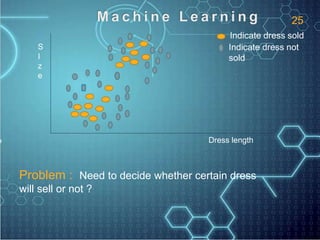
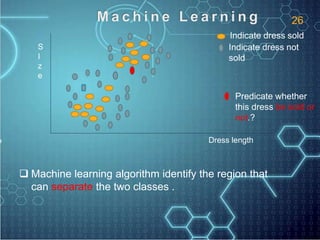
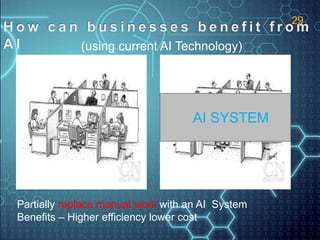
The document discusses artificial intelligence (AI) and defines it as the science and engineering of making intelligent machines, especially intelligent computer programs that have the abilities to learn, reason, perceive and understand language. It outlines several key AI technologies like machine learning, computer vision, natural language processing and speech recognition. It provides examples of applications in areas such as game playing, robotics, education, medical diagnosis and more. The document also gives a brief history of AI and discusses some programming languages commonly used in AI like Lisp.