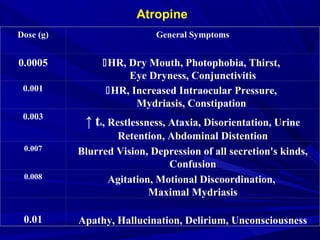
The document outlines the principles and treatments for managing adverse drug reactions (ADRs) and acute drug poisoning according to WHO guidelines. It details types of ADRs, statistics regarding their prevalence, and various treatment modalities including gastric decontamination and the use of antidotes. It also provides specific protocols for handling different classifications of drug reactions and associated symptoms.





















![ClozapineClozapine [non-typical Neuroleptic][non-typical Neuroleptic]
Drowsiness, Sedation, Delirium, Coma,Drowsiness, Sedation, Delirium, Coma, ⇓⇓BPBP,, ⇑⇑HR,HR,
hypersalivation,hypersalivation, RRespiratory Depression, Seizures.espiratory Depression, Seizures.
TreatmentTreatment::
Hypotension is treated with IV fluids,Hypotension is treated with IV fluids,
StrophanthineStrophanthine 0.025% 1 ml in 20 ml 0.9% NaCl IV,0.025% 1 ml in 20 ml 0.9% NaCl IV,
PrednisolonePrednisolone oror HydrocortisoneHydrocortisone..
Avoid Adrenaline and derivatives!!!Avoid Adrenaline and derivatives!!!
Seizures are treated withSeizures are treated with DiaDiazzepamepam oror GOBAGOBA;;
ArArrhythmias – withrhythmias – with DifeninDifenin;;
EExtrapyramidal reactions withxtrapyramidal reactions with BiperidineBiperidine oror
parenteralparenteral DimedroleDimedrole ((DiphenhytdramineDiphenhytdramine))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20poisonings-150722080135-lva1-app6891/85/Adverse-Drugs-Reactions-23-320.jpg)








![ClophelineClopheline ((ClonidineClonidine)) [α[α22-agonist]-agonist]
⇓⇓BPBP,, ⇓⇓HRHR,, ⇓⇓ttoo
, CNS and, respiratory depression,, CNS and, respiratory depression,
apnea, seizures, lethargy, irritability.apnea, seizures, lethargy, irritability.
TreatmentTreatment::
Gastric lavage, activated charcoal.Gastric lavage, activated charcoal.
VVasopressors –asopressors – Mesatone, NorepinephrineMesatone, Norepinephrine,,
ββ1 AM1 AM DobutamineDobutamine
AnalepticsAnaleptics Cordiamin, CaffeineCordiamin, Caffeine](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20poisonings-150722080135-lva1-app6891/85/Adverse-Drugs-Reactions-33-320.jpg)









