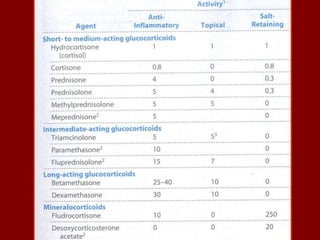
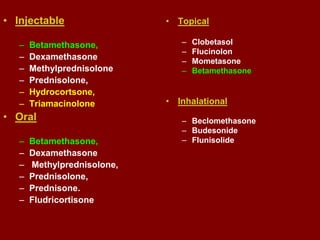
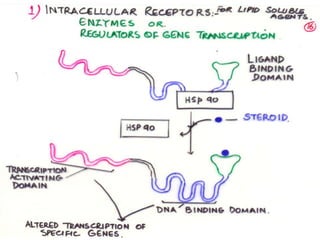
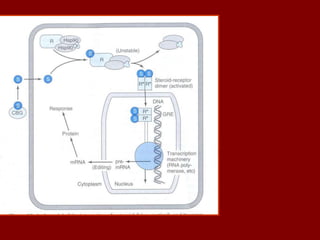
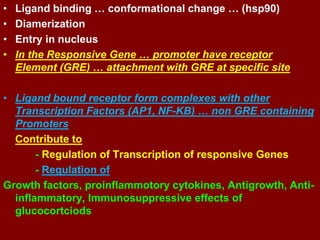
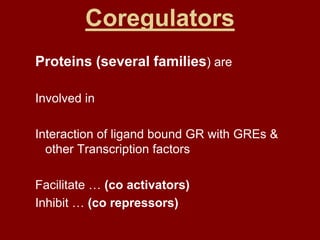
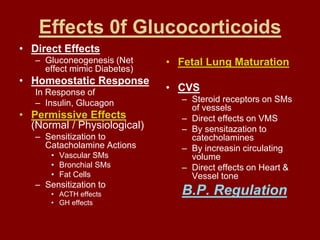
This document discusses adrenocortical hormones and corticosteroids. It begins by describing how corticosteroids are derived from cholesterol and the different zones of the adrenal cortex that produce glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, and androgens. It then covers the mechanisms of action of glucocorticoids like cortisol via glucocorticoid receptors, their therapeutic uses to treat inflammatory and autoimmune disorders, and their potential side effects. The document also discusses mineralocorticoids like aldosterone, their effects on sodium reabsorption, and synthetic alternatives like fludrocortisone. Inhibitors of corticosteroid synthesis and antagonists of mineralocorticoid receptors