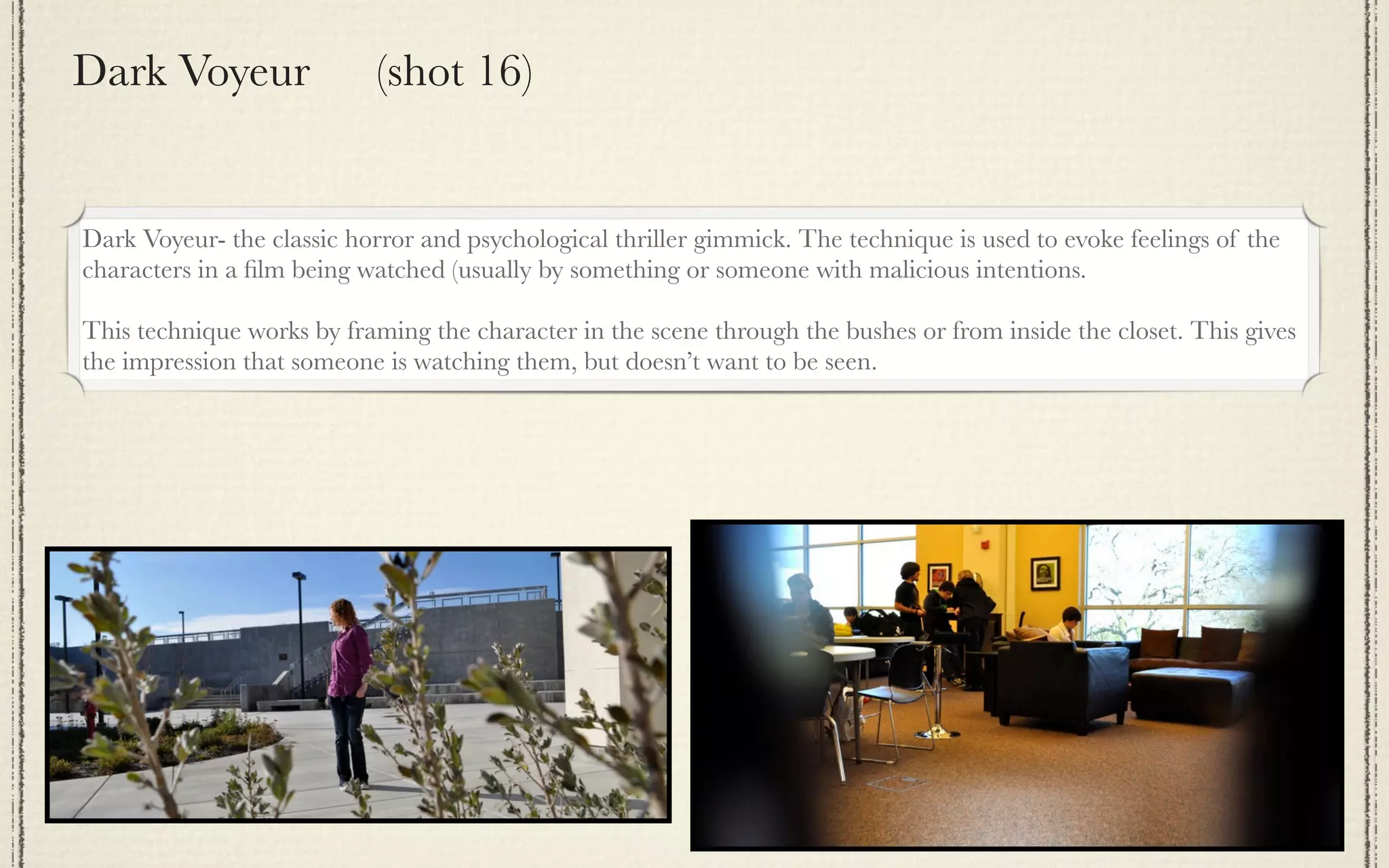
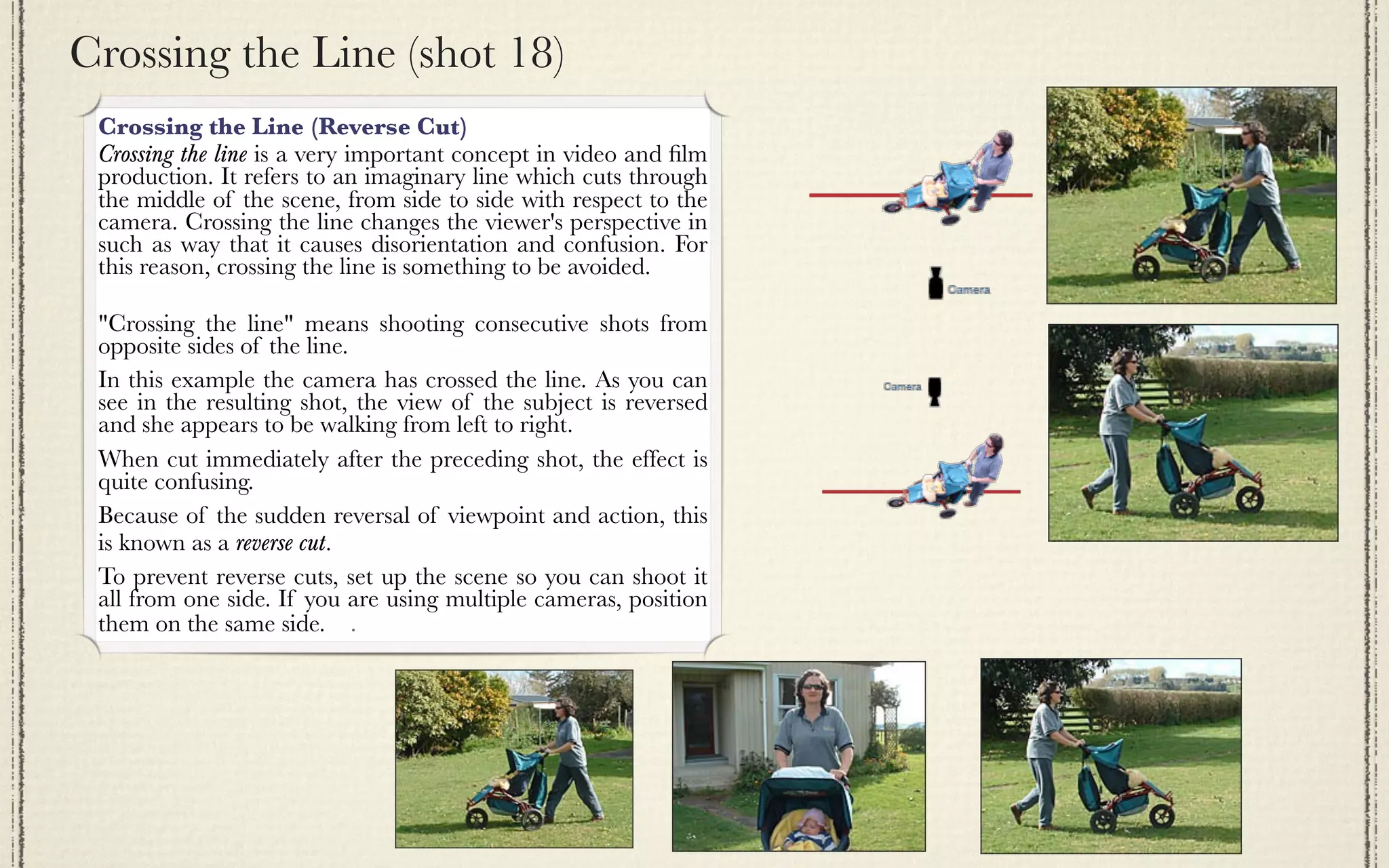
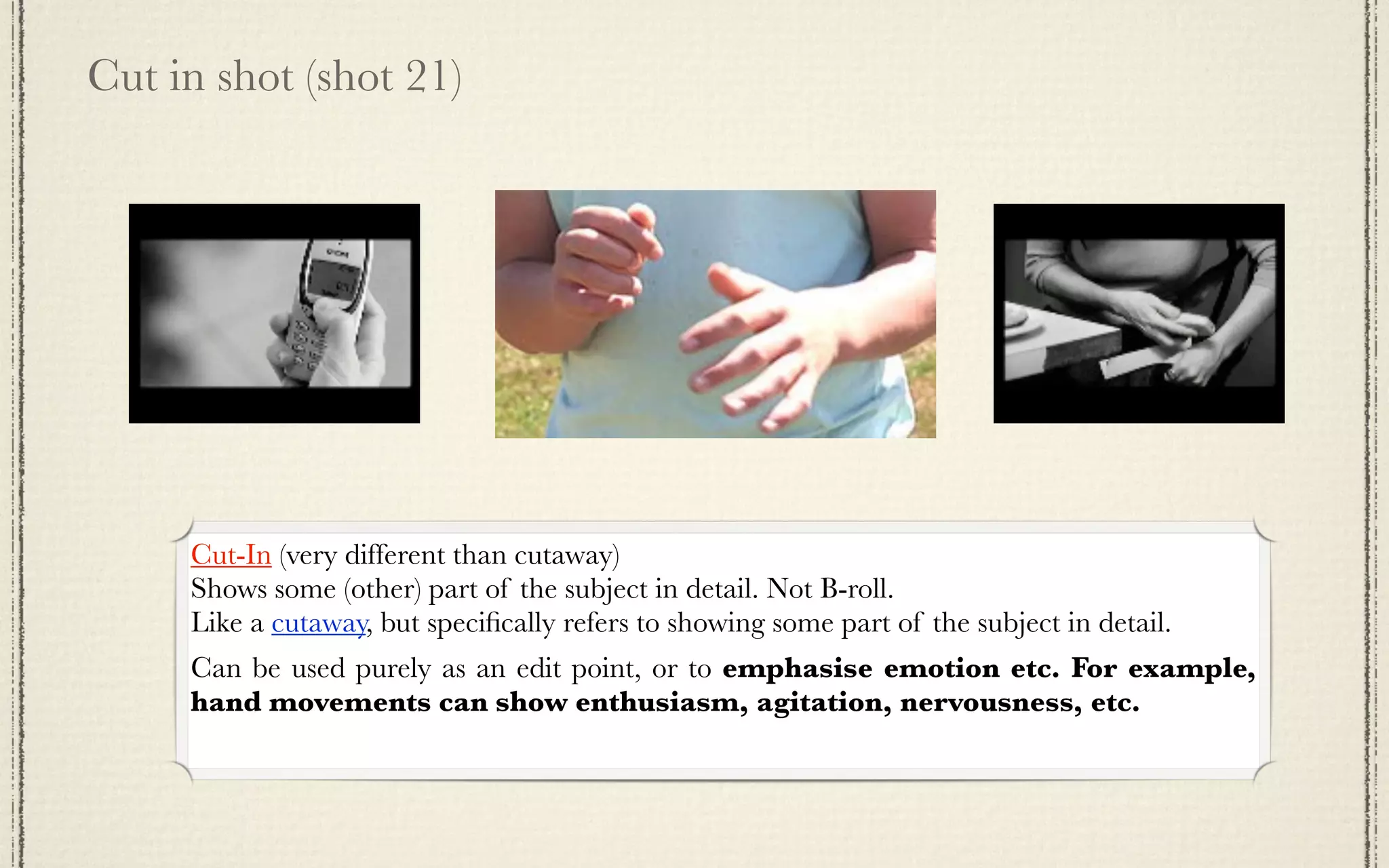
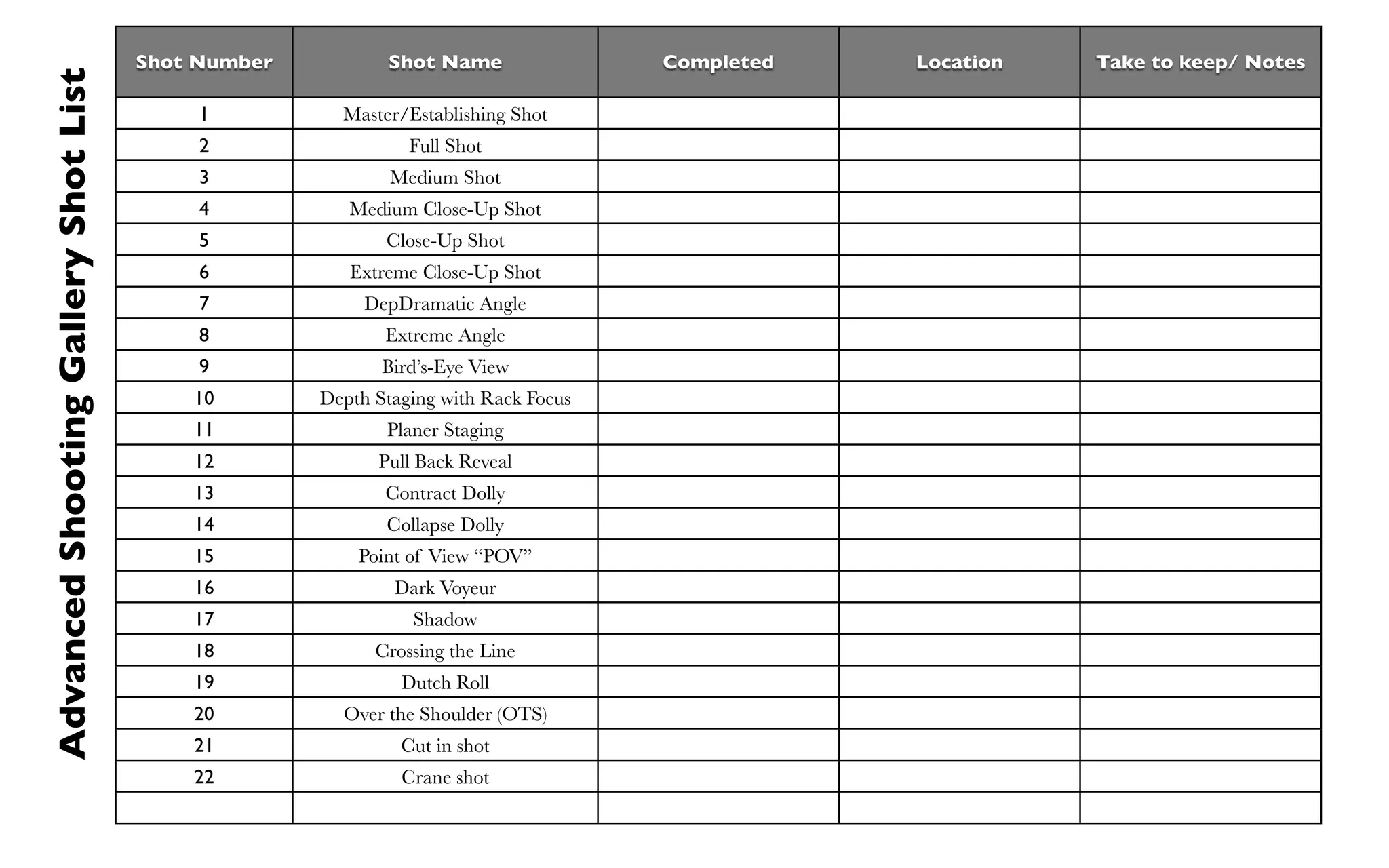
The document outlines a detailed plan for shooting a video project consisting of 22 specified camera shots, emphasizing themes and creative titles. It provides technical insights into various shot types, camera techniques, and the emotional impact of each shot on the audience. It also includes tips for editing and framing to enhance storytelling in film production.