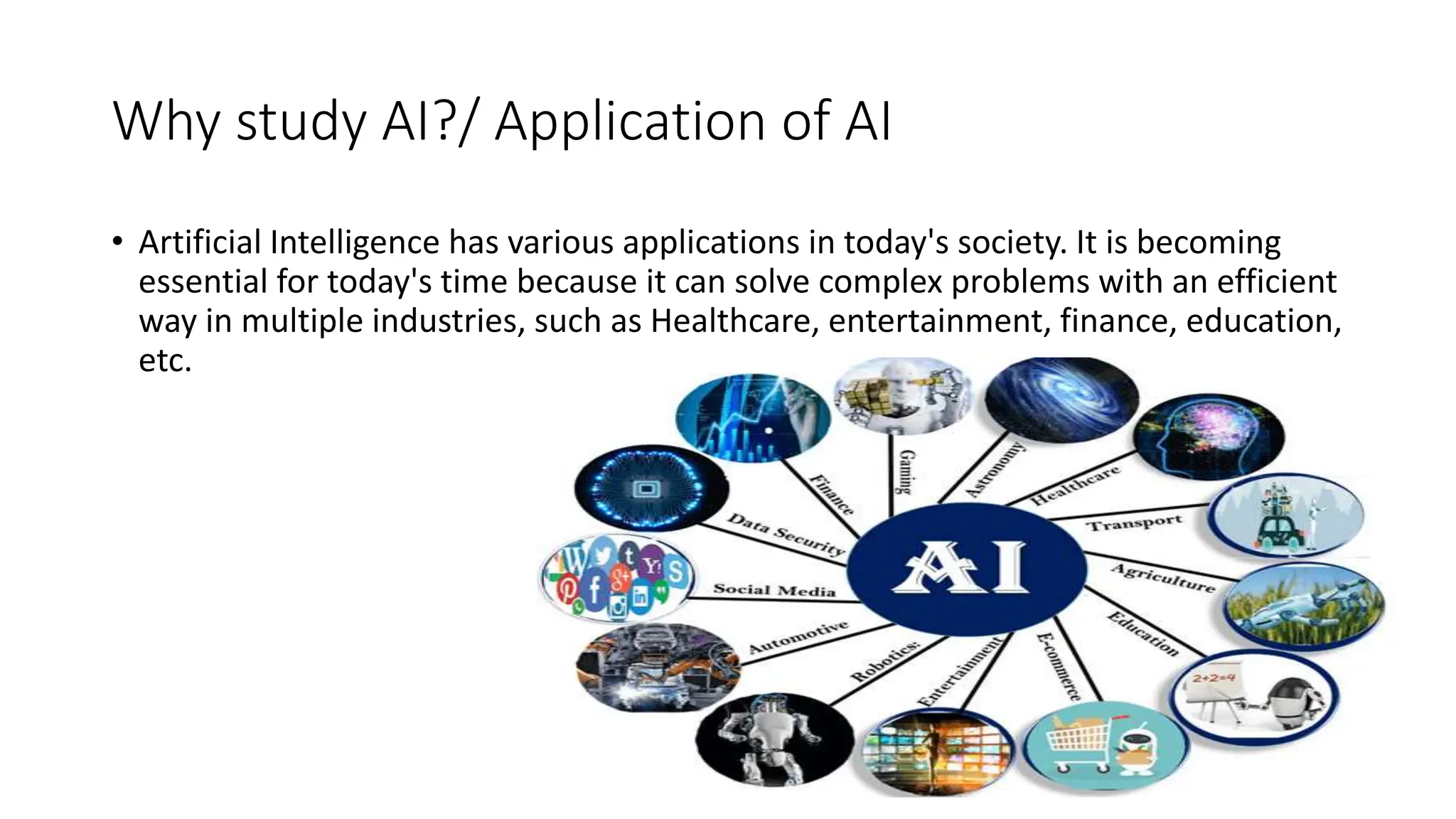
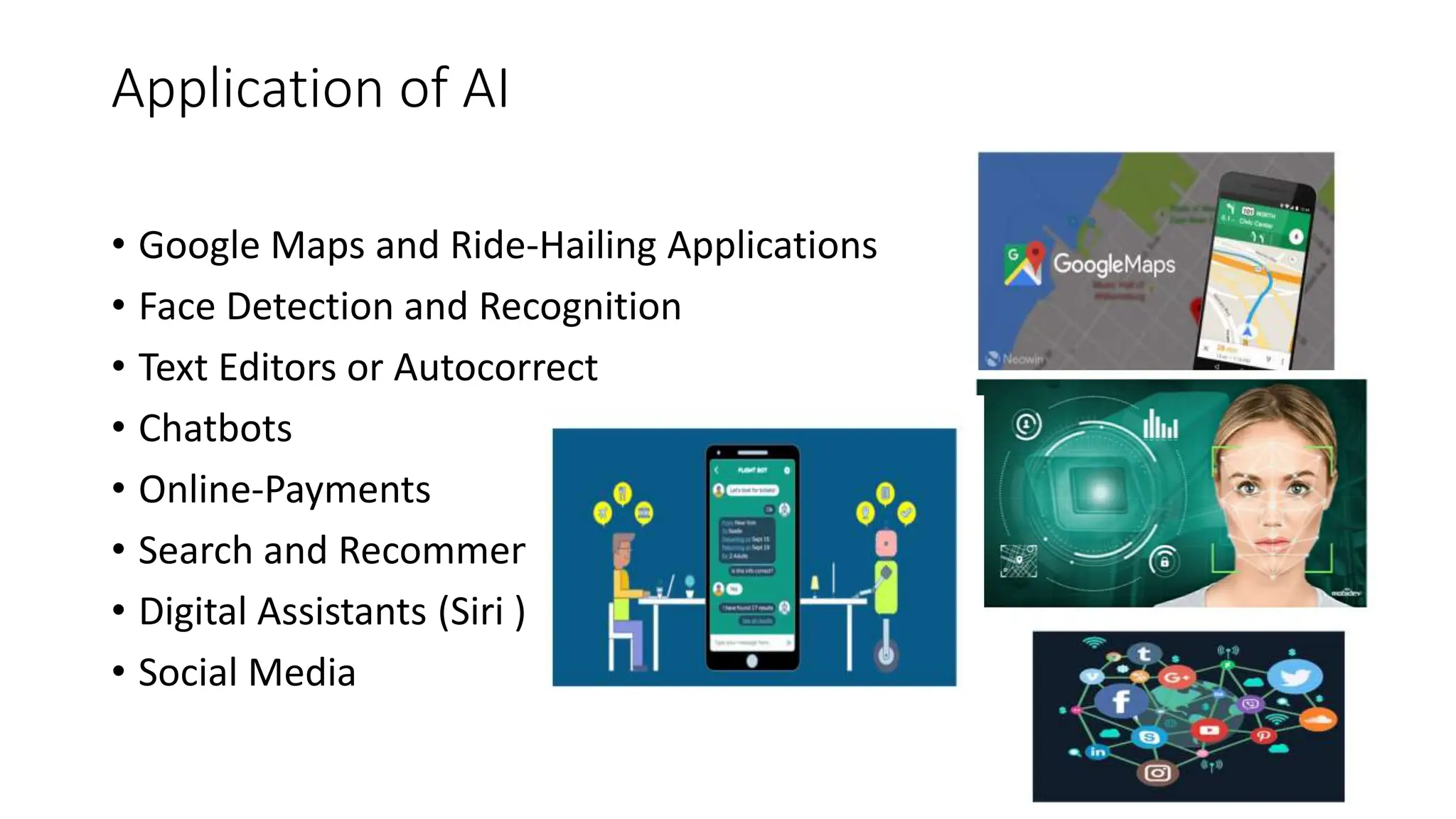
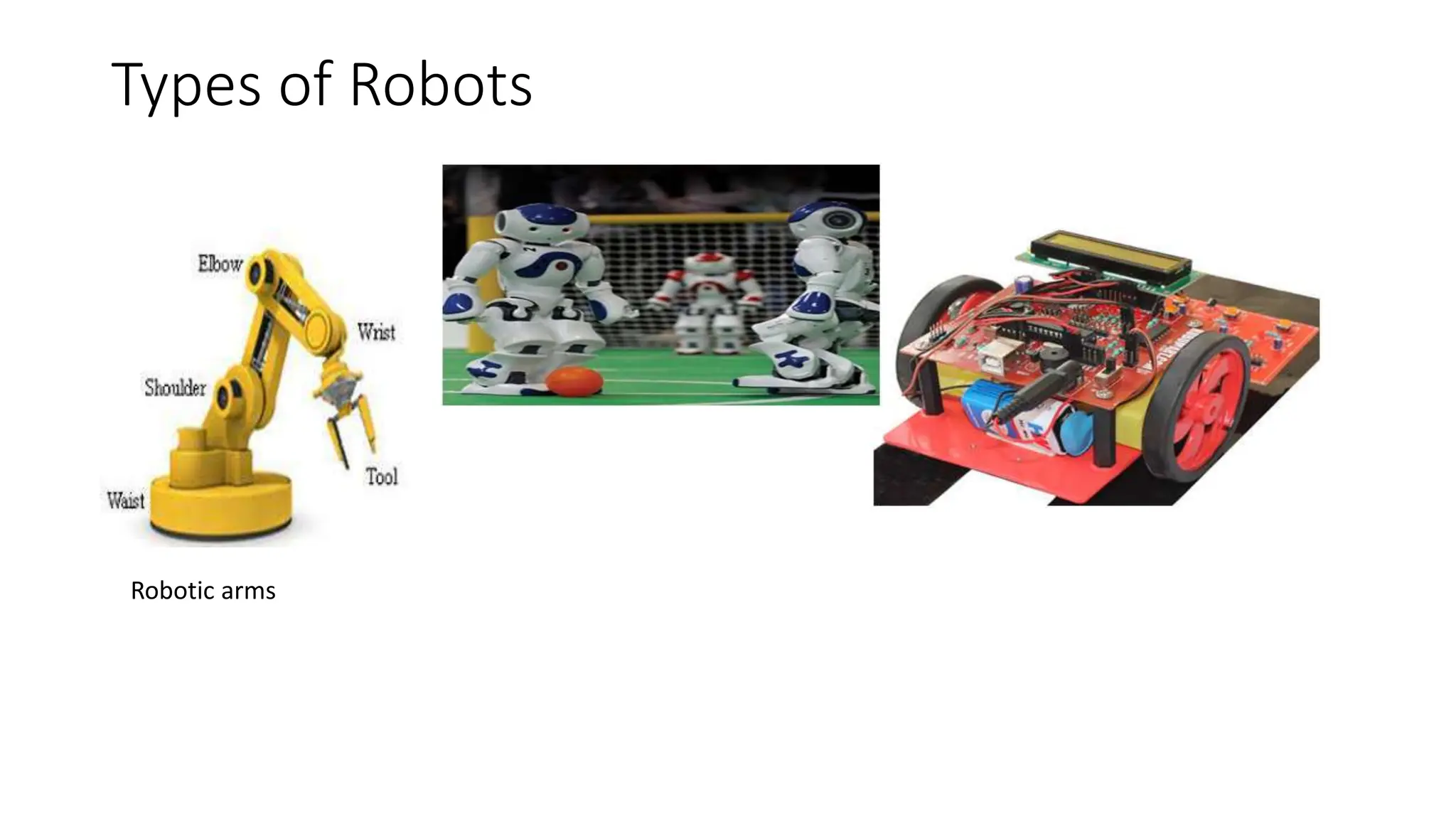
Artificial intelligence (AI) simulates human intelligence in machines, with roots tracing back to 1956 when it was first coined as a field by John McCarthy. AI has diverse applications across industries, including healthcare and finance, and is characterized by its ability to learn, make accurate decisions, and operate in high-risk environments. Additionally, robots are computer-controlled machines designed to achieve specific goals, featuring various types such as mobile robots, robotic arms, and autonomous vehicles.