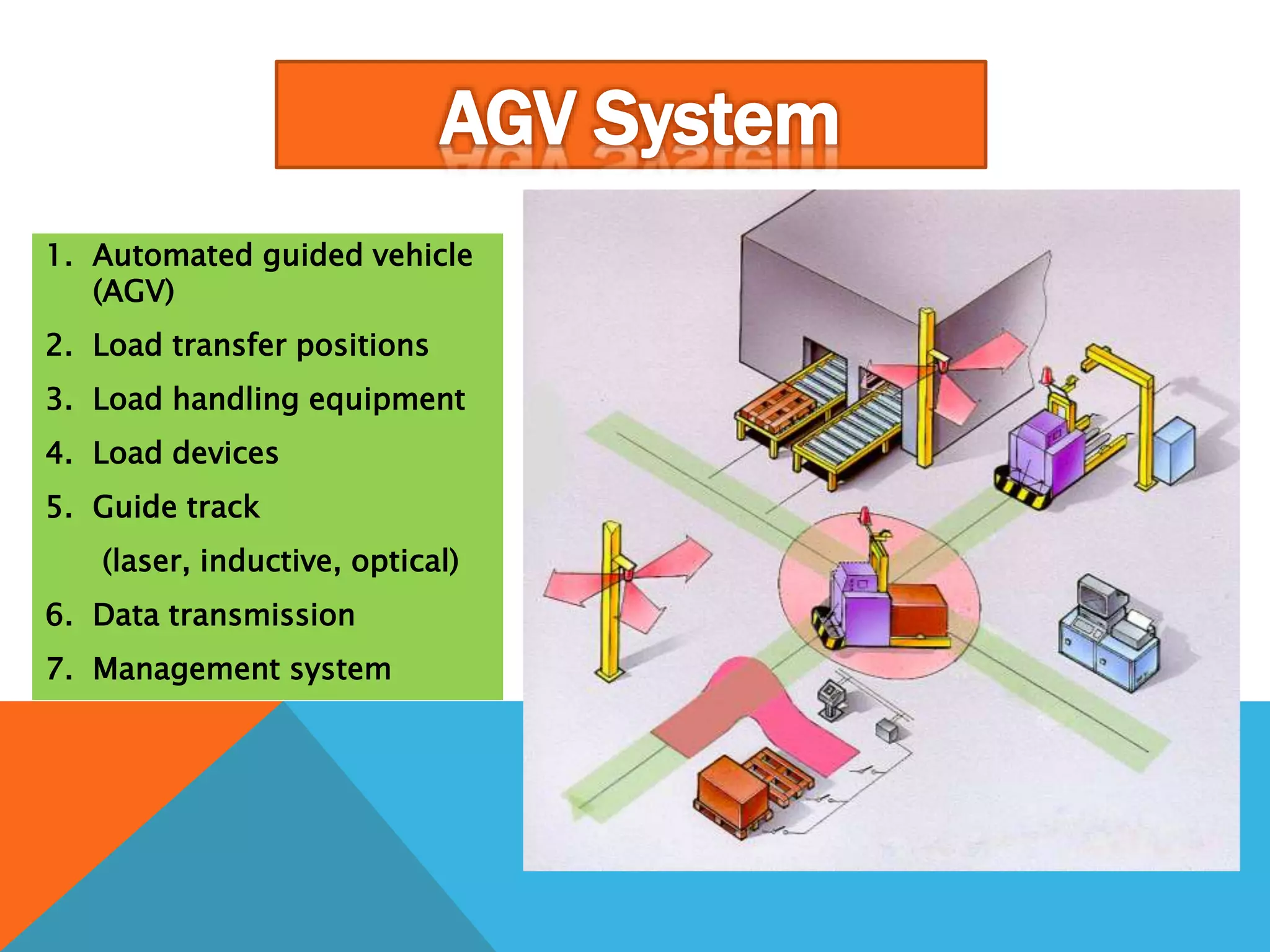
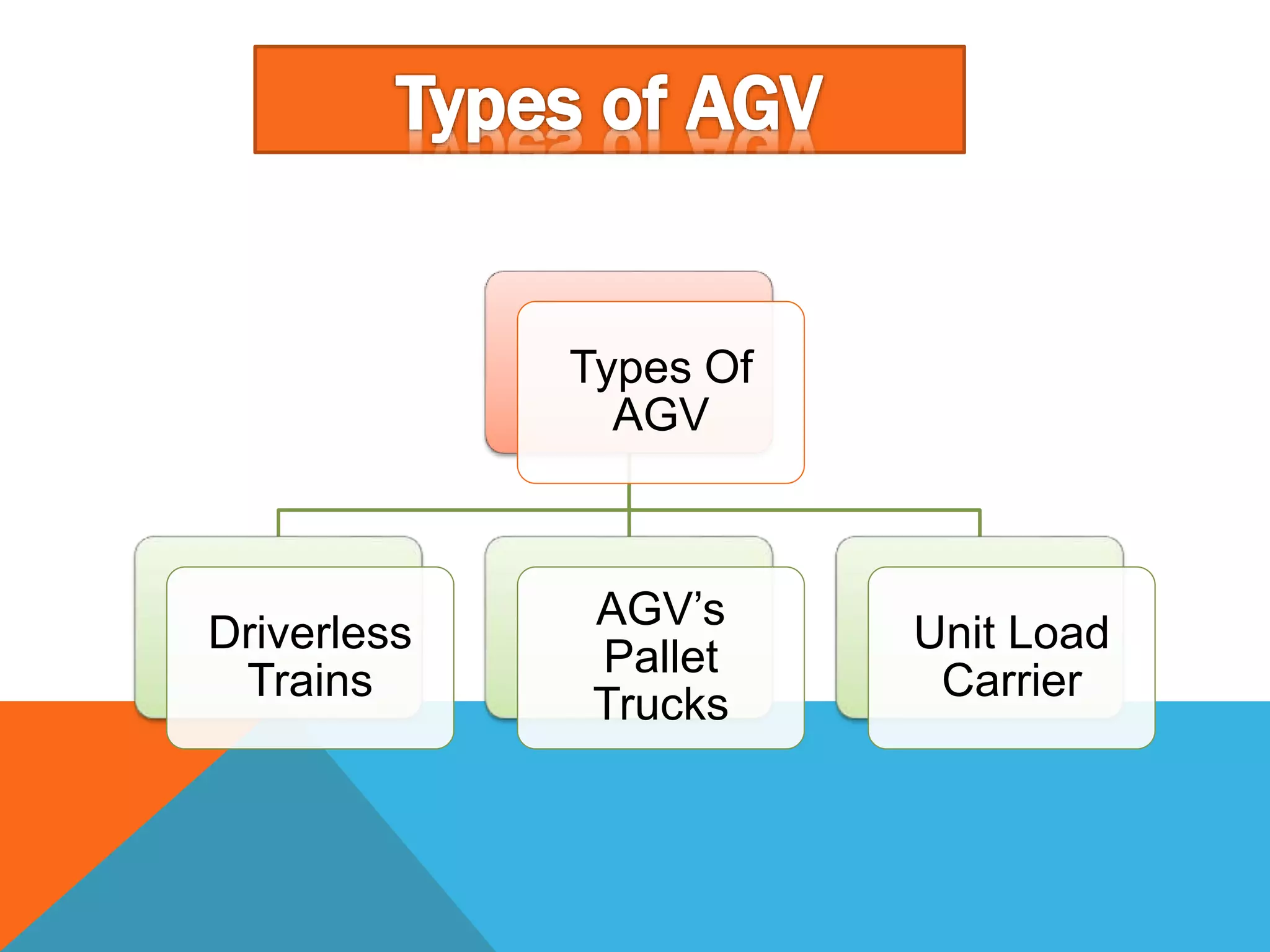
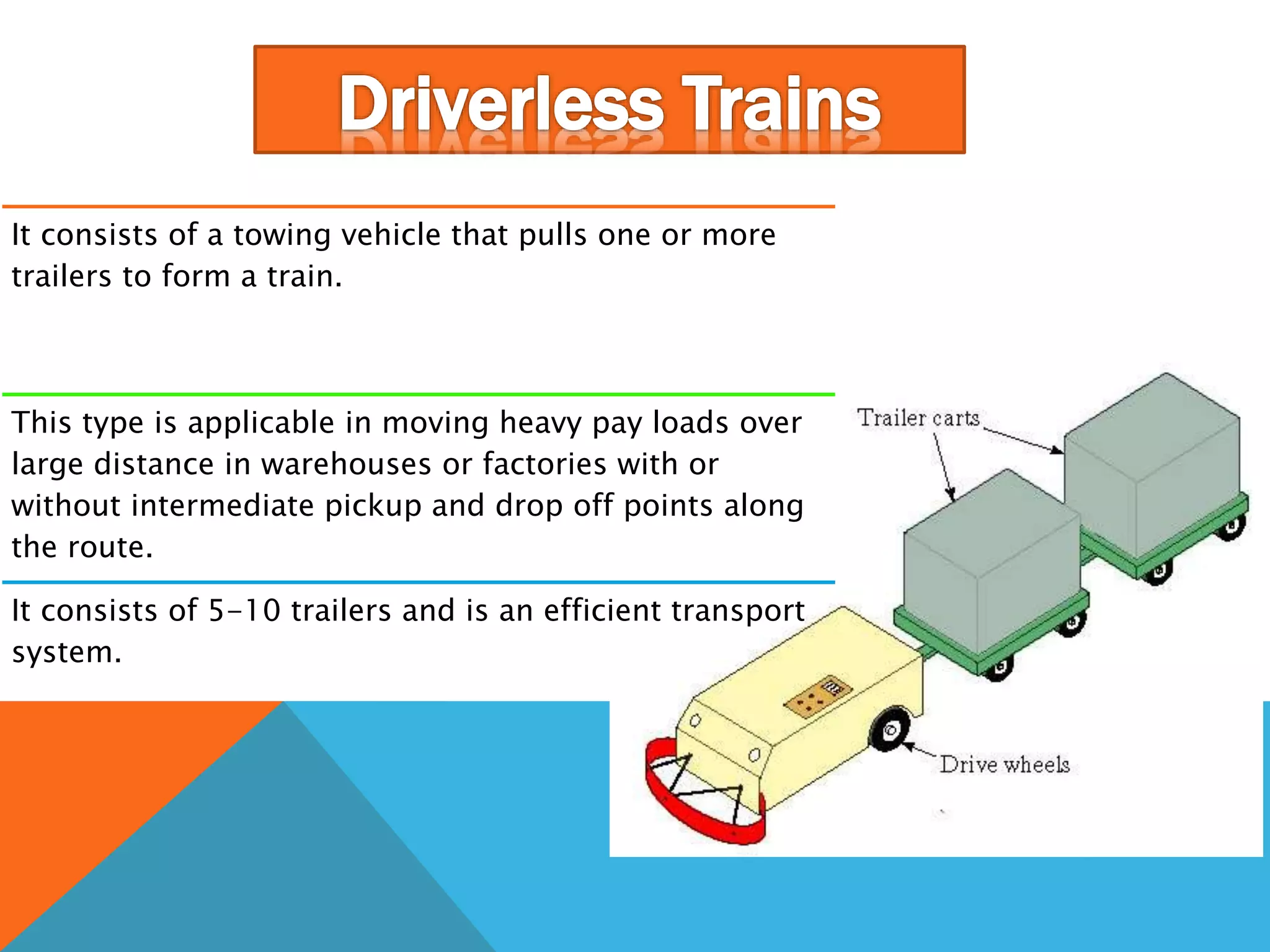
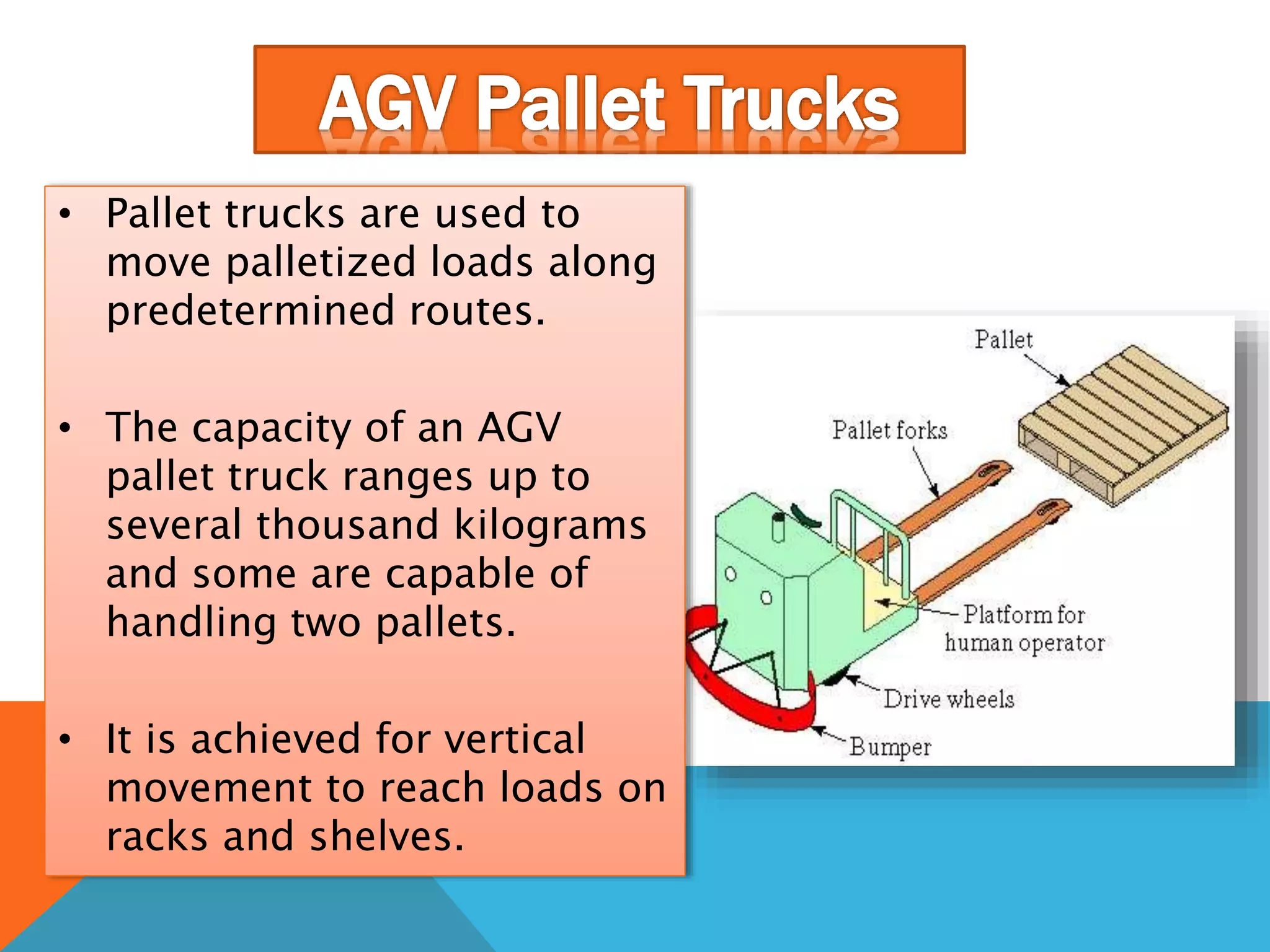
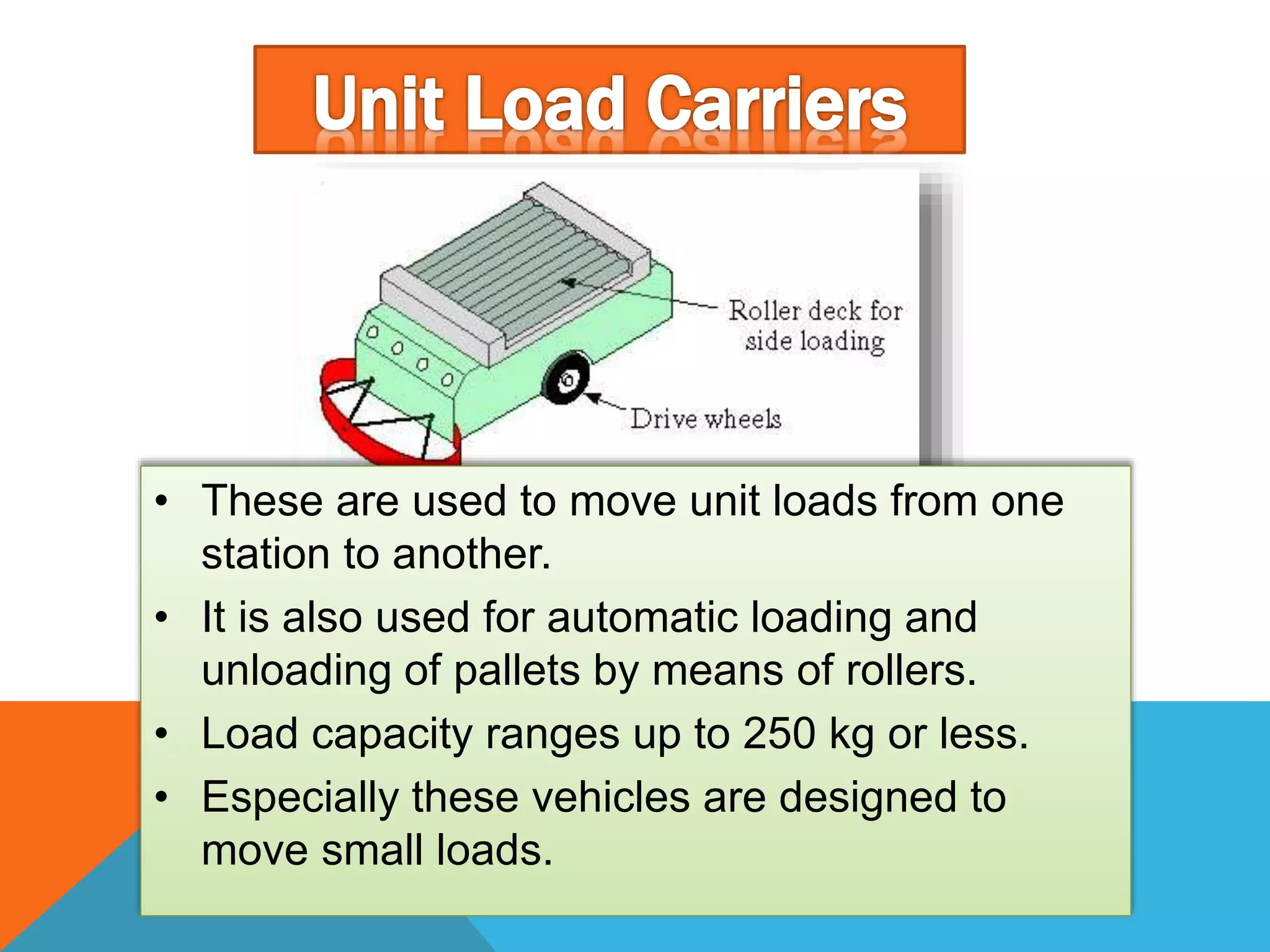
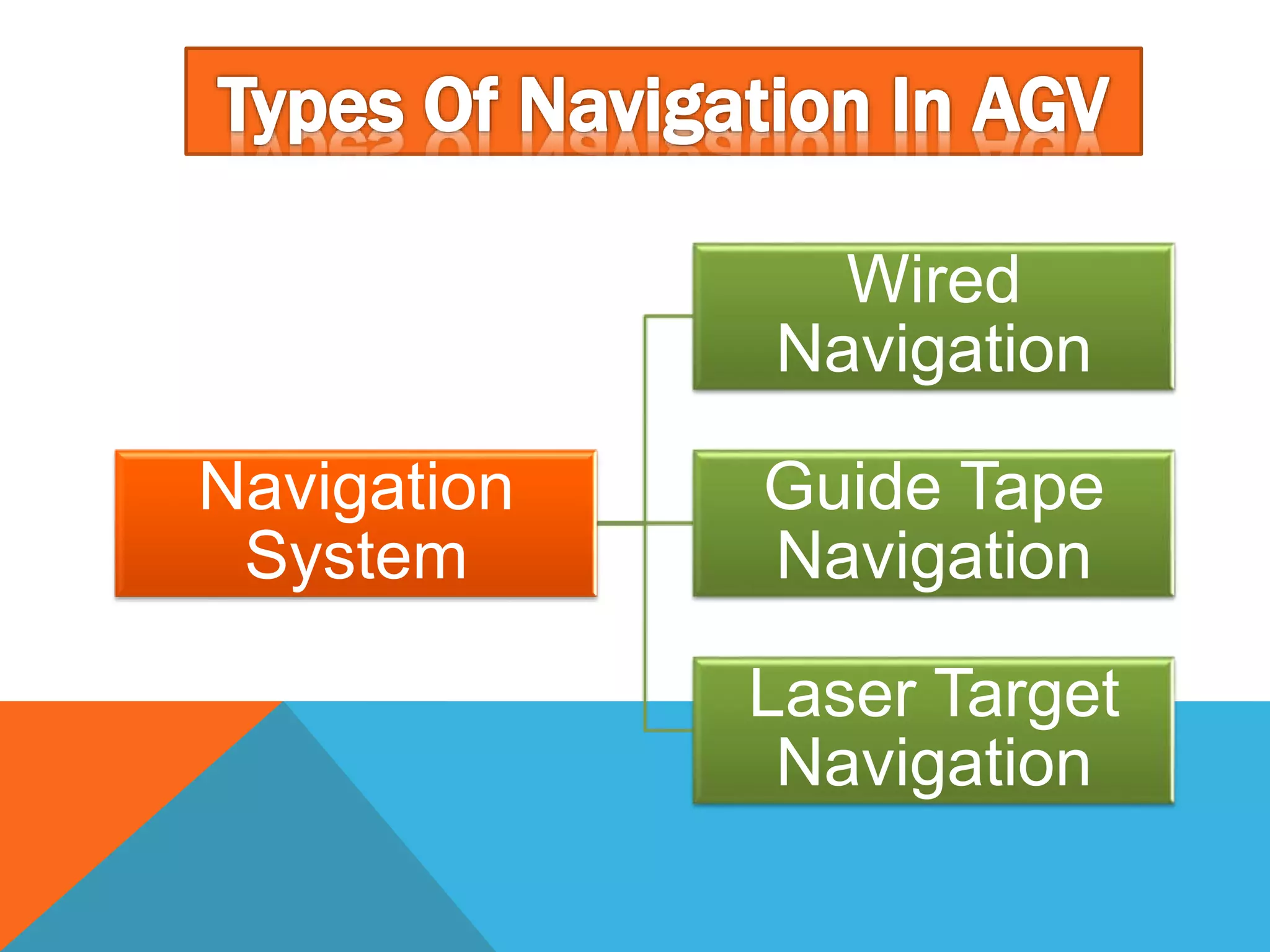
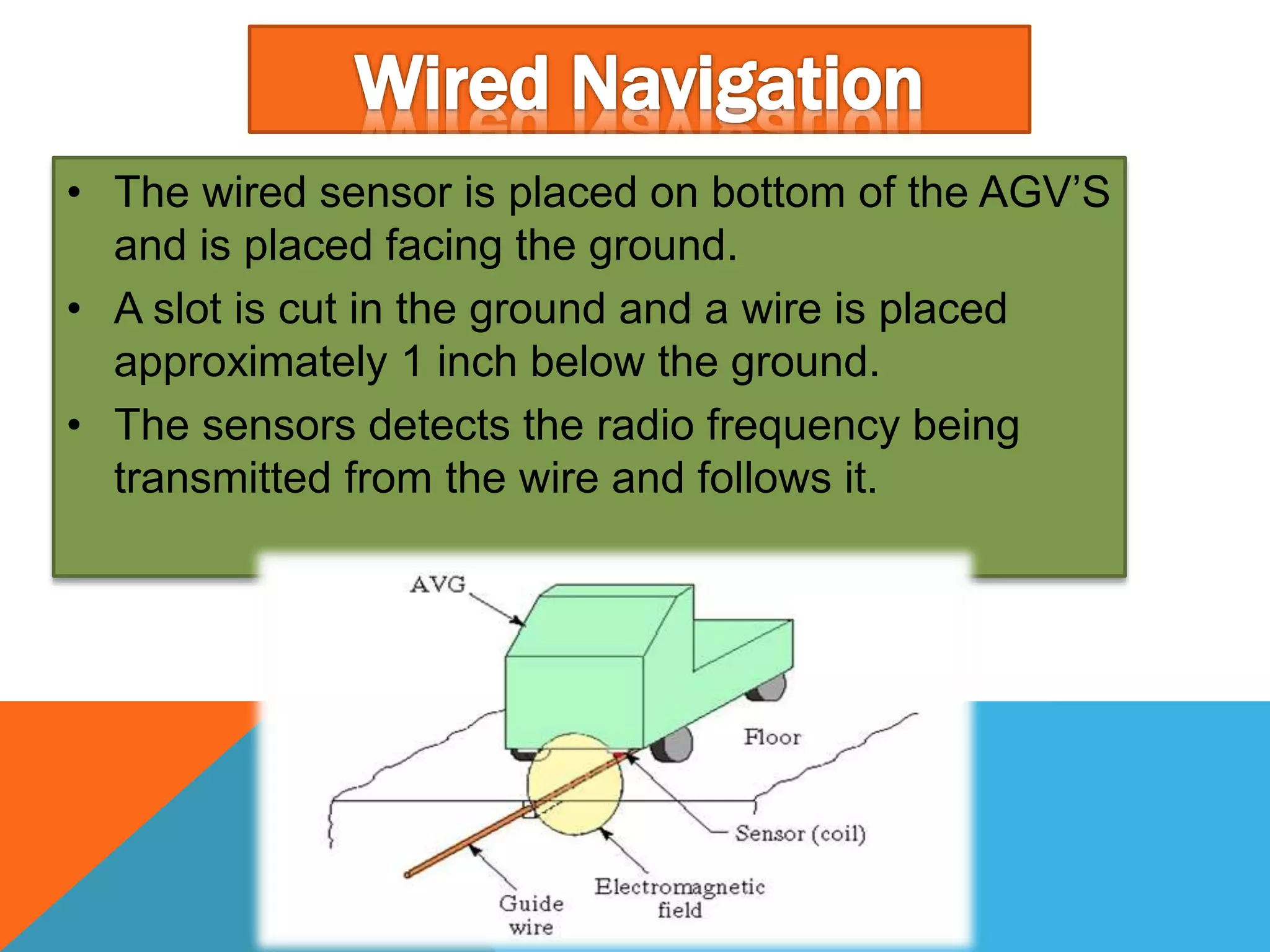
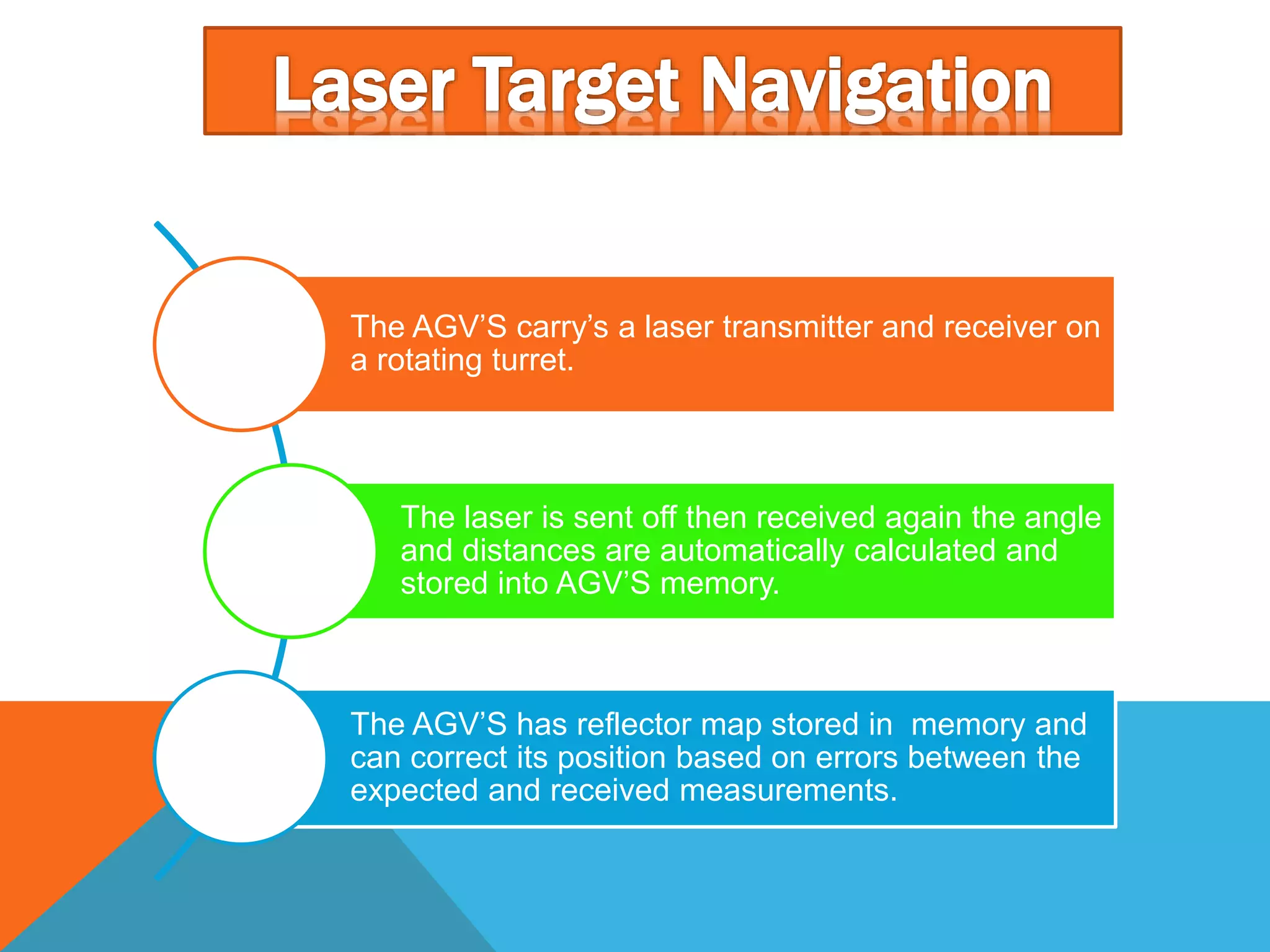
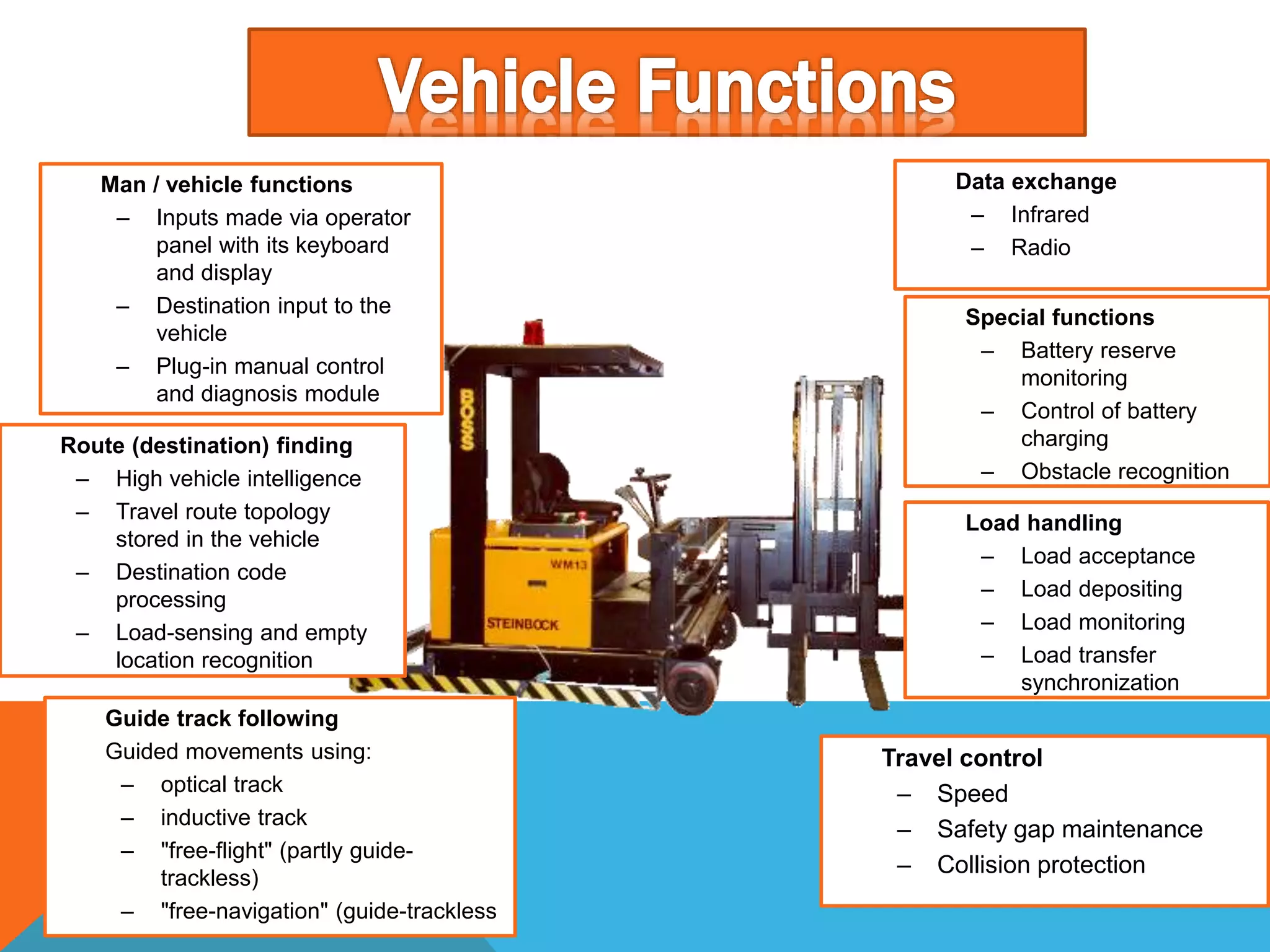
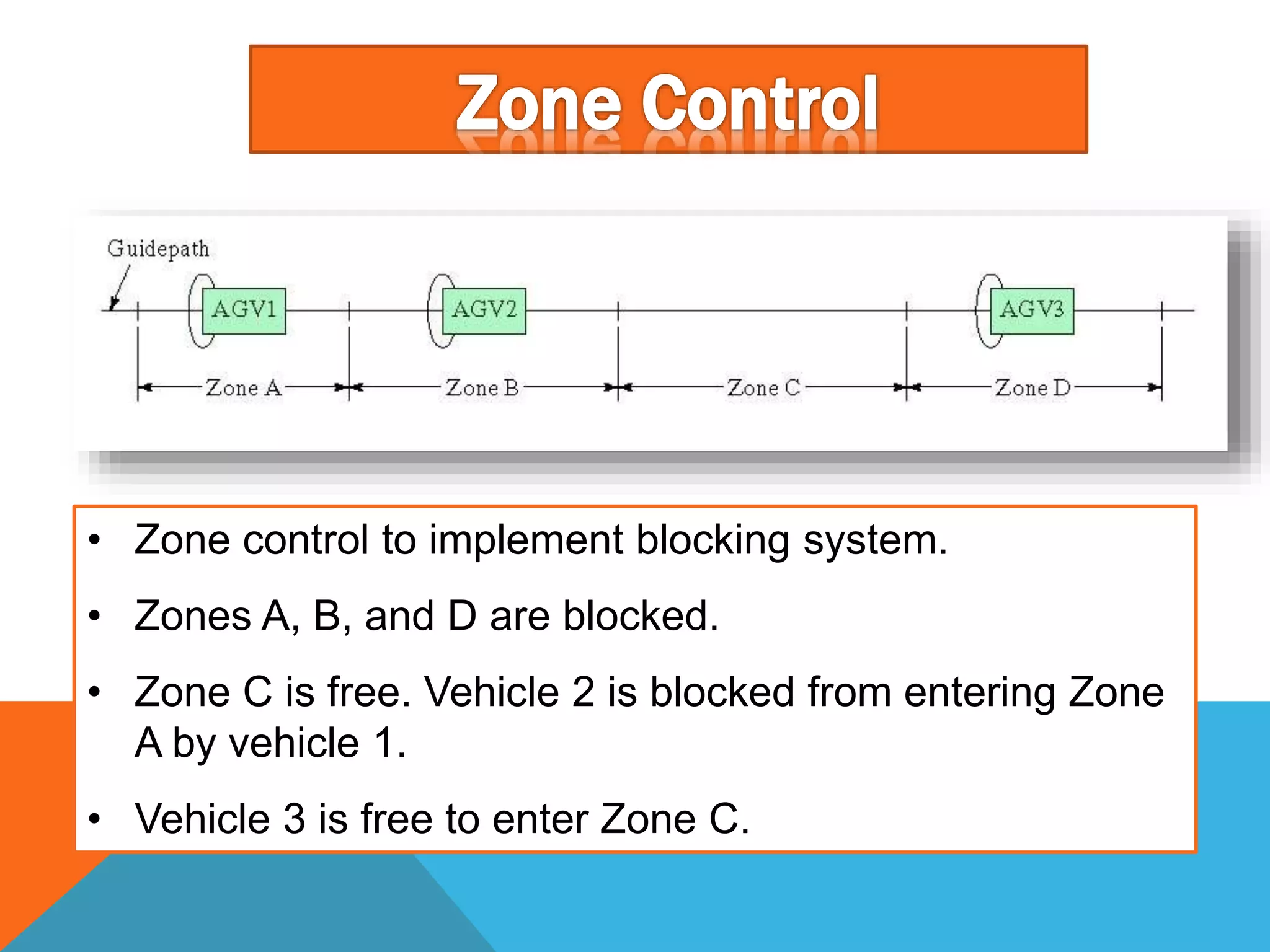
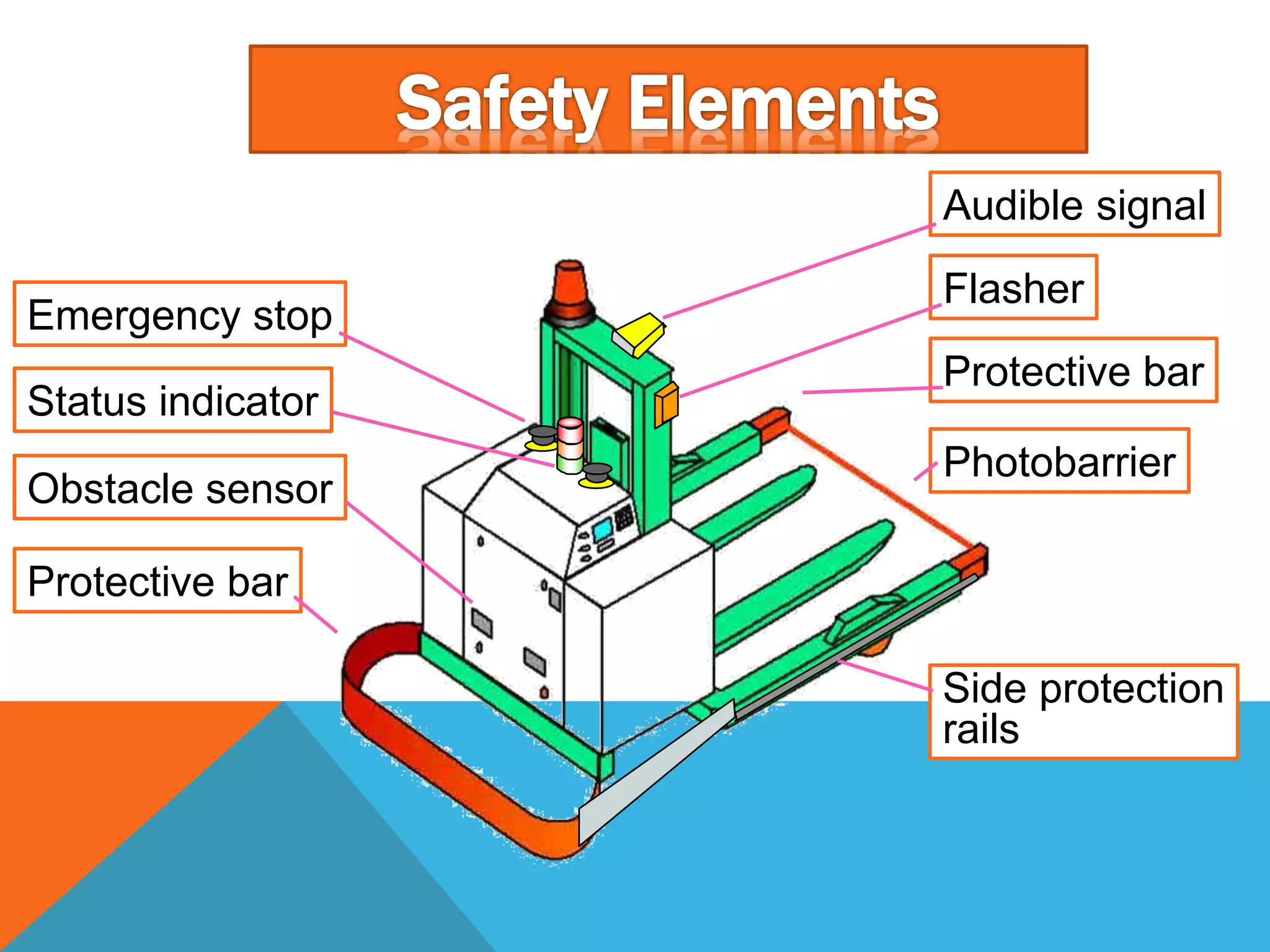
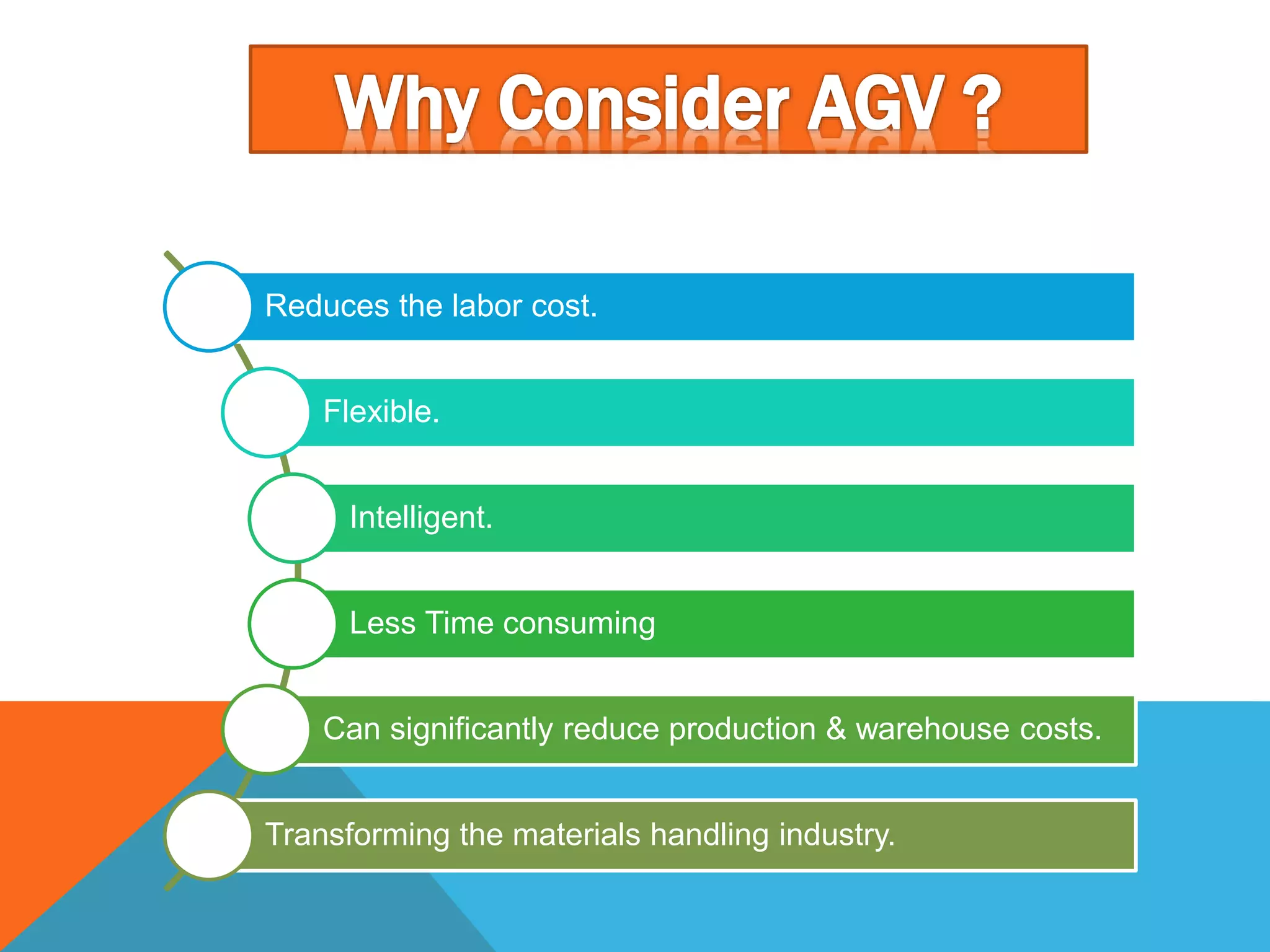
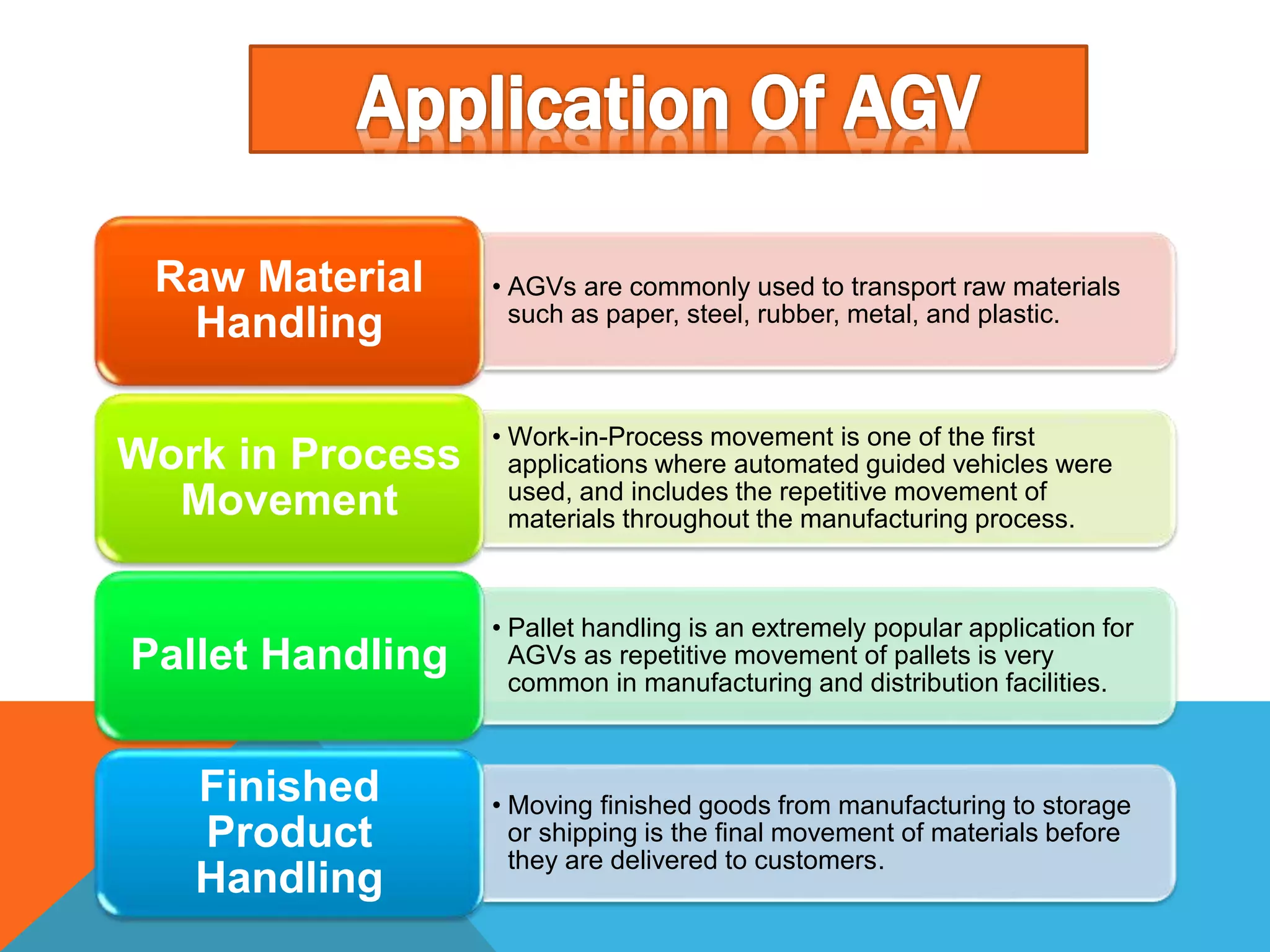
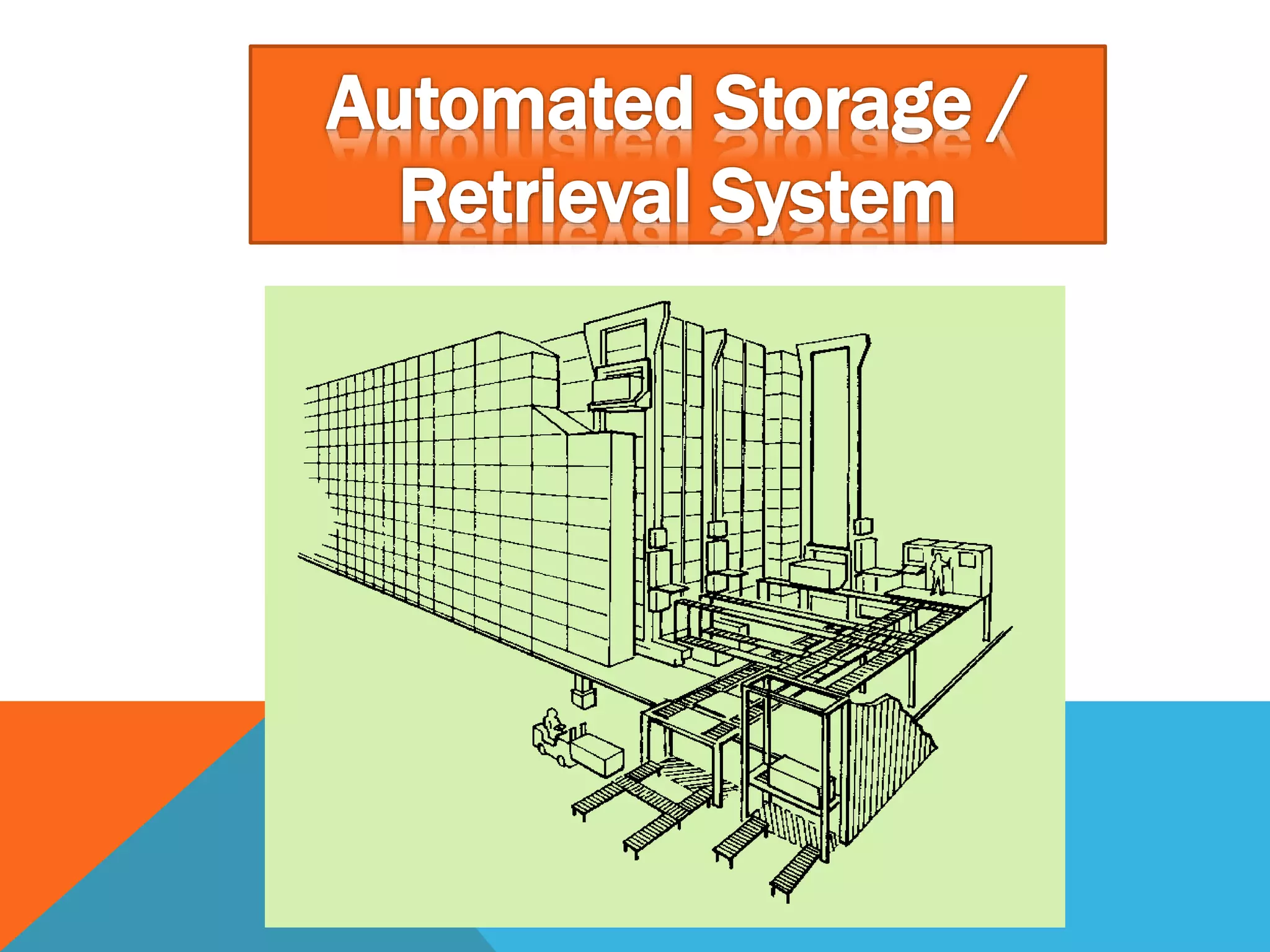
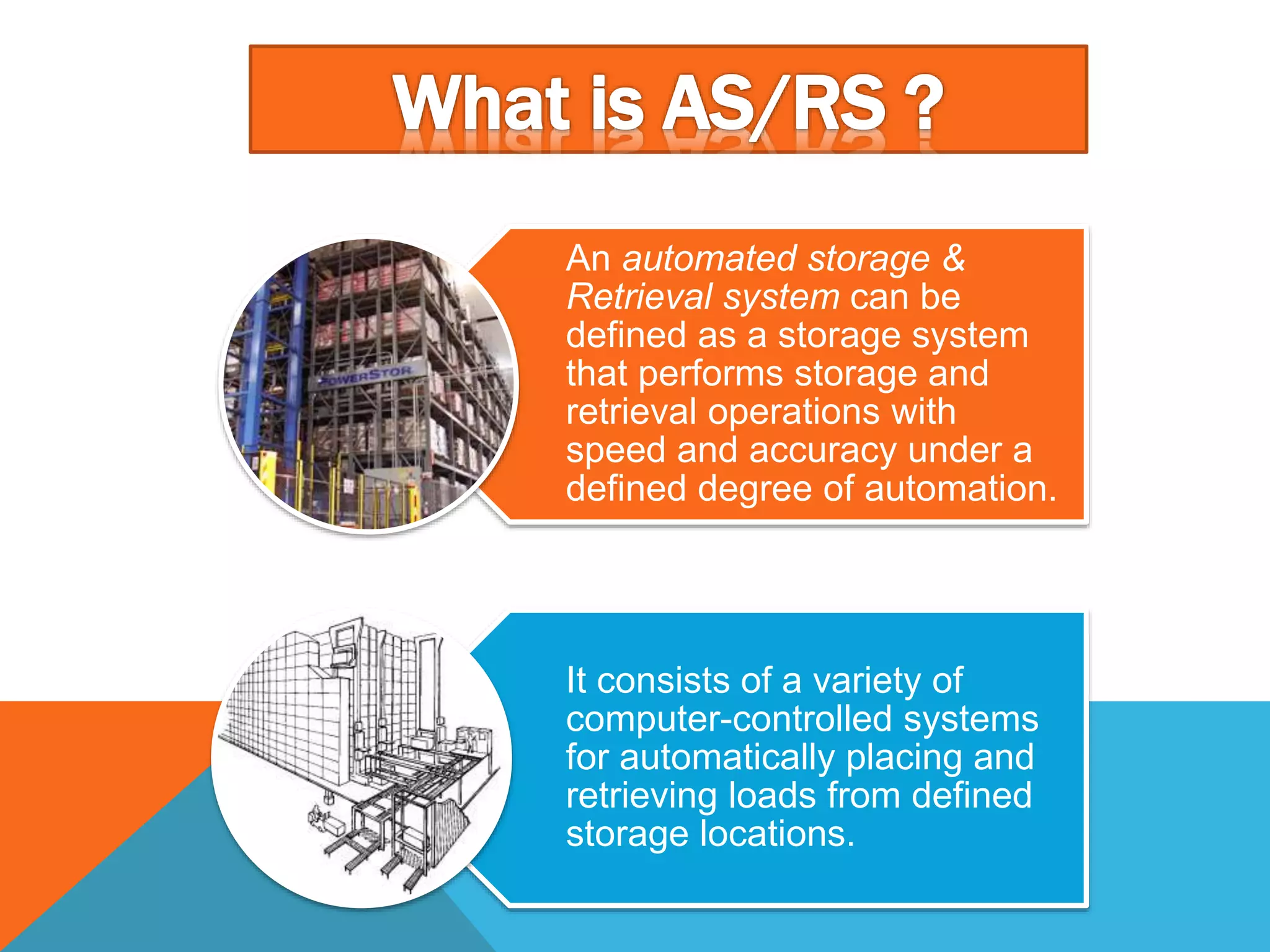
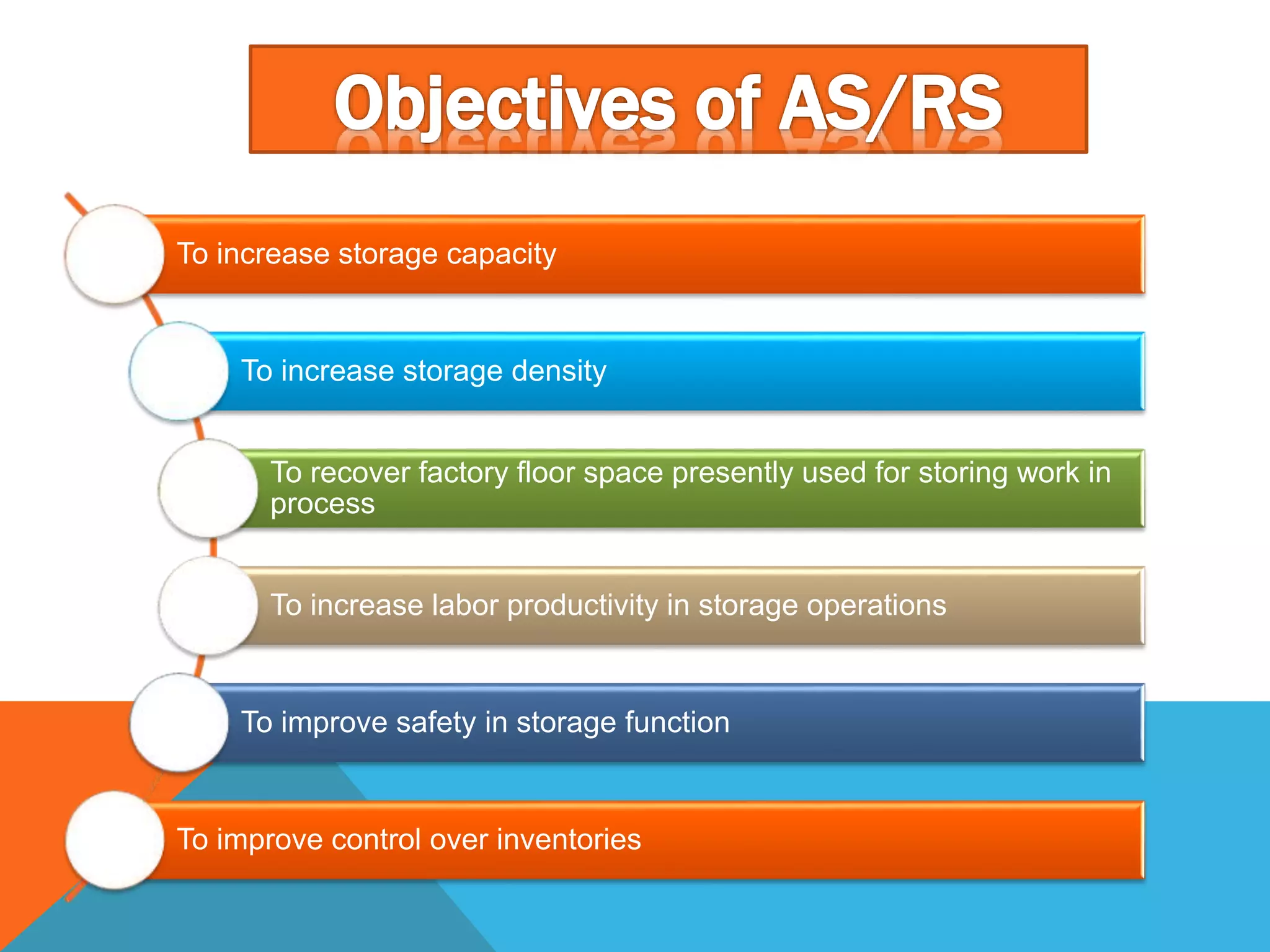
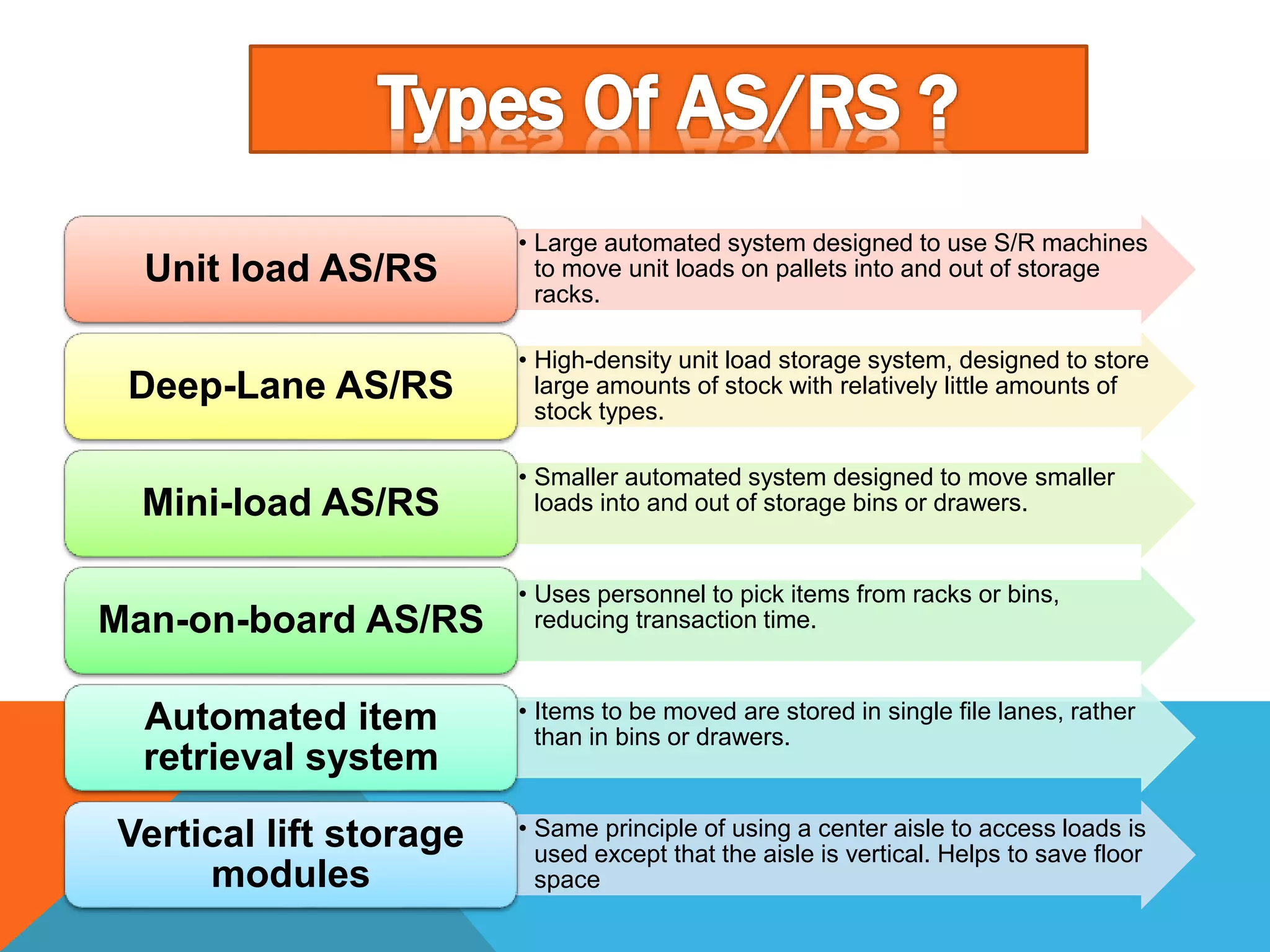
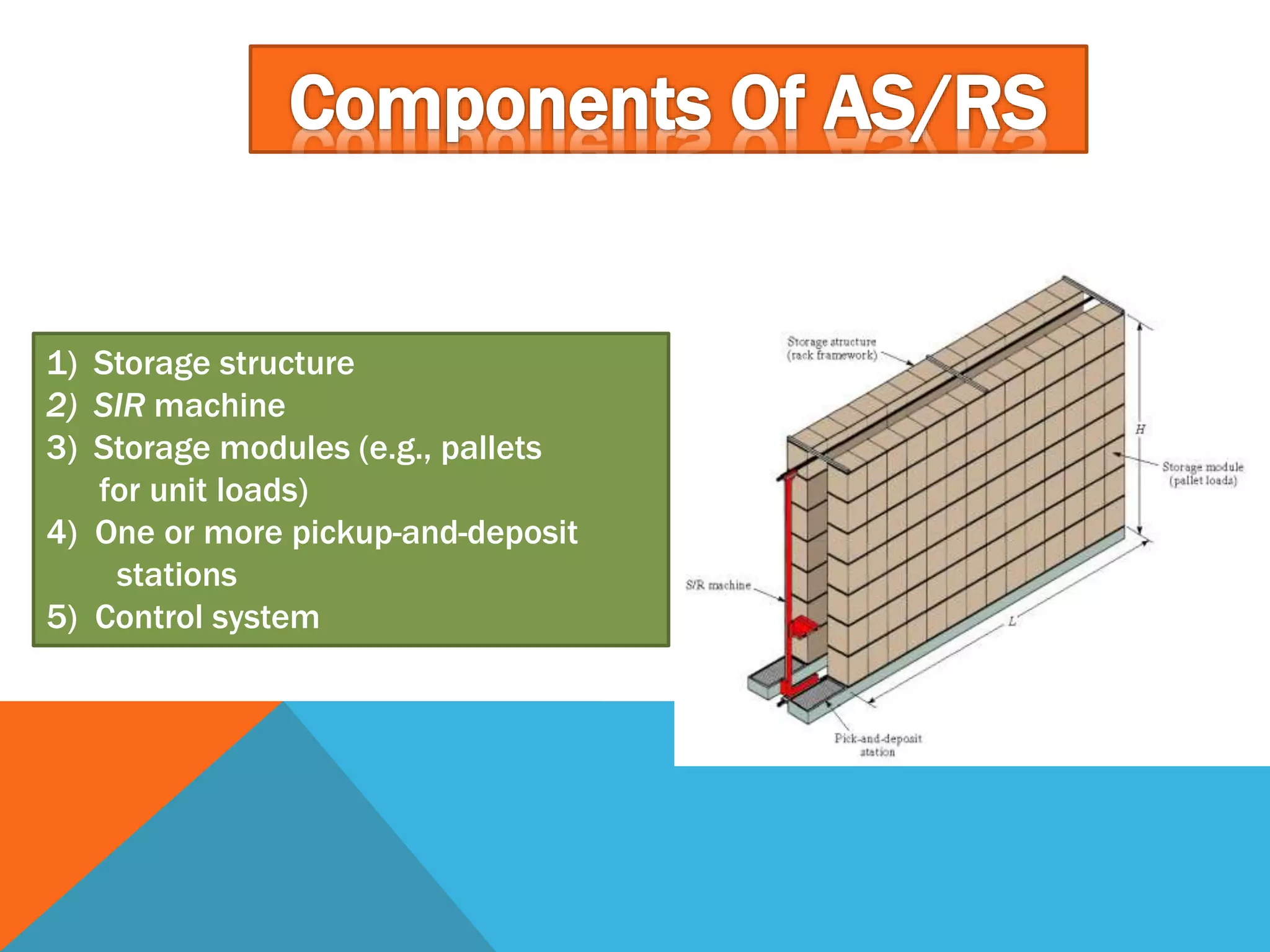
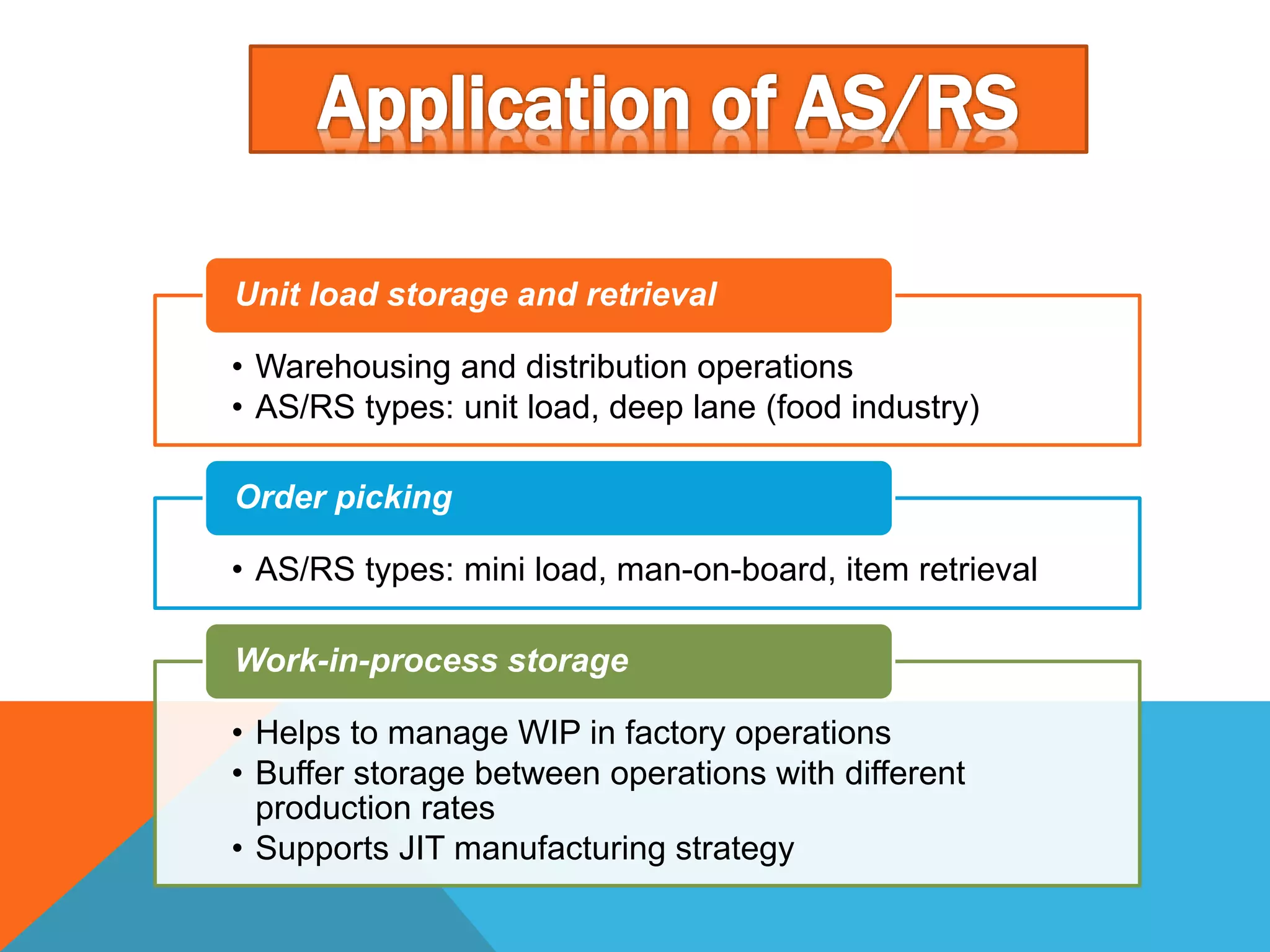
The document discusses automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS). It defines an AGV as a material handling system that uses self-propelled vehicles guided along defined pathways. It describes different types of AGVs including driverless trains, pallet trucks, and unit load carriers. It also explains various AGV navigation systems and functions. The document then defines an AS/RS as an automated storage system that stores and retrieves loads under computer control. It outlines the objectives and components of an AS/RS system and describes applications in warehousing, distribution and manufacturing.