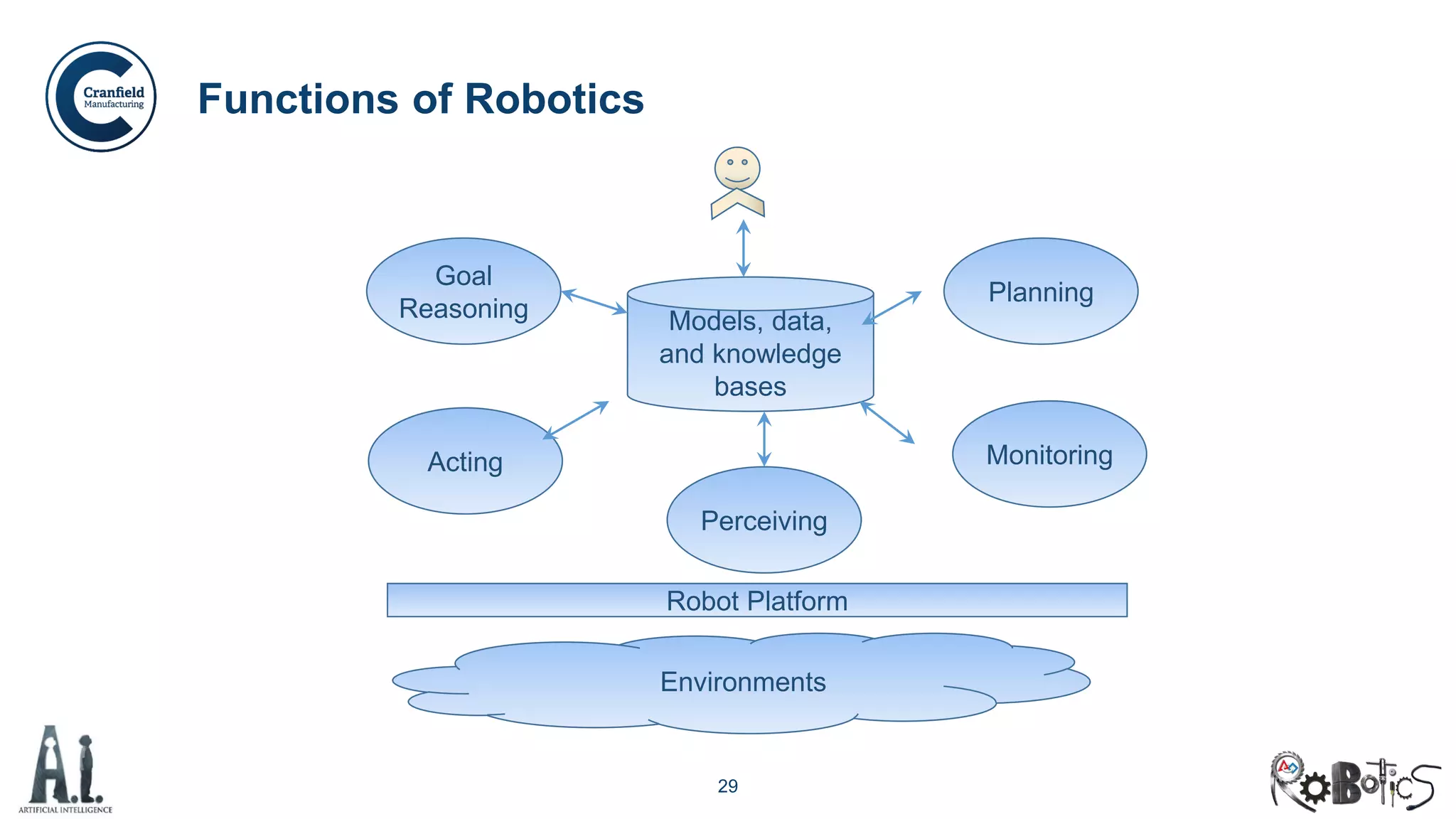
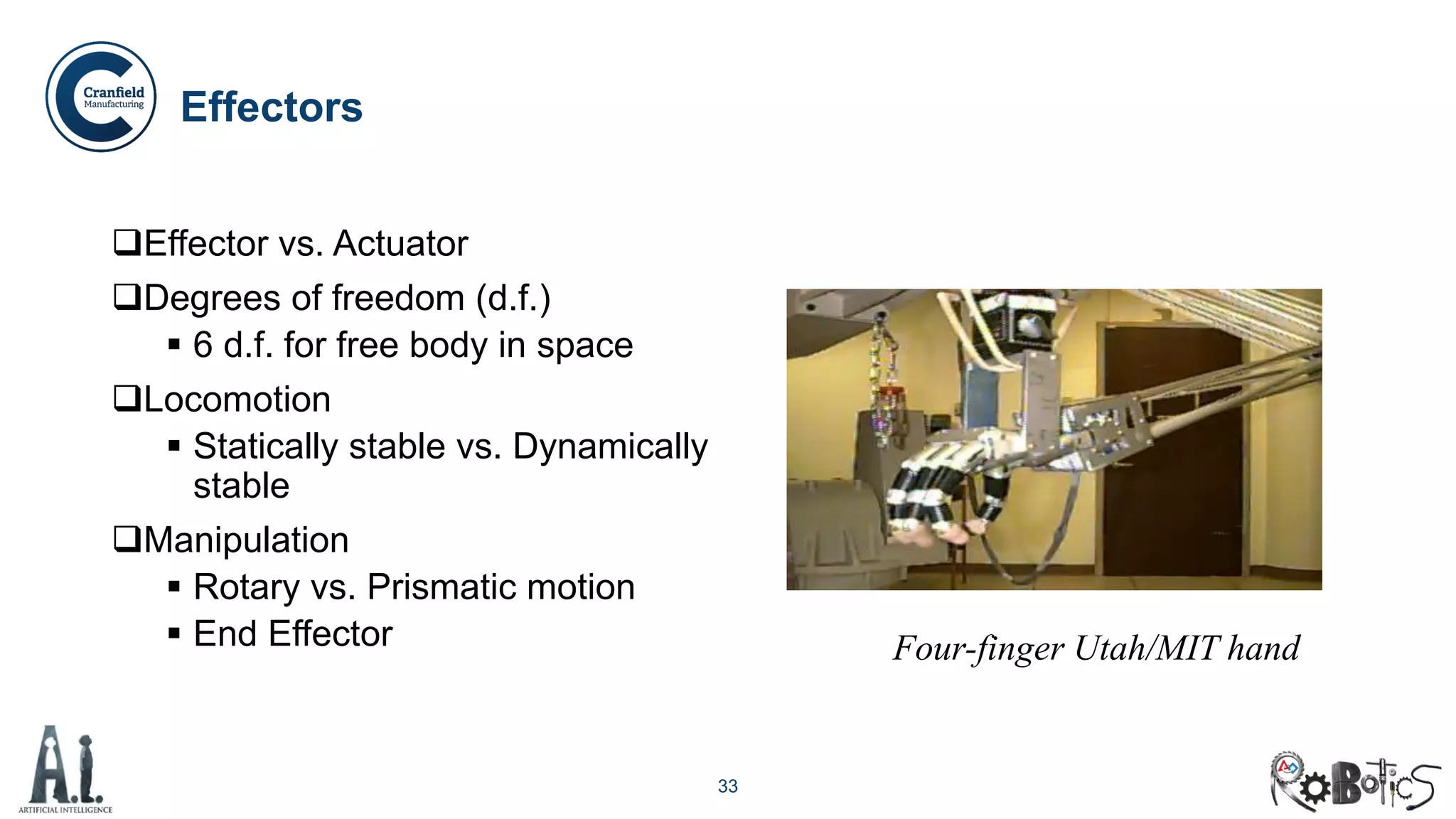
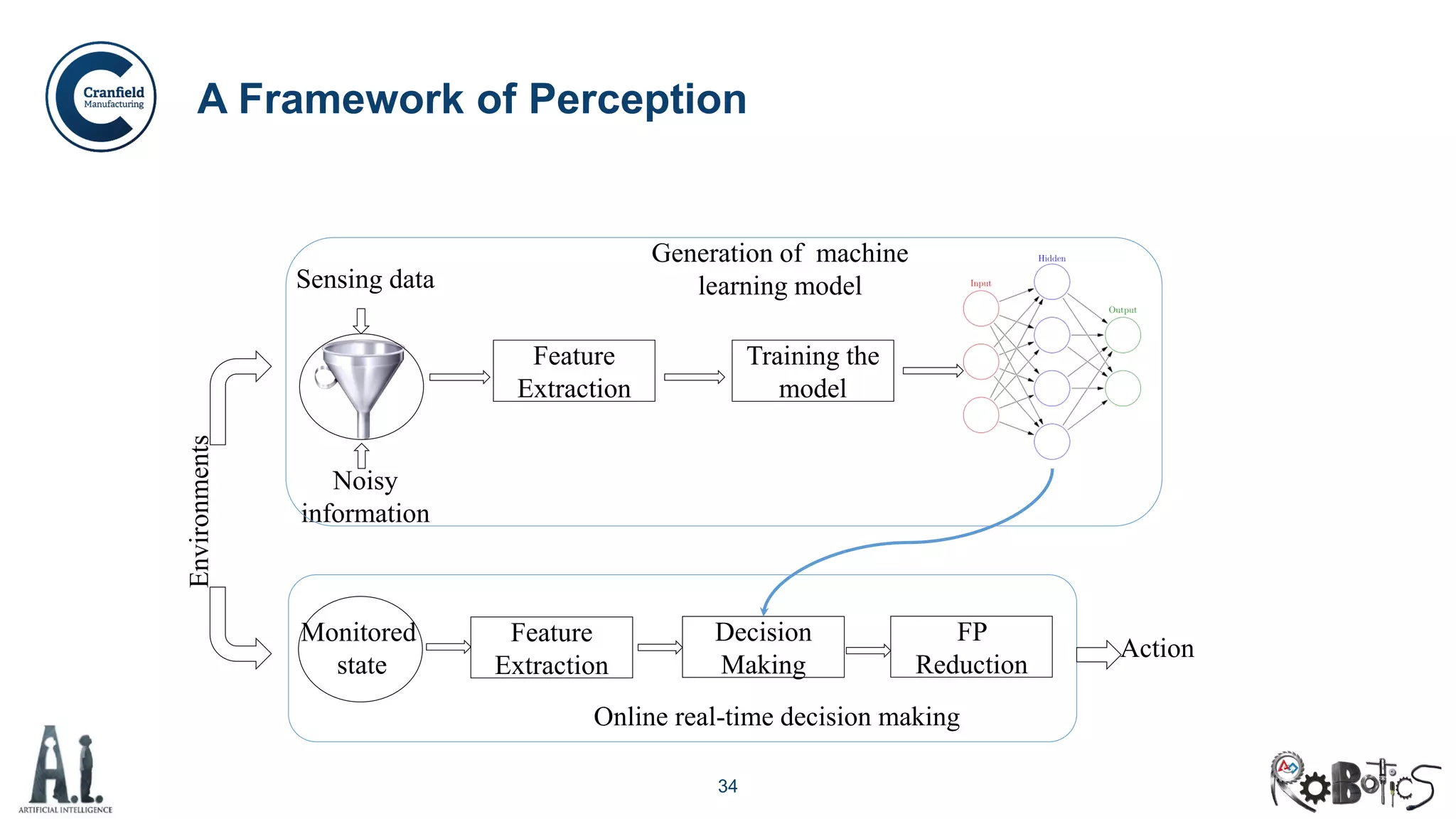
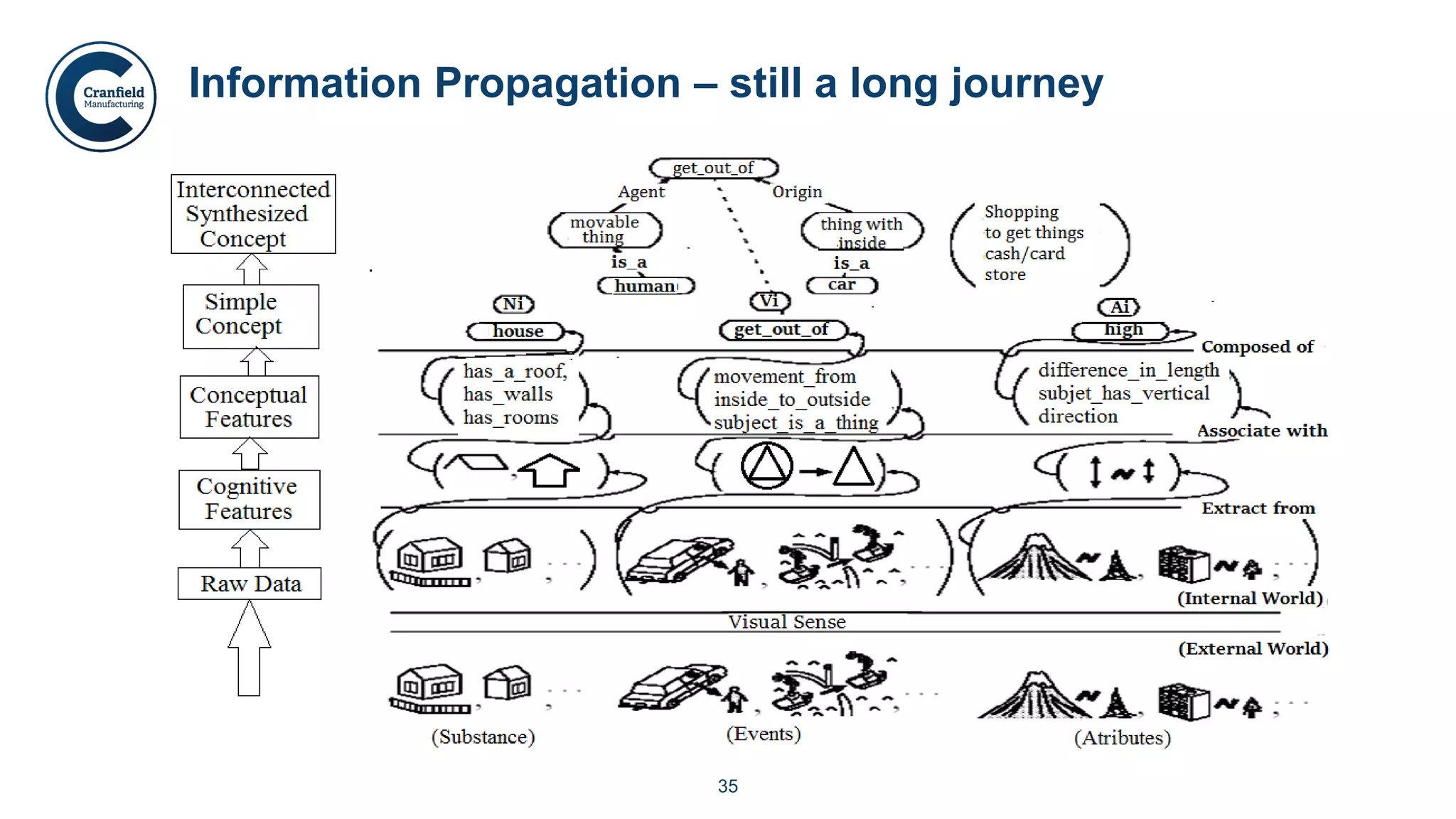
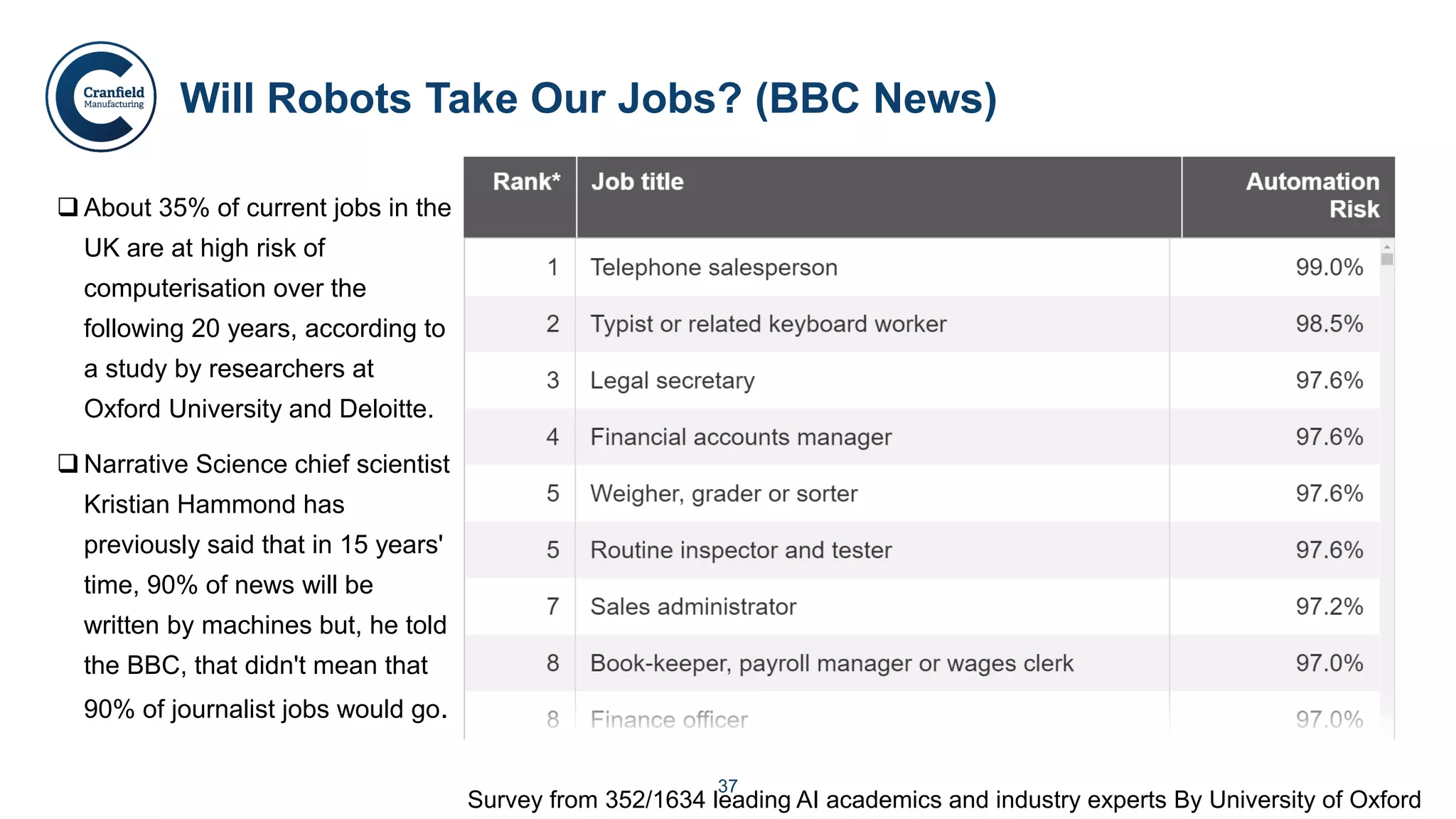
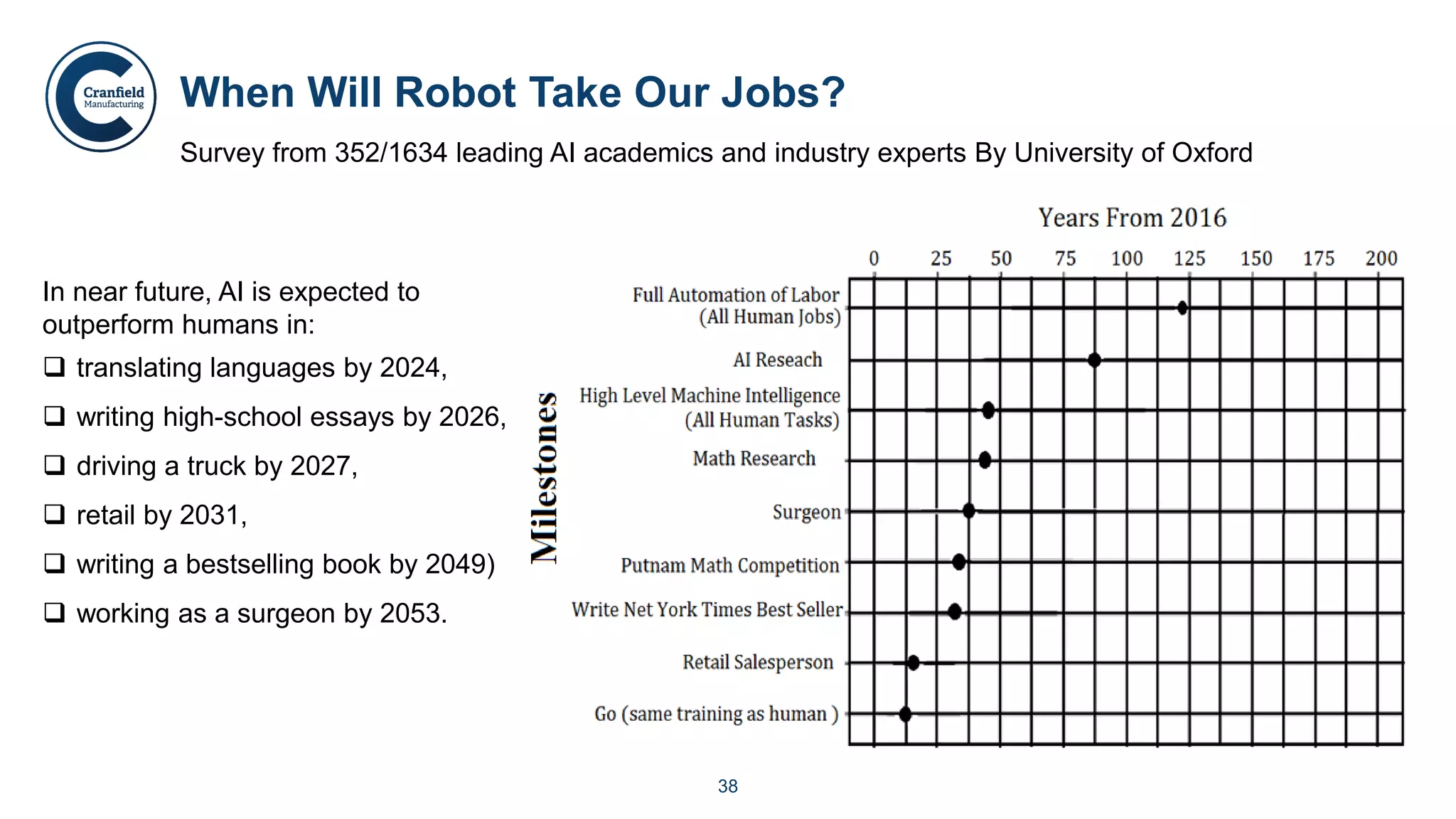
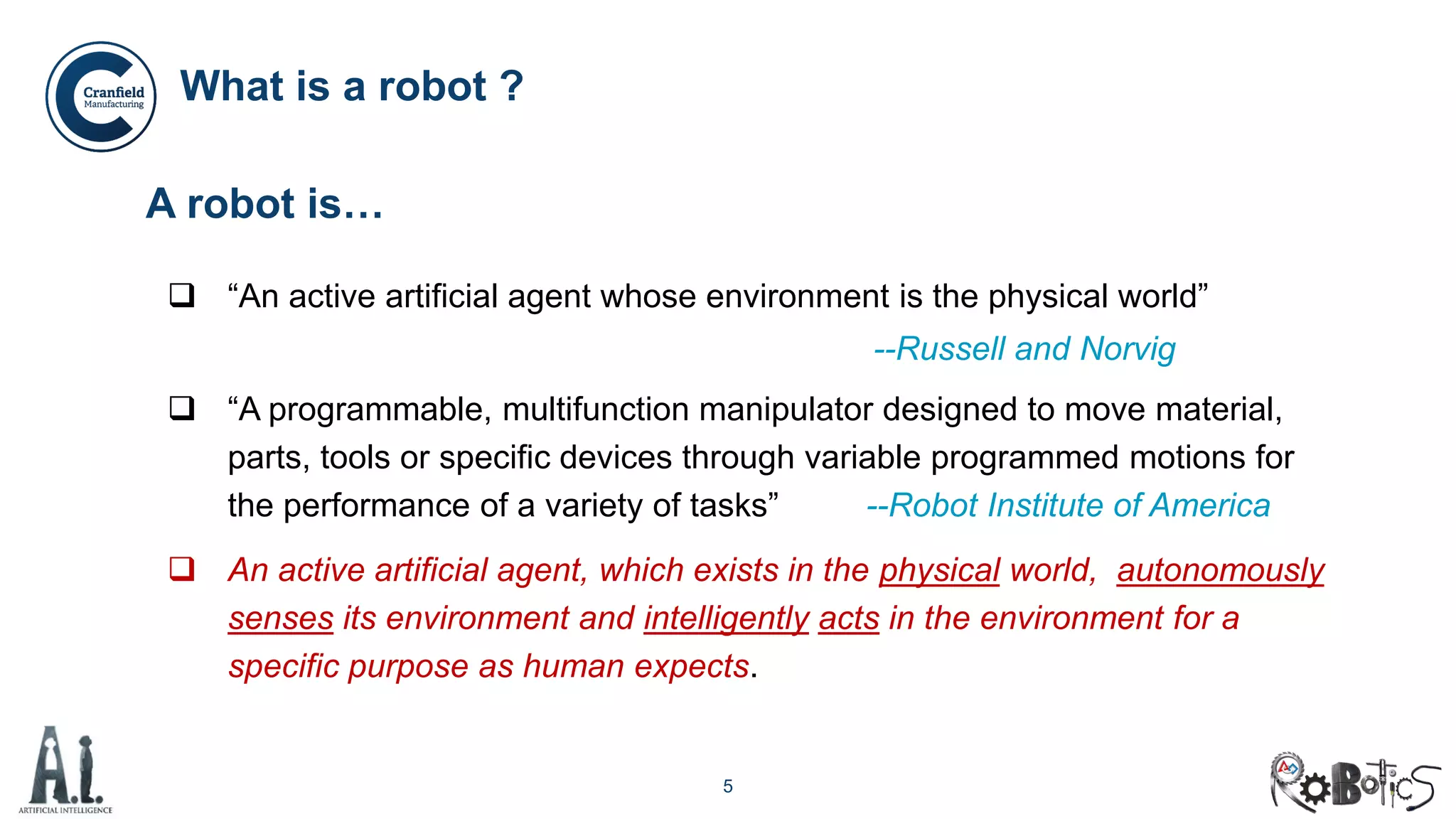
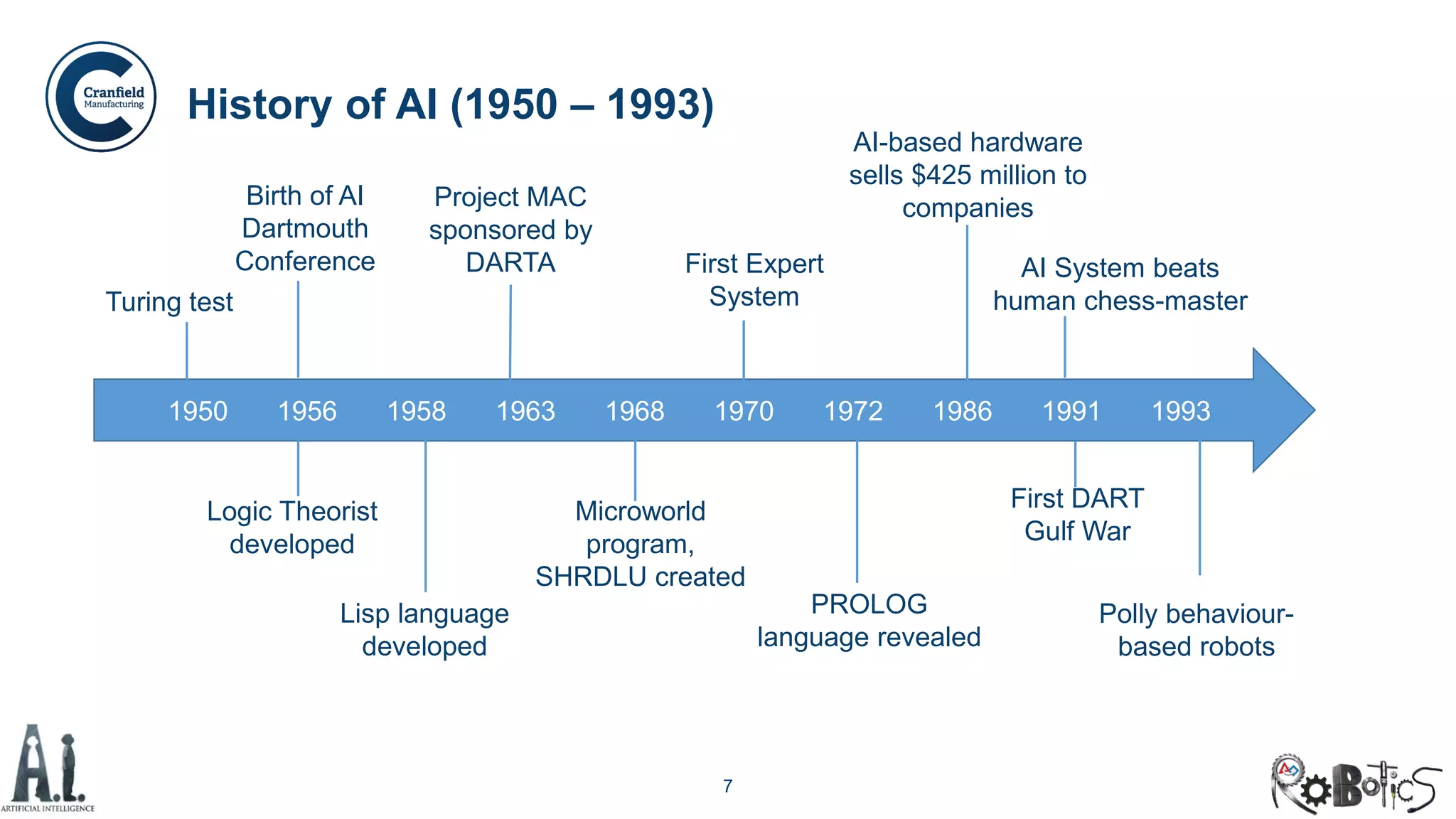
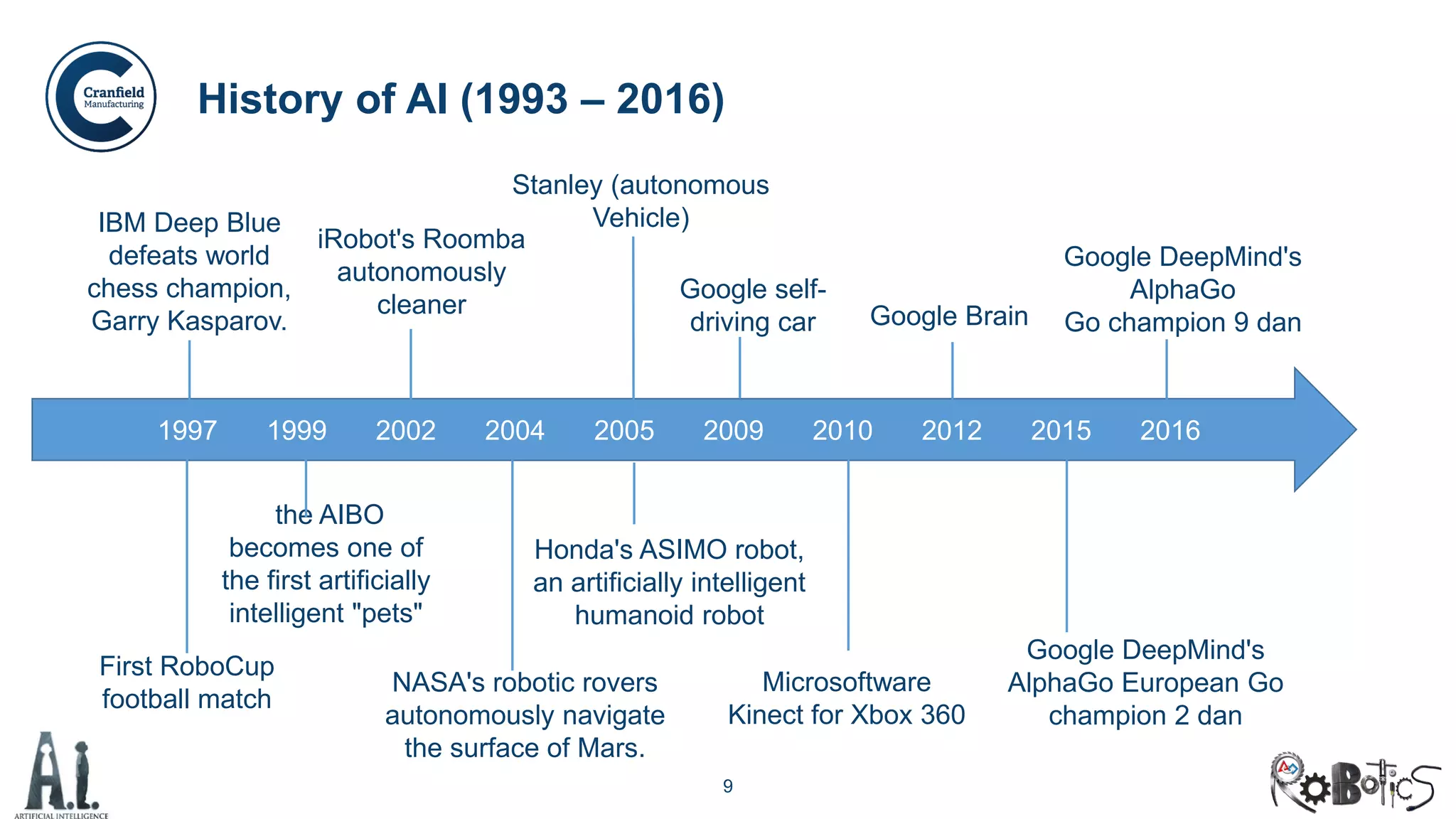
The document outlines the concepts of robotics and artificial intelligence (AI), detailing their history, types, and present applications in various sectors. It also discusses the ethical challenges posed by advancements in AI, the potential impact on employment, and the rise of autonomous intelligent systems. Key milestones in AI and robotics development are highlighted, along with projections for future capabilities and societal implications.


![4
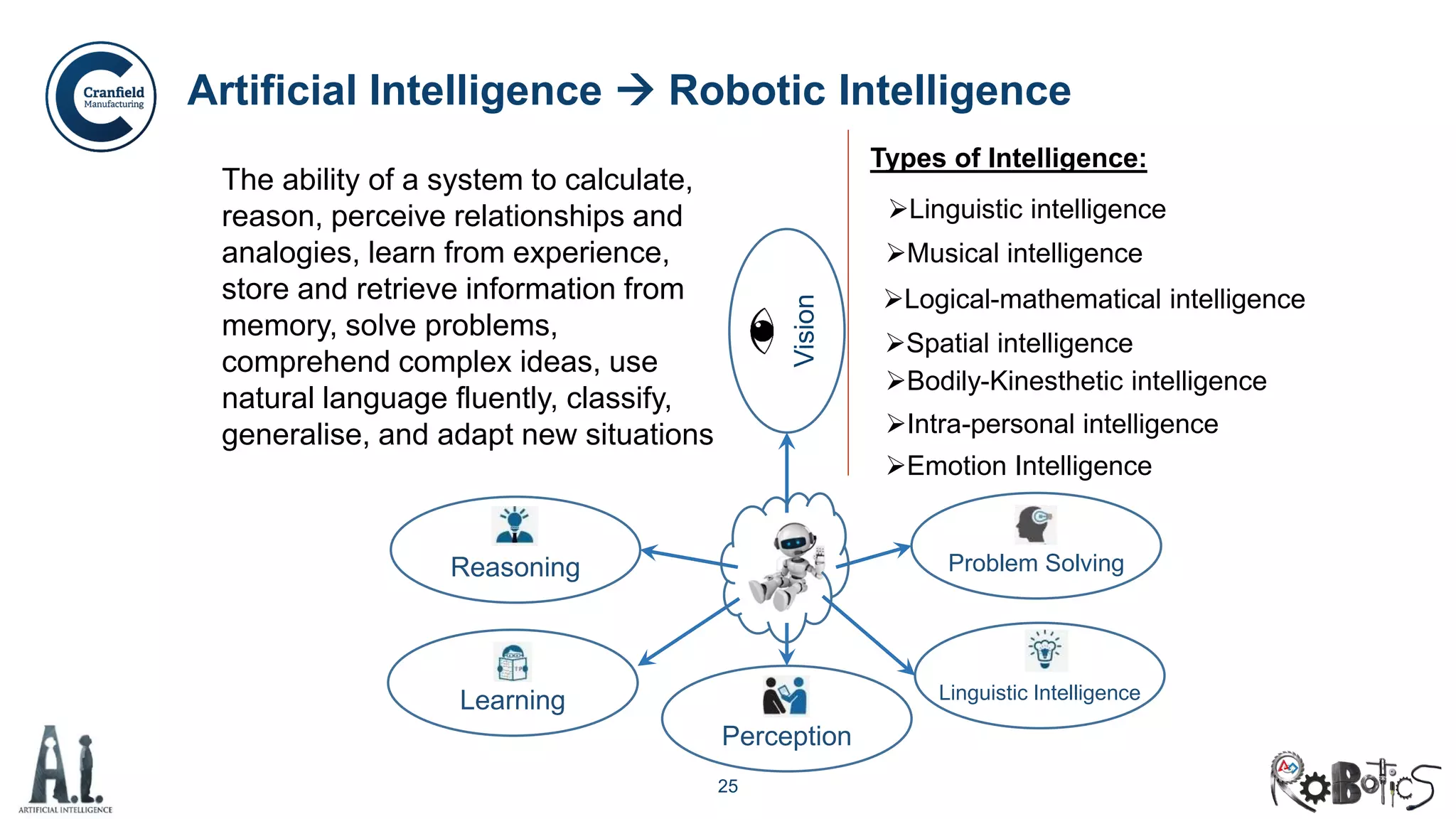
Artificial Intelligence System [1]
[1] PwC Analysis: Sizing the prize -- What’s the real value of AI for your business and how can you capitalise?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ai-robotics-update26oct2019-191026111211/75/AI-robotics-Past-Present-and-Future-4-2048.jpg)


![10
Ten Milestones of Robotics [2]
1941 1961 1964 1973 1985 1986 1997 2002 2011 2012
Isaac Asimov
Outlines Three
Laws of
Robotics
General Motors
Uses World’s First
Industrial Robot
U.S. Military
Begins Using
Drone Aircraft in
Vietnam"
Honda Begins Work
on Independent
Walking Robot
NASA Launches
First Human-Like
Robot Into Orbit
First
Anthropomorphic
Robot
Doctor Performs First
Robot-Assisted Surgery
Roomba Changes
Perception of
Robots
Google Self-Driving
Car Passes Driver’s
License Test
[2] http://listosaur.com/science-a-technology/10-milestones-robotics-history/
First RoboCup
football match](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ai-robotics-update26oct2019-191026111211/75/AI-robotics-Past-Present-and-Future-10-2048.jpg)
![12
Artificial Intelligence Today [1]
Human in the loop No human in the loop
Hardware/Specific
System
Assisted intelligence:
Helping people to perform
tasks faster and better.
Automated intelligence:
Automation of
manual/cognitive and
routine/nonroutine tasks.
Adaptive Systems Augmented intelligence:
Helping people to make
better decisions.
Autonomous intelligence:
Automating decision making
processes without human
intervention.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ai-robotics-update26oct2019-191026111211/75/AI-robotics-Past-Present-and-Future-12-2048.jpg)

![14
Robots in Terms of the 4 AI Forms
Domestic robots
Medical robots
Service robots
Assisted intelligence: Automated intelligence:
Medical robots (surgery robots) Manufacturing machines
Industry arms/hands/robots
Augmented intelligence: Autonomous intelligence:
Machine translators
Entertainment robots (AlphaGo)
Domestic robots (home care robots)
Robotic nurses/doctors
(cannot replace human doctors) [3]
Entertainment robots (Robot Football)
Service robots
Domestic robots (robotic cleaner)
Mobile robots
Space robots
Military robots
[3] Stephen K. Klasko , Robots, Augmented Intelligence, and Things Only Humans Can Do
MARY ANN LIEBERT, INC. • DOI:10.1089/heat.2016.29028.skk](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ai-robotics-update26oct2019-191026111211/75/AI-robotics-Past-Present-and-Future-14-2048.jpg)








![26
Robotics Vision for Autonomous Vehicles [4]
Background-absorbing Markov chain
Spatial Pyramid Pooling (SPP) + CNN:
Output:
• 7 classes
• {10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70}
Recognition Rate: 98.98%
The recognition rate is up to 9.32% higher than that obtained by SPP-CNN
working on raw dataset directly
[4] Z. L. Zhu, G. Xu, H. He, J. Jiang, Recognition of Speed Signs in Uncertain and Dynamic
Environments, 2018 3rd International Conference on Information Science, Computer Technology
and Transportation (ISCTT2018), Xi’an, Shanxi, China, 28-30 Dec. 2018.
.
Background-Absorbing Markov chain](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ai-robotics-update26oct2019-191026111211/75/AI-robotics-Past-Present-and-Future-26-2048.jpg)
![27
A case study: Robot Route Learning with a Linguistic Decision Tree
Learning from experience [5]
Human drives robot
along a path for several
times
Record the data from
laser sensor, which scan
the environment when
robot is driven
Robot has four basic
actions: turn left, turn
right, forward and
backward
[5] H. He, T. M. McGinnity, S. Coleman and B. Gardiner, Linguistic Decision Making for Robot Route Learning,
IEEE Transaction on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 25(1), Jan 2014, pp. 203 – 215.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ai-robotics-update26oct2019-191026111211/75/AI-robotics-Past-Present-and-Future-27-2048.jpg)