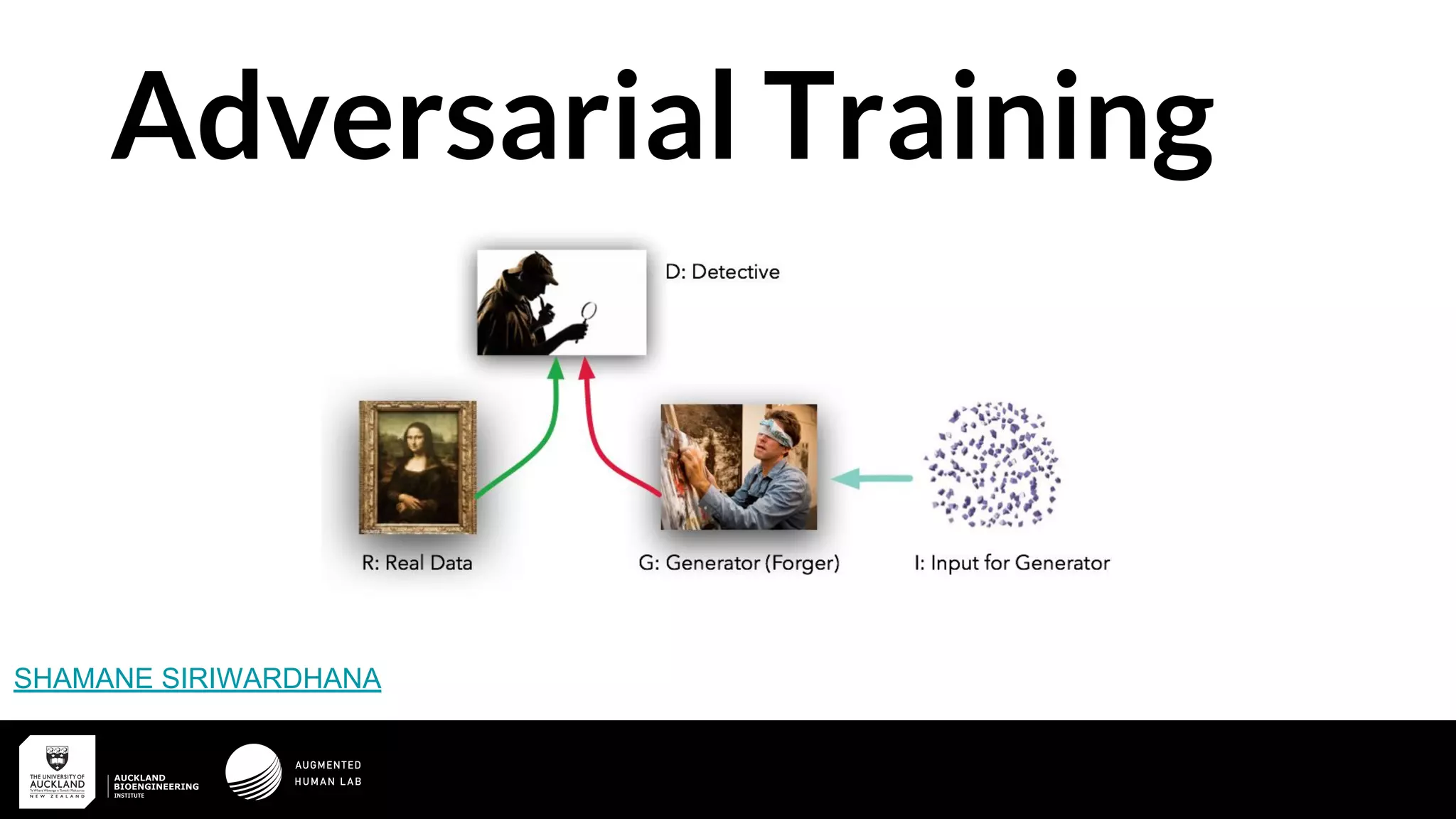
This document discusses generative adversarial networks (GANs) and their training process. It covers the basic GAN architecture of a generator and discriminator in an adversarial relationship. The training involves optimizing the discriminator to identify real vs. fake samples, while optimizing the generator to fool the discriminator and generate more realistic samples. Issues like discriminator saturation and mode collapse are addressed. Later sections discuss Wasserstein GANs and how they provide a more stable training approach using Earth Mover's distance as the loss function. Applications to imitation learning and visual navigation are also mentioned.