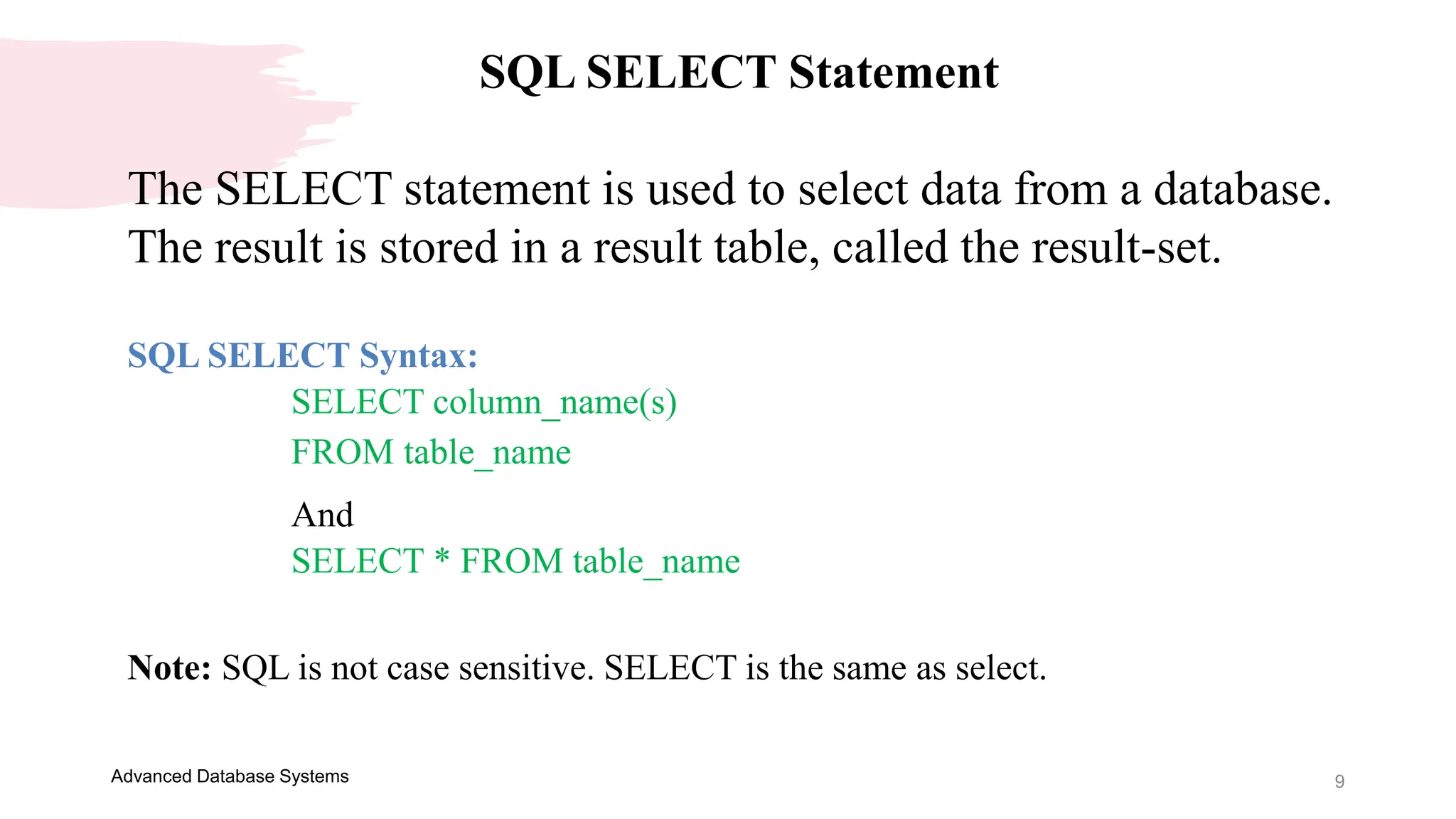
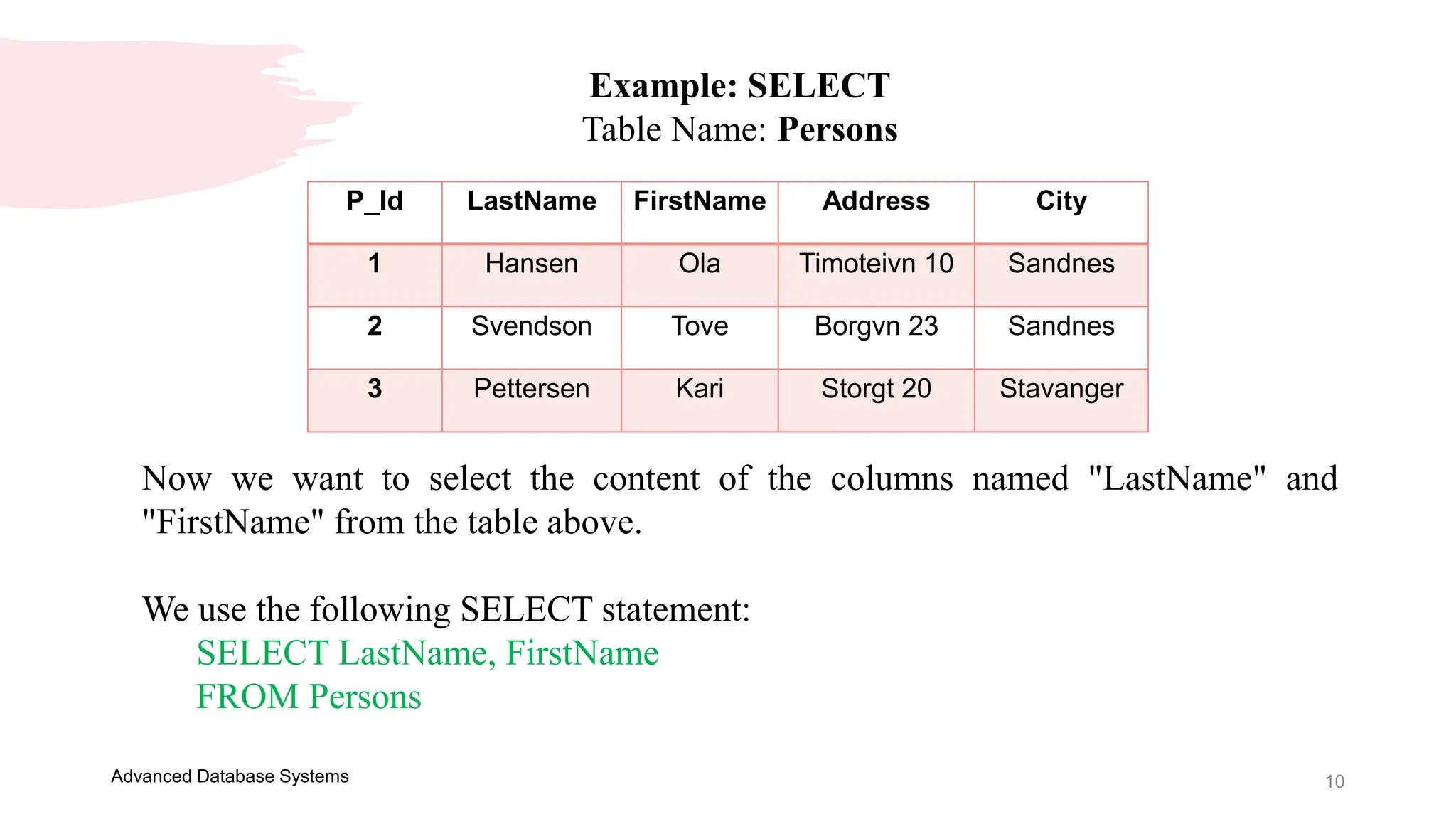
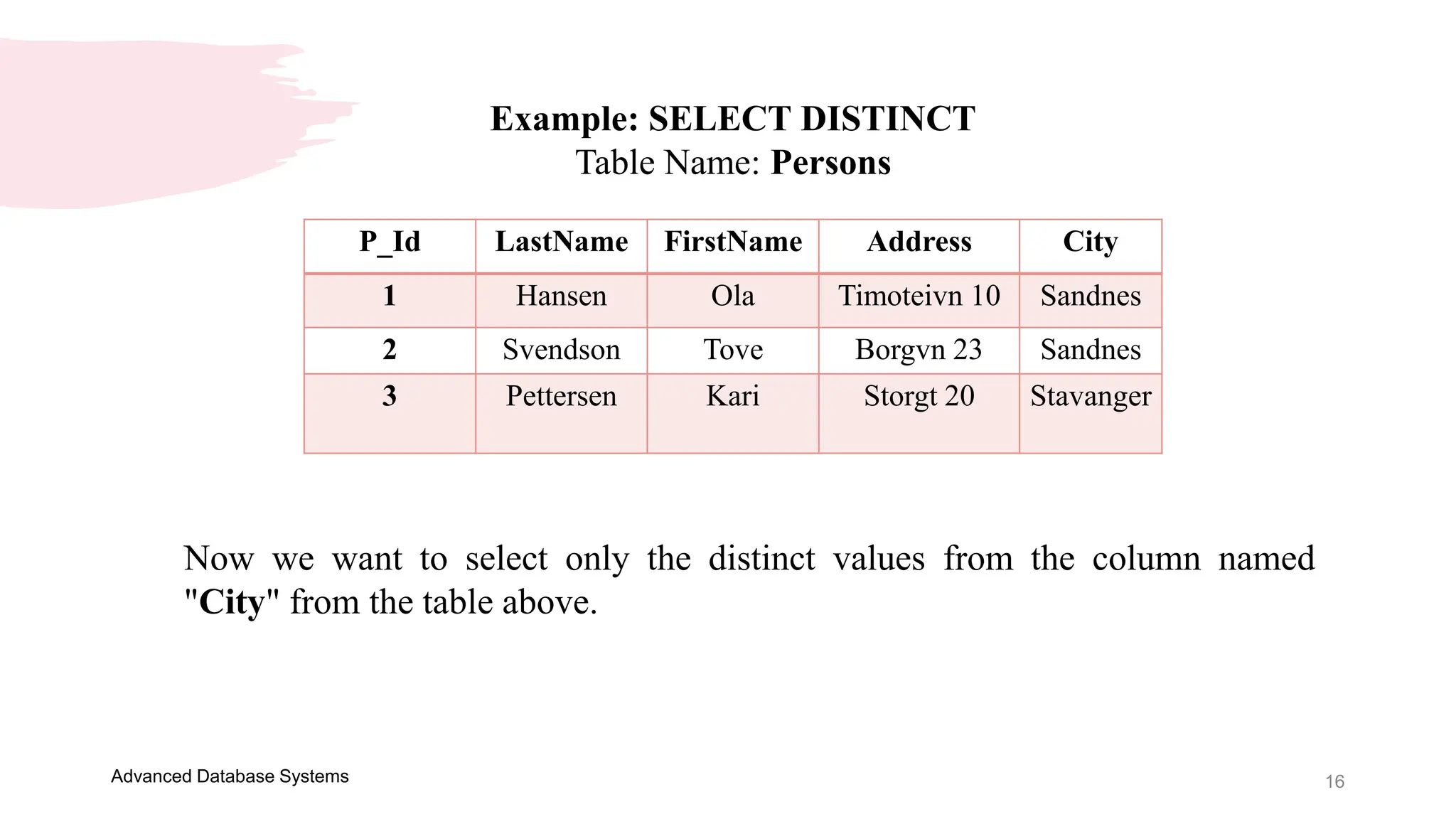
This document provides an overview of an Advanced Database Systems course. It discusses how SQL can be used to retrieve data from multiple tables using joins and subqueries. It also defines the Data Manipulation Language and Data Definition Language components of SQL. Examples are provided of key SQL statements like SELECT, SELECT DISTINCT, CREATE TABLE, ALTER TABLE and DROP TABLE. The SELECT statement is used to query and retrieve data from one or more tables, with the ability to select all columns or specific columns.