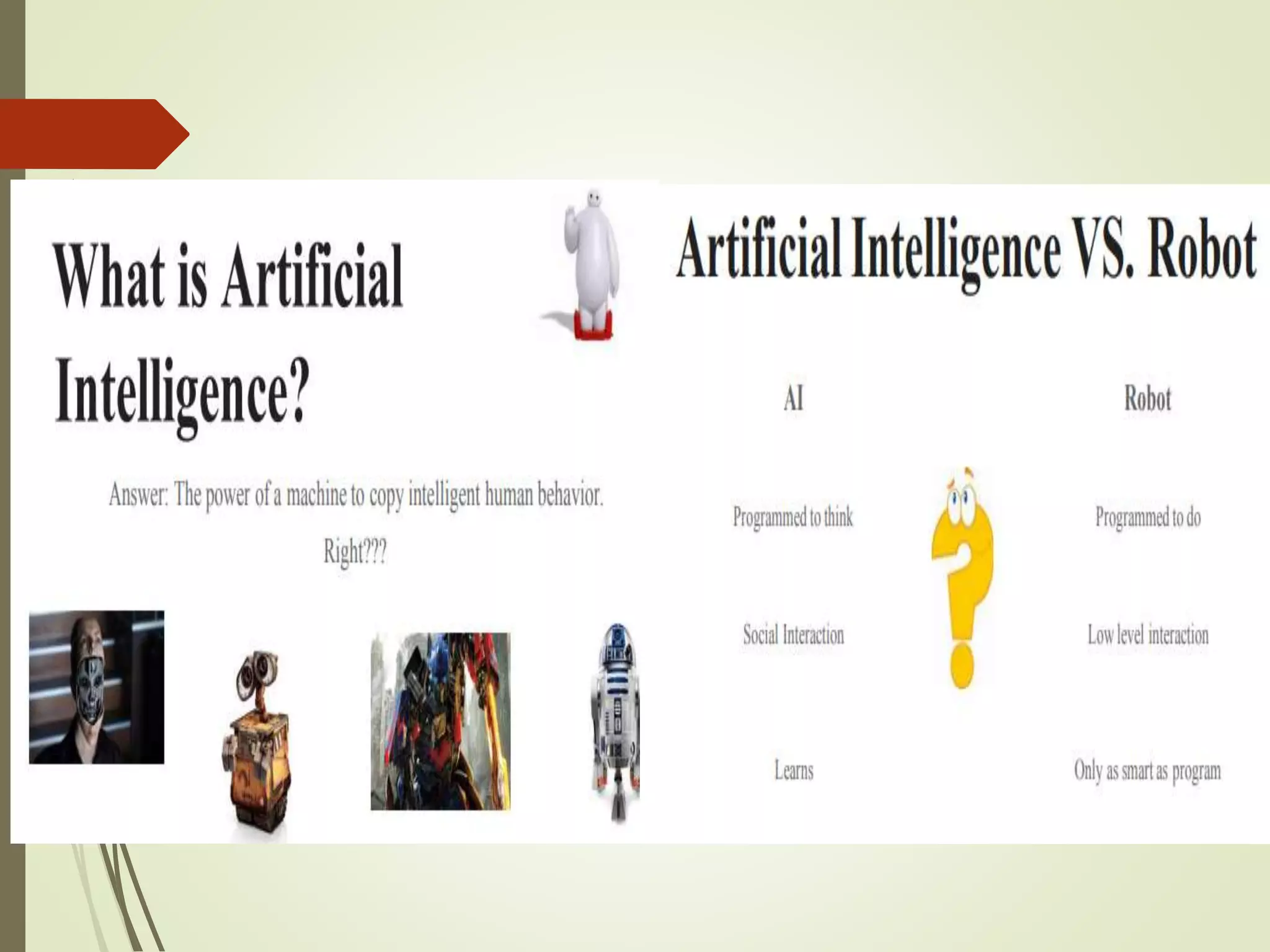
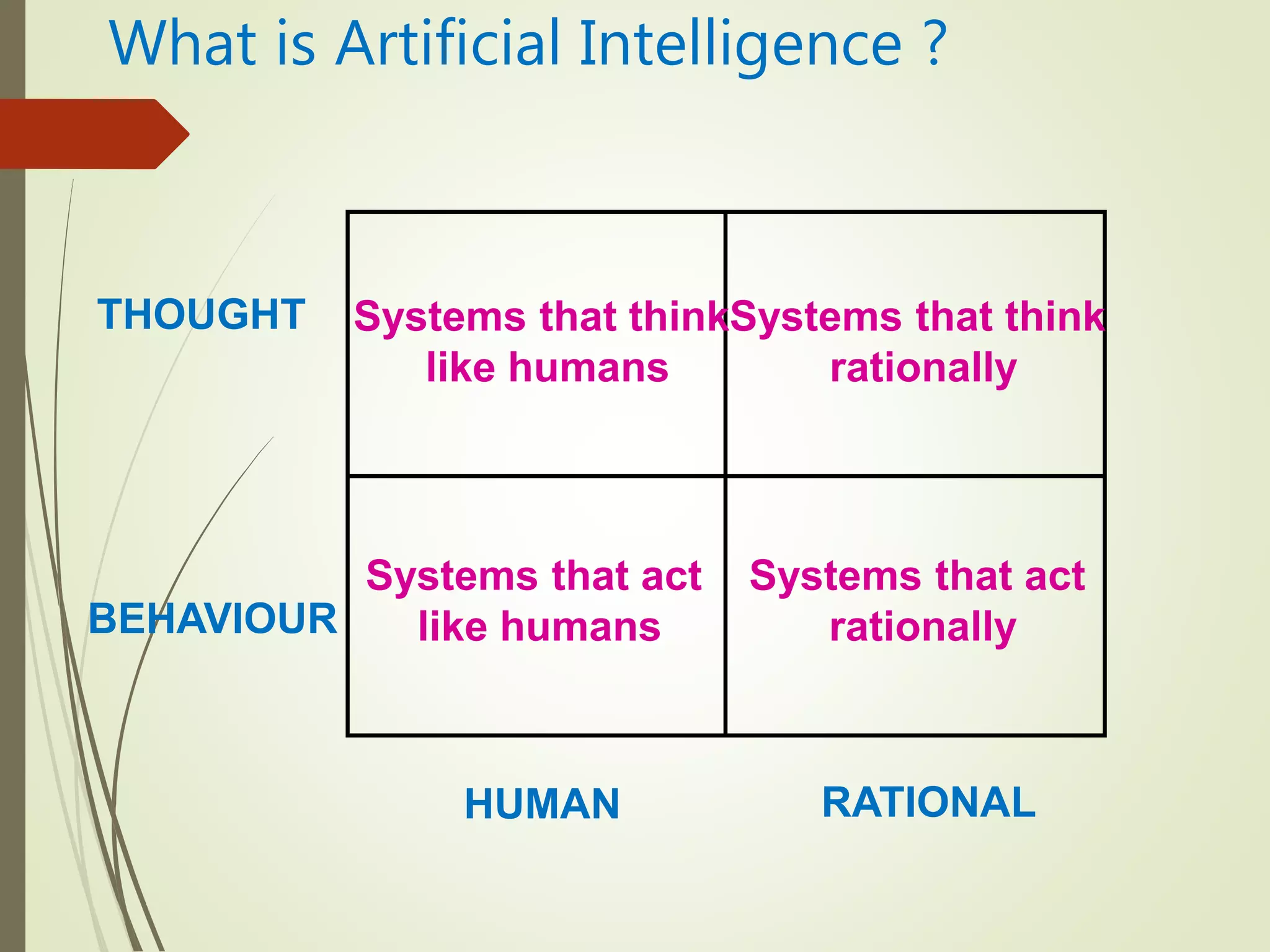
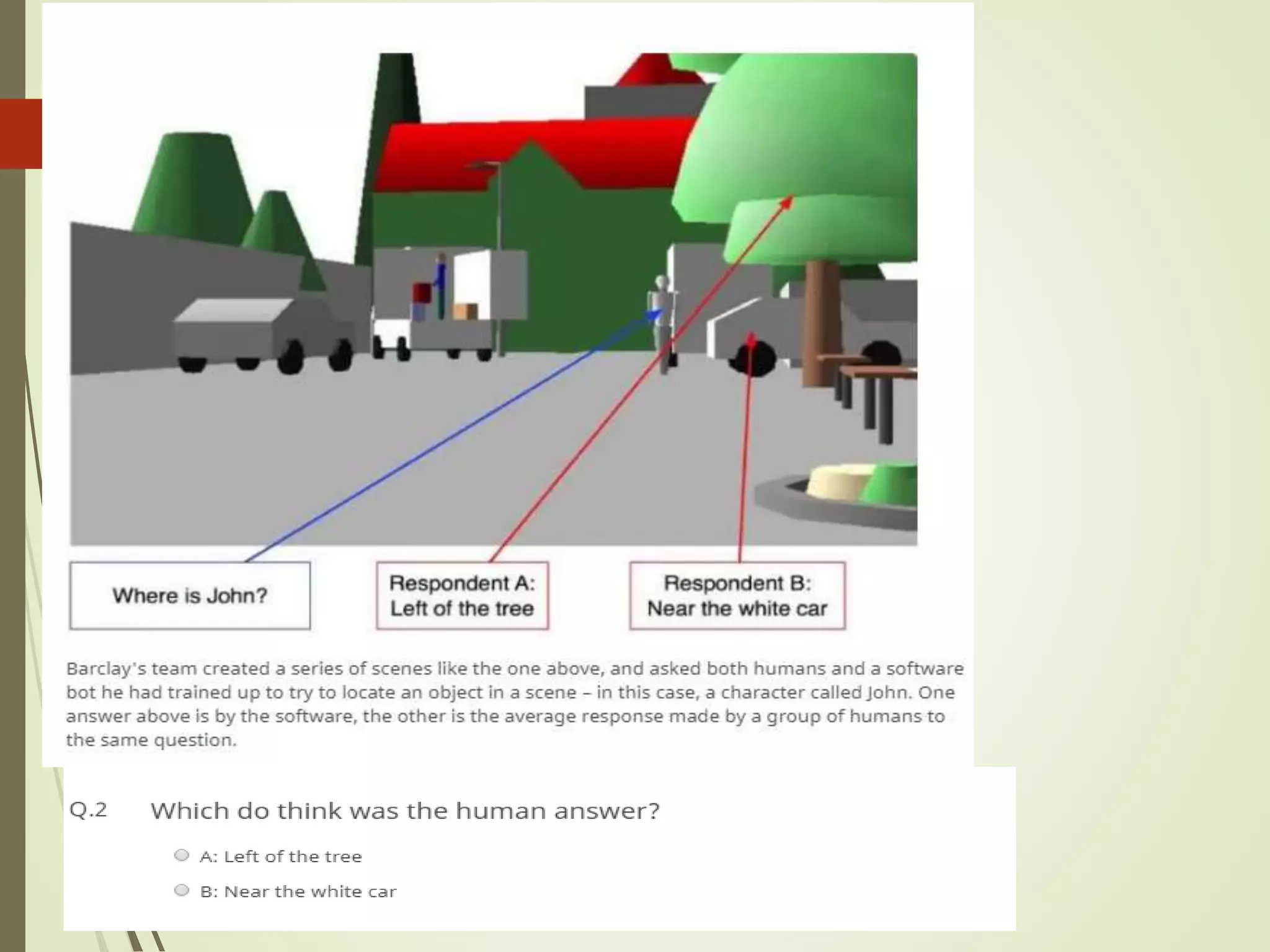
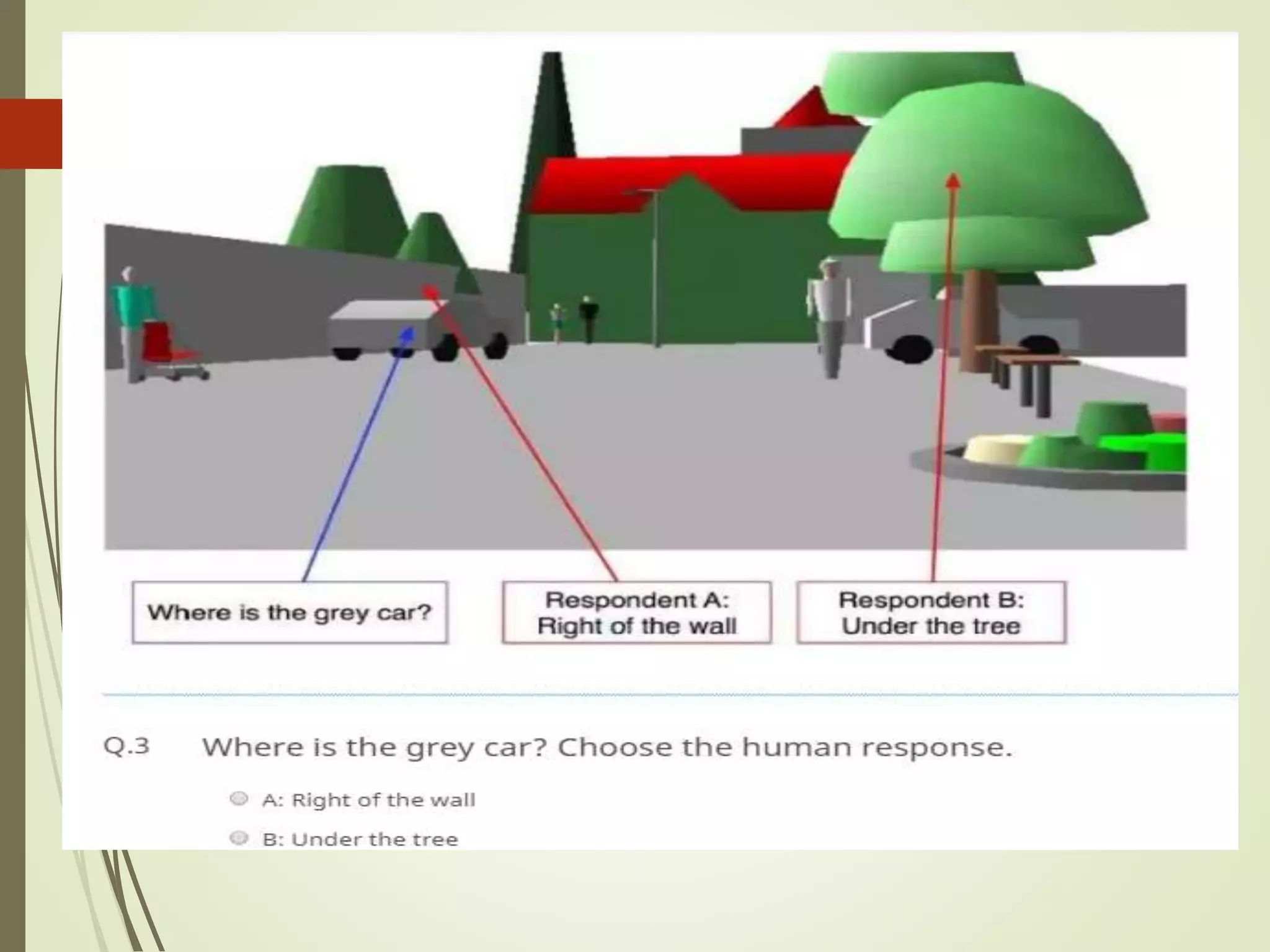
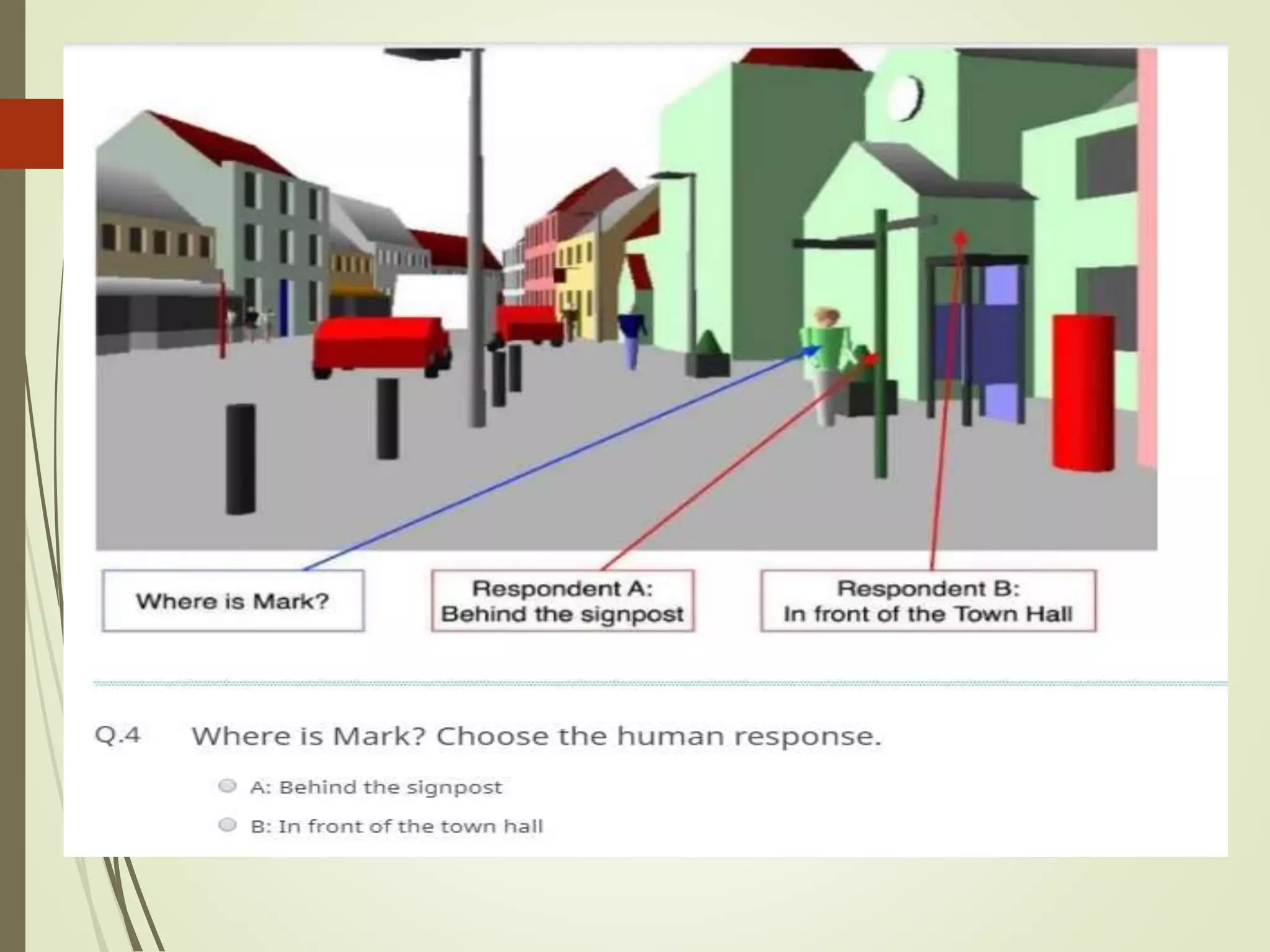
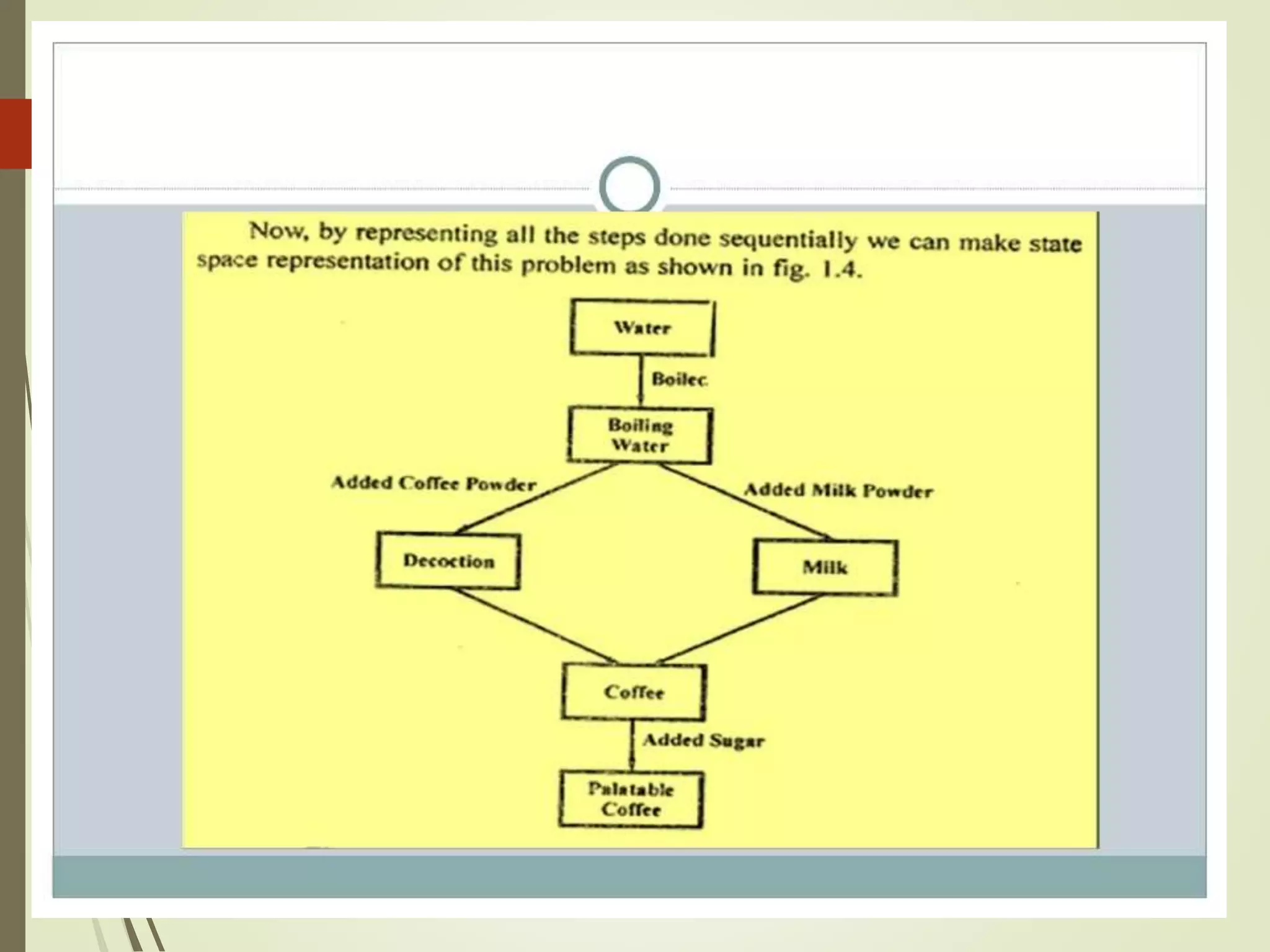
The document discusses what artificial intelligence is, including defining it as machines that can exhibit intelligent behavior like learning and problem solving. It also discusses how AI works by using large data to train algorithms that can then be used to make predictions, and gives examples of goals for AI like creating expert systems and developing machines that can perform human-like tasks.