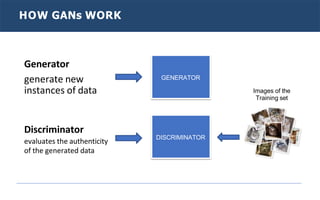
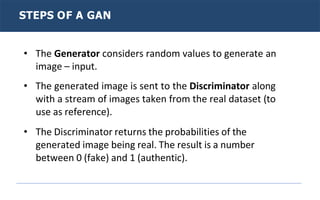
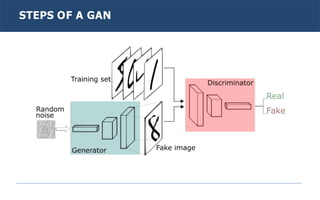
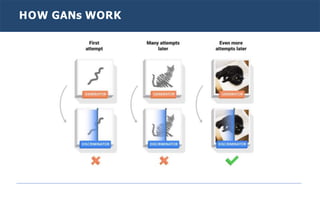
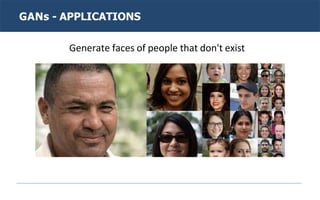
Generative adversarial networks (GANs) are a type of neural network introduced in 2014. GANs consist of two neural networks, a generator and discriminator, that compete against each other. The generator creates new data instances to fool the discriminator, while the discriminator evaluates whether instances are real or generated. Through this adversarial training process, GANs can generate highly realistic new images, text, and other data types. Common applications of GANs include image-to-image translation, super resolution, text-to-image generation, and more. Researchers continue advancing GAN techniques and exploring new applications.