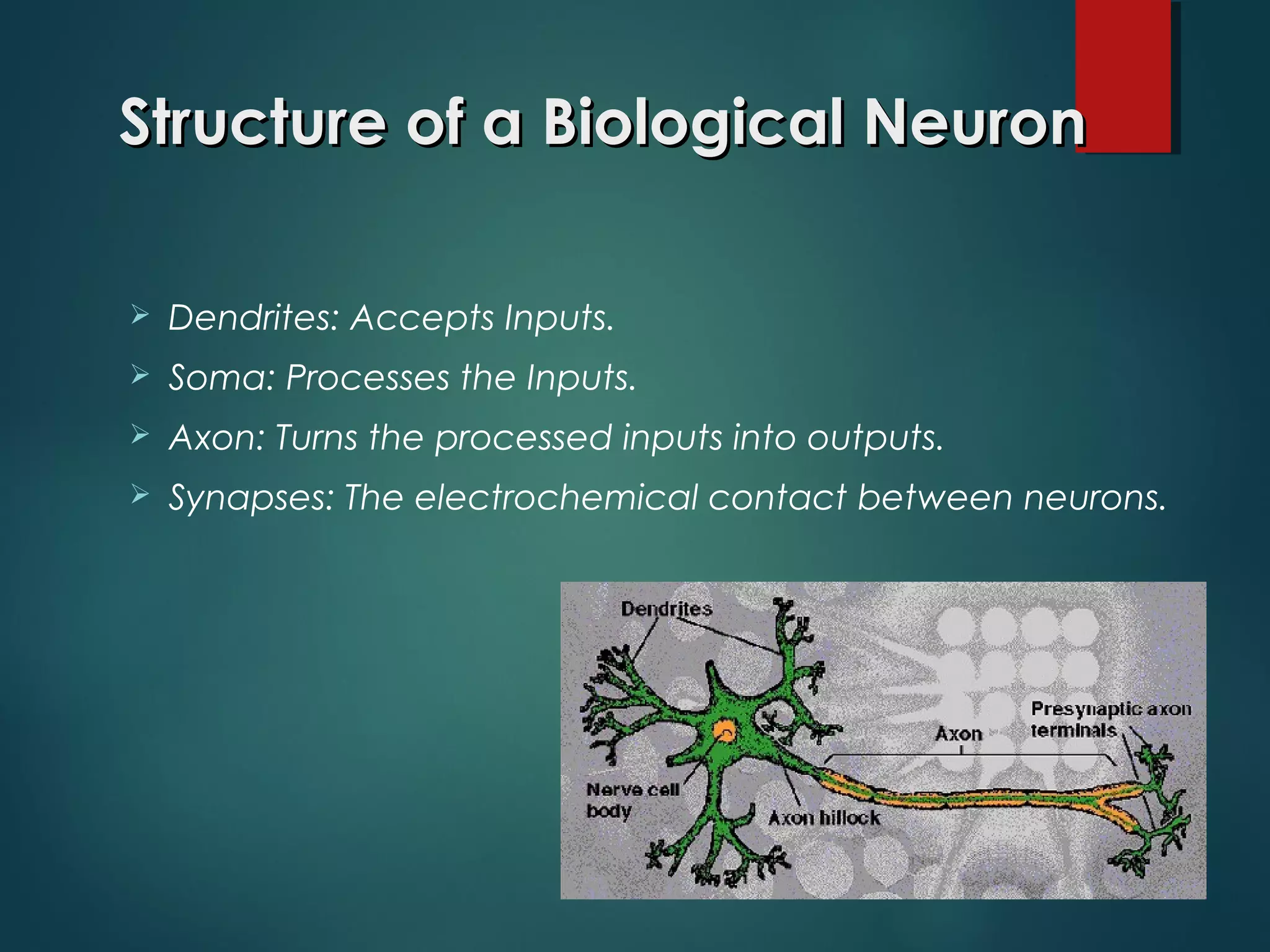
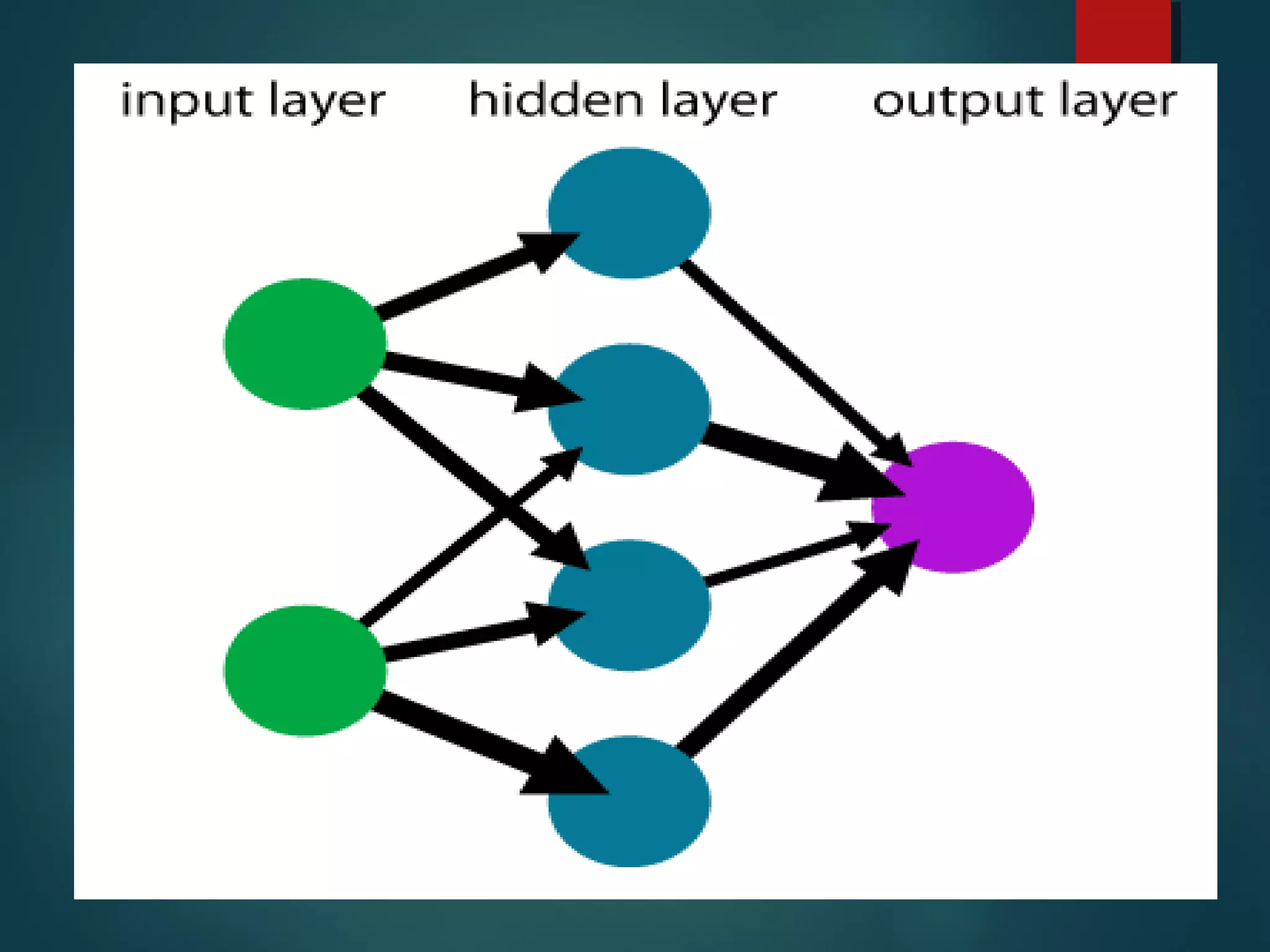
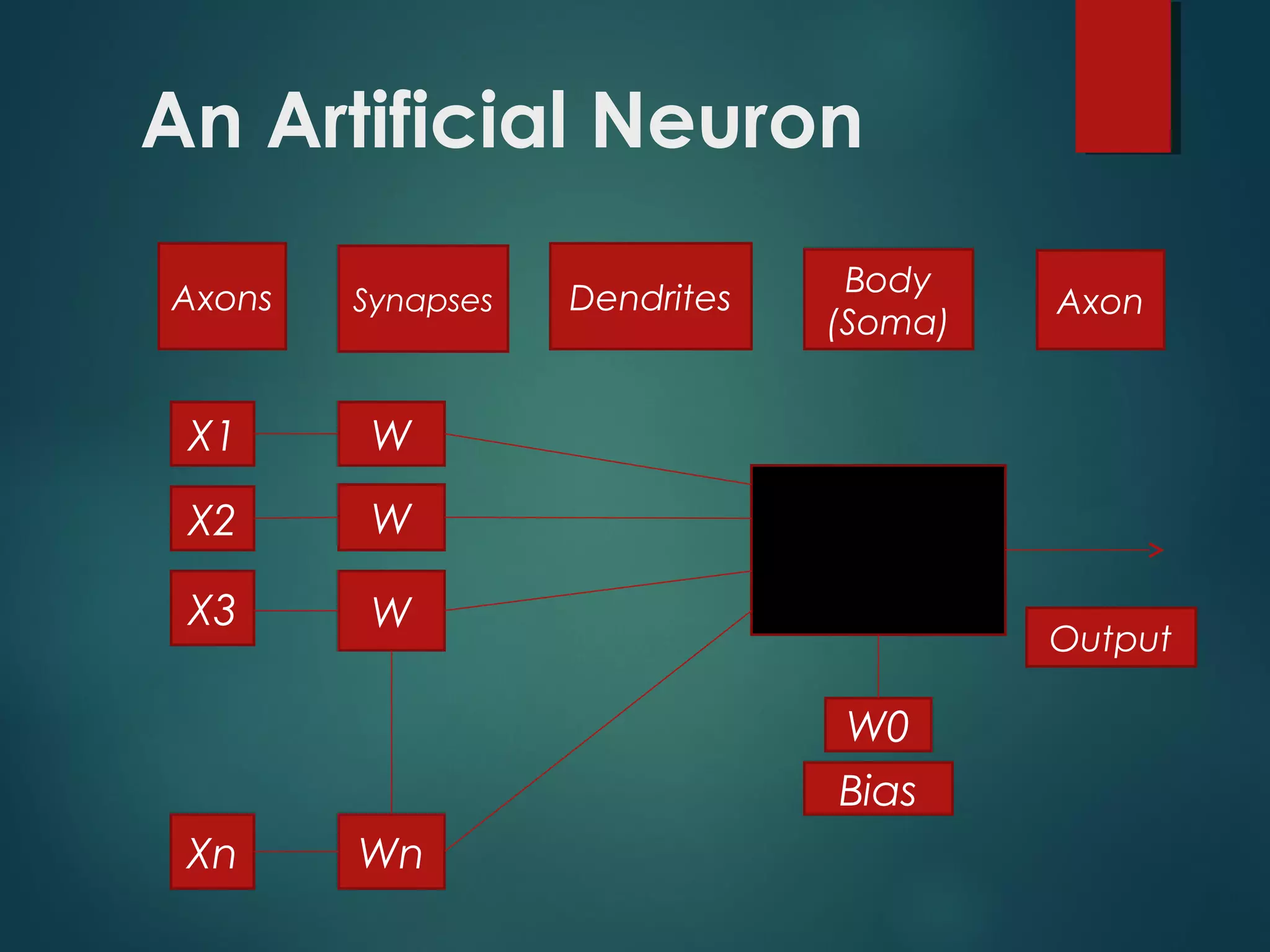
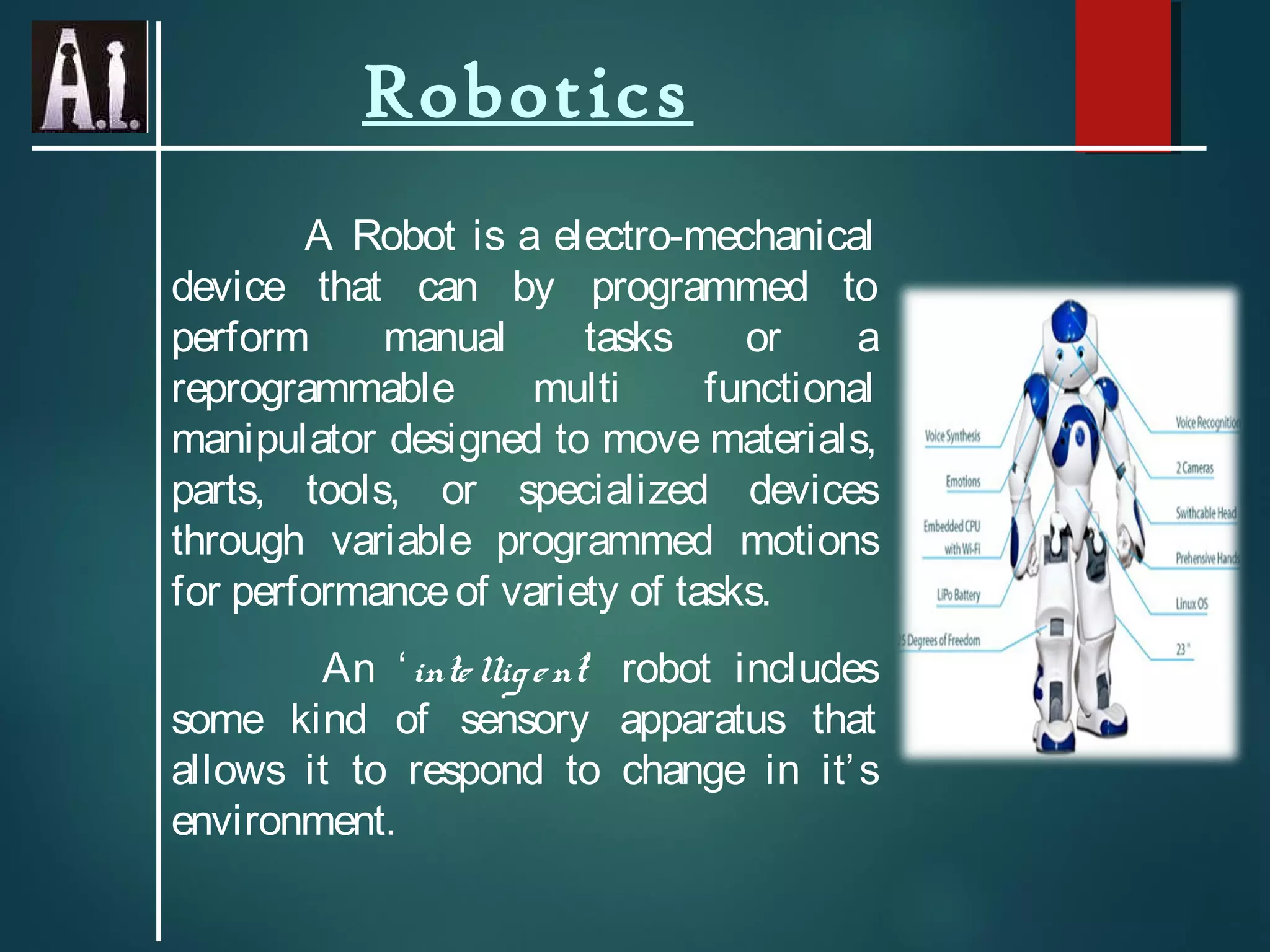
This document provides an introduction to artificial intelligence (AI), including how it works, its evolution and branches, applications, and conclusions. It defines AI as making computers do things that require human intelligence. AI works using artificial neurons and scientific theorems to mimic the human brain. The document outlines the history of AI from early programs in the 1950s to current applications in expert systems, natural language processing, computer vision, robotics, and more. It concludes that AI has increased understanding of intelligence while revealing the complexity of modeling human reasoning.