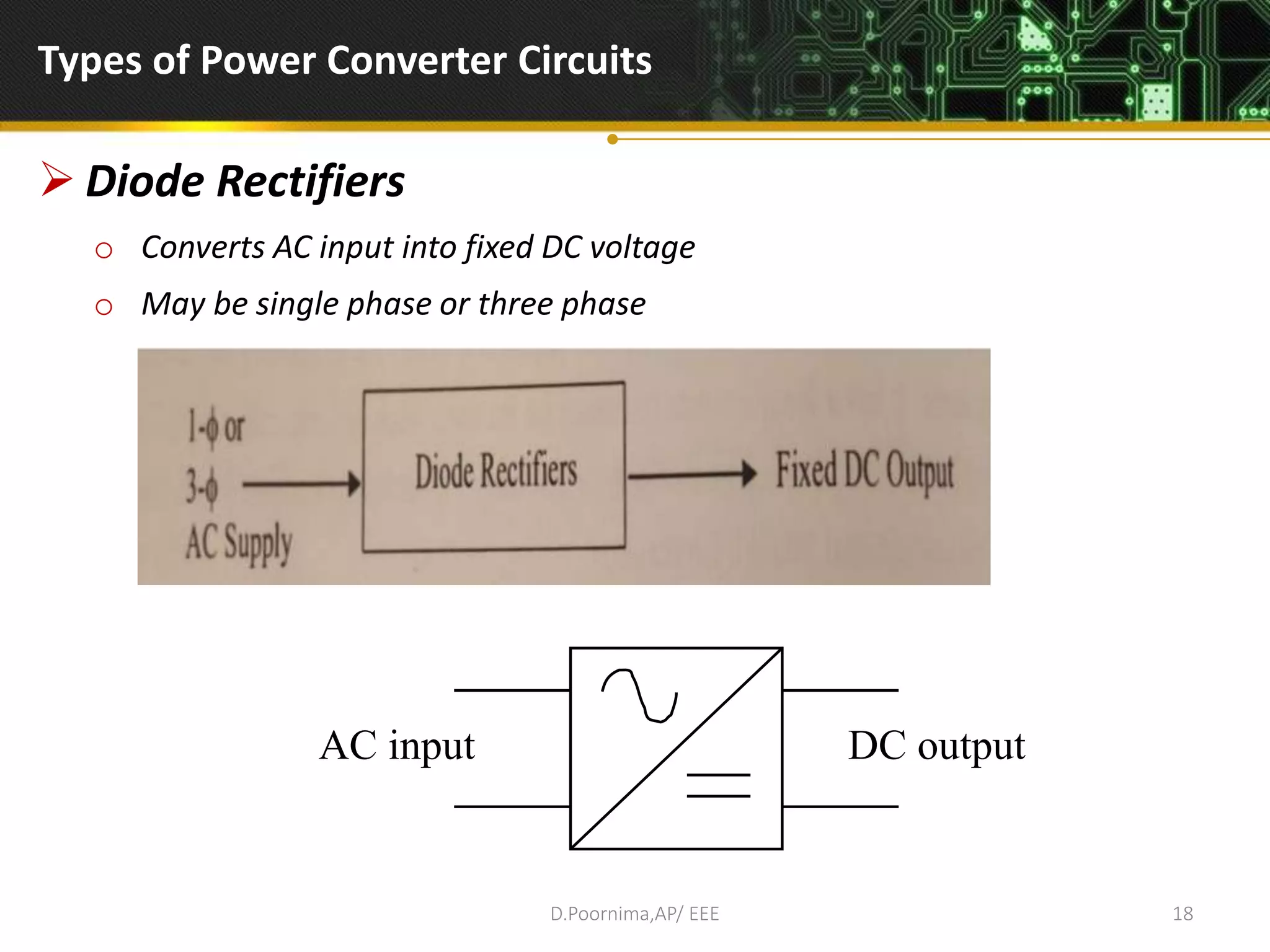
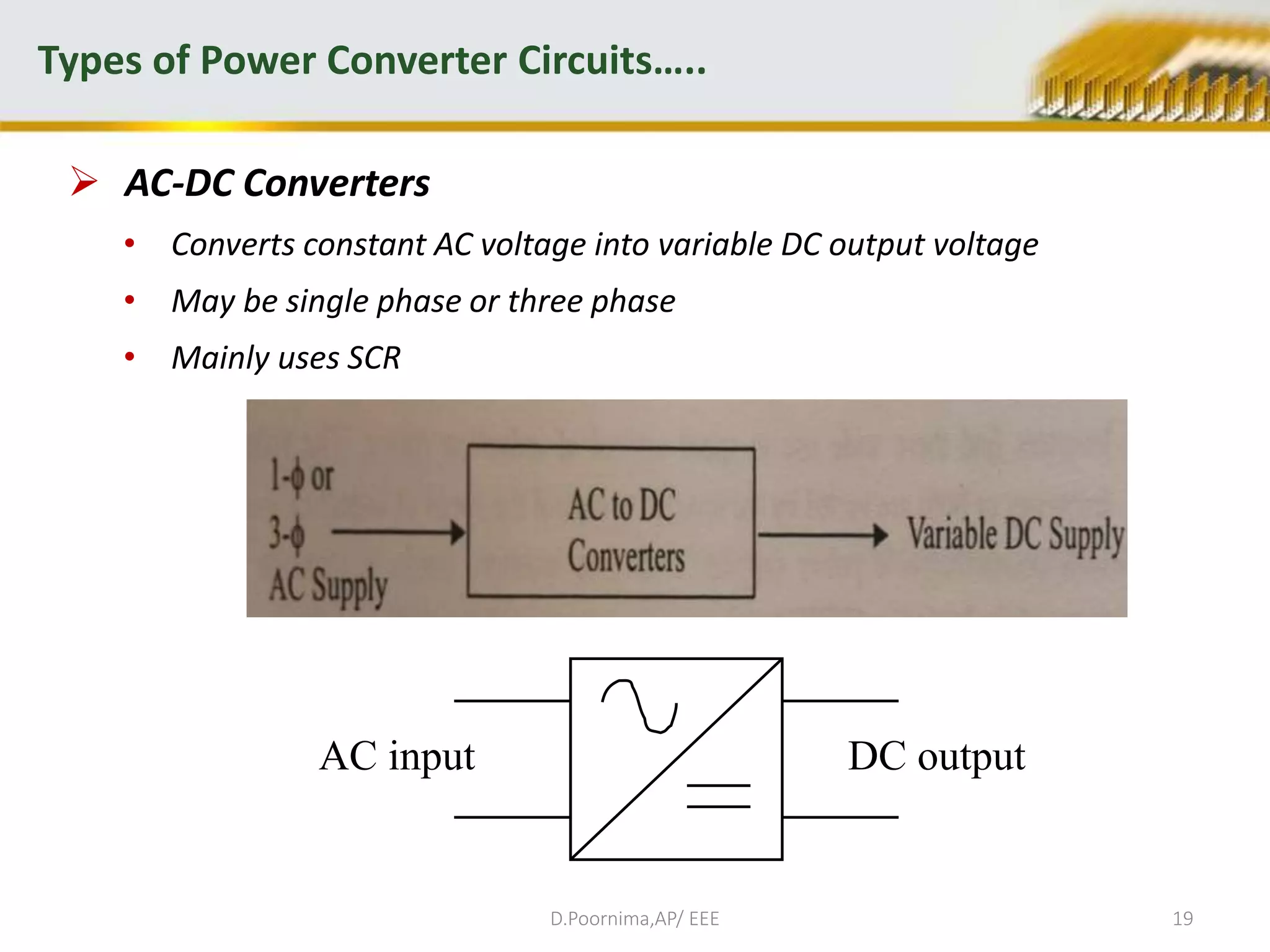
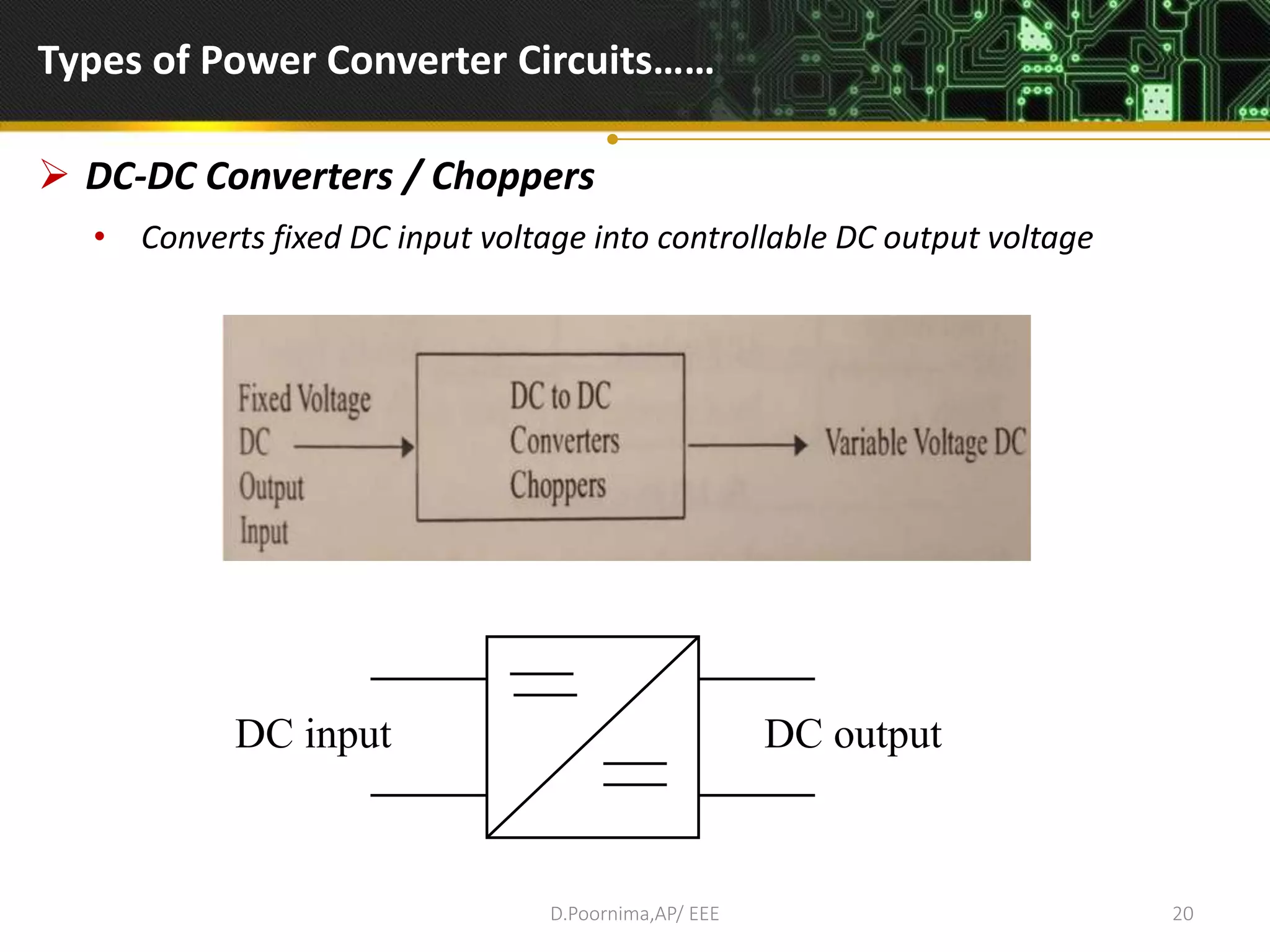
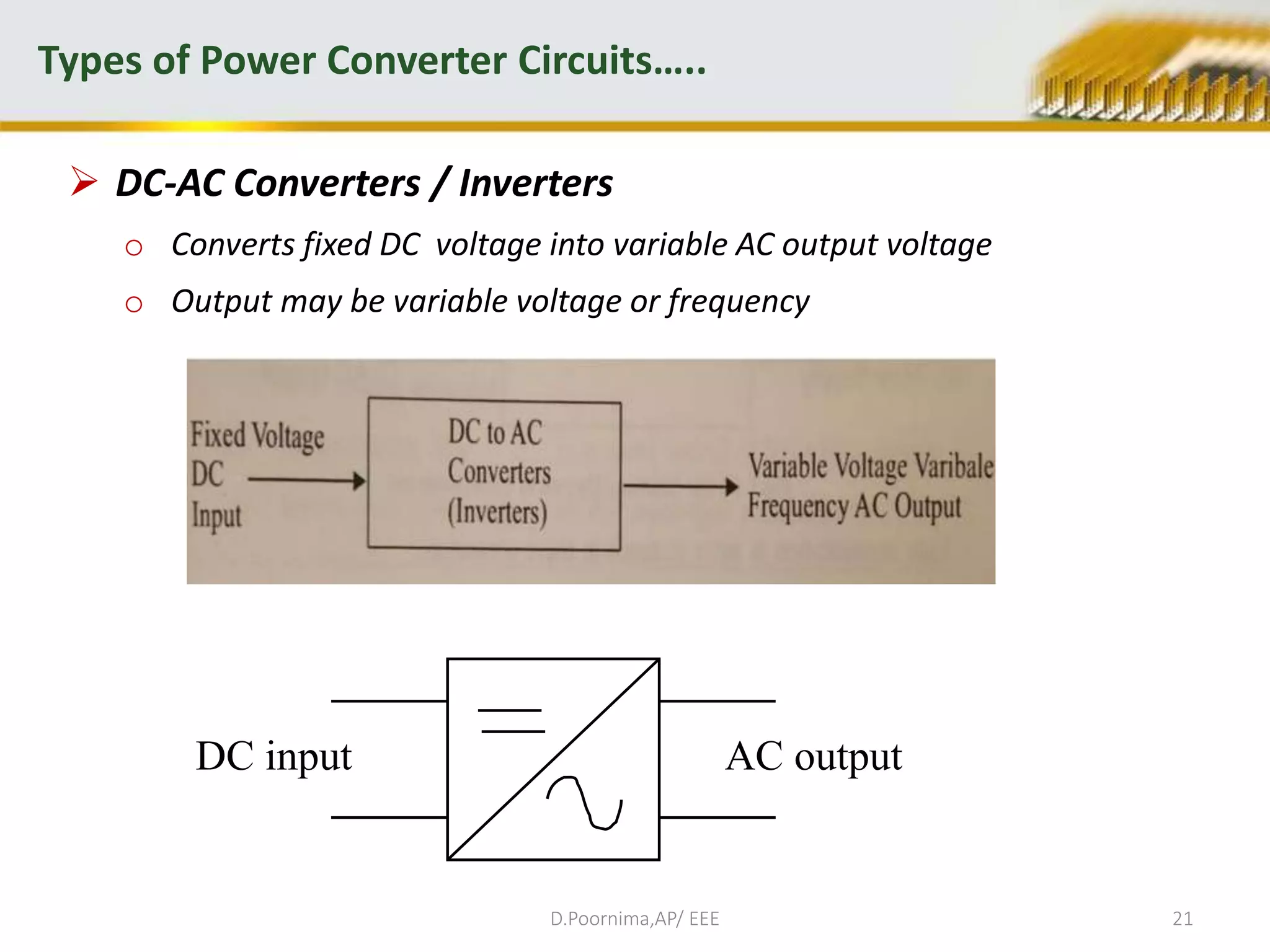
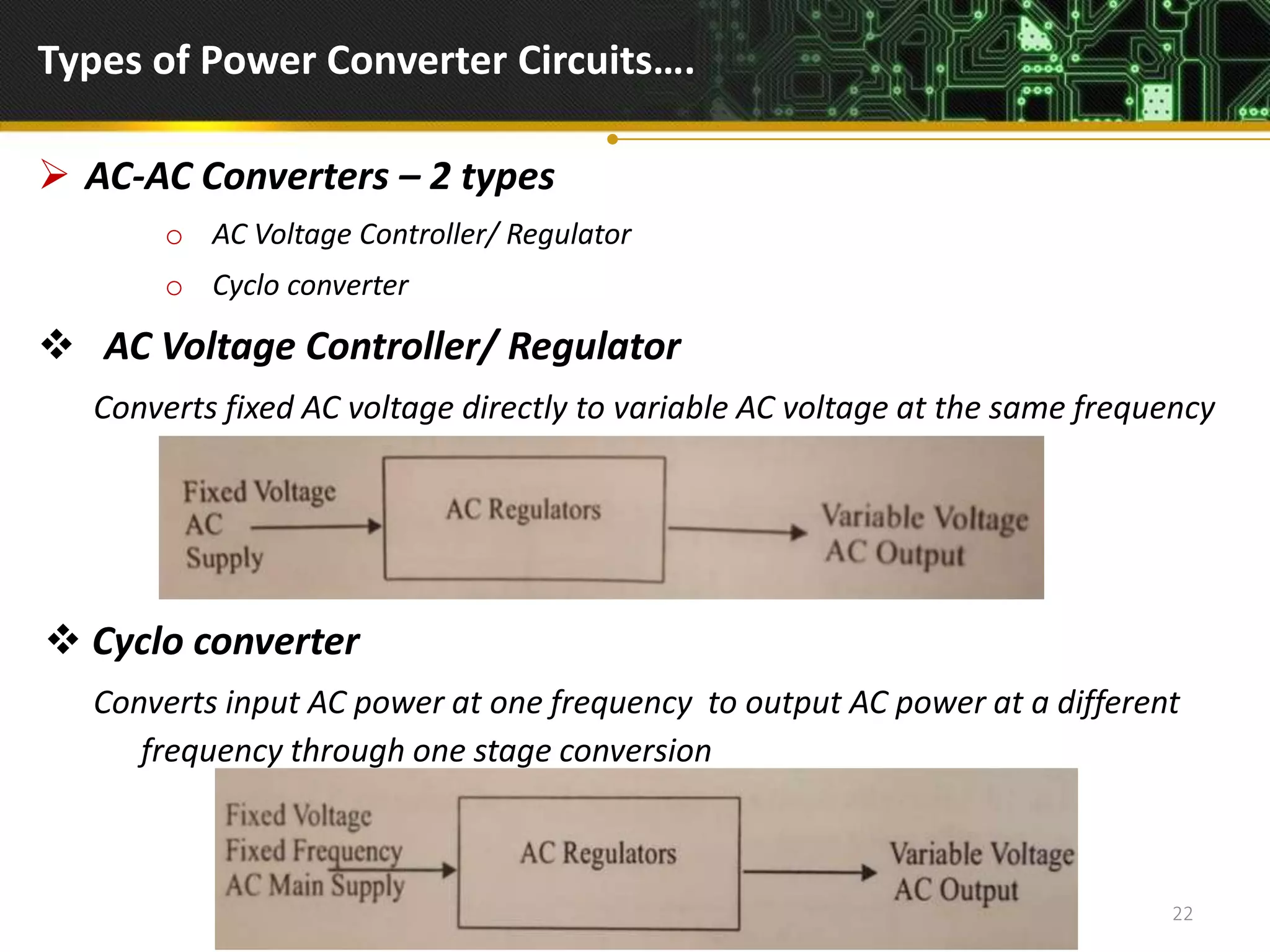
This document provides an introduction to power electronics. It defines power electronics as the technology associated with efficient conversion and control of electric power using power semiconductor devices. The future of global society will be dominated by computers and power electronics, with the former providing intelligence and the latter providing the means. Power electronics has many applications and is multidisciplinary, drawing from fields like signal processing, electronics, electromagnetics, and control theory. It describes the types of power electronic circuits like rectifiers, converters, choppers, inverters, and AC-AC converters. Power devices are also classified based on the number of terminals, charge carriers, and degree of controllability.