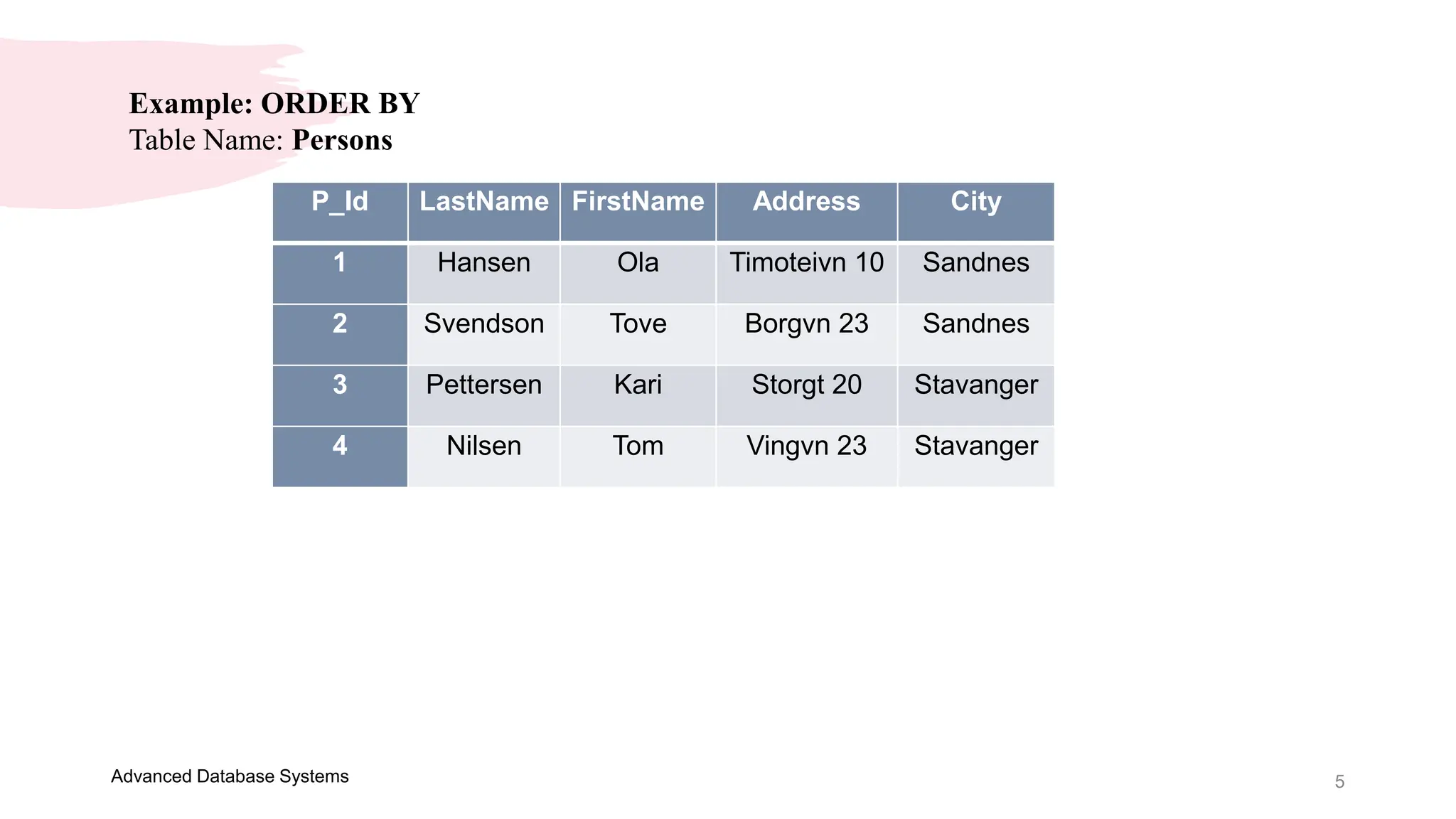
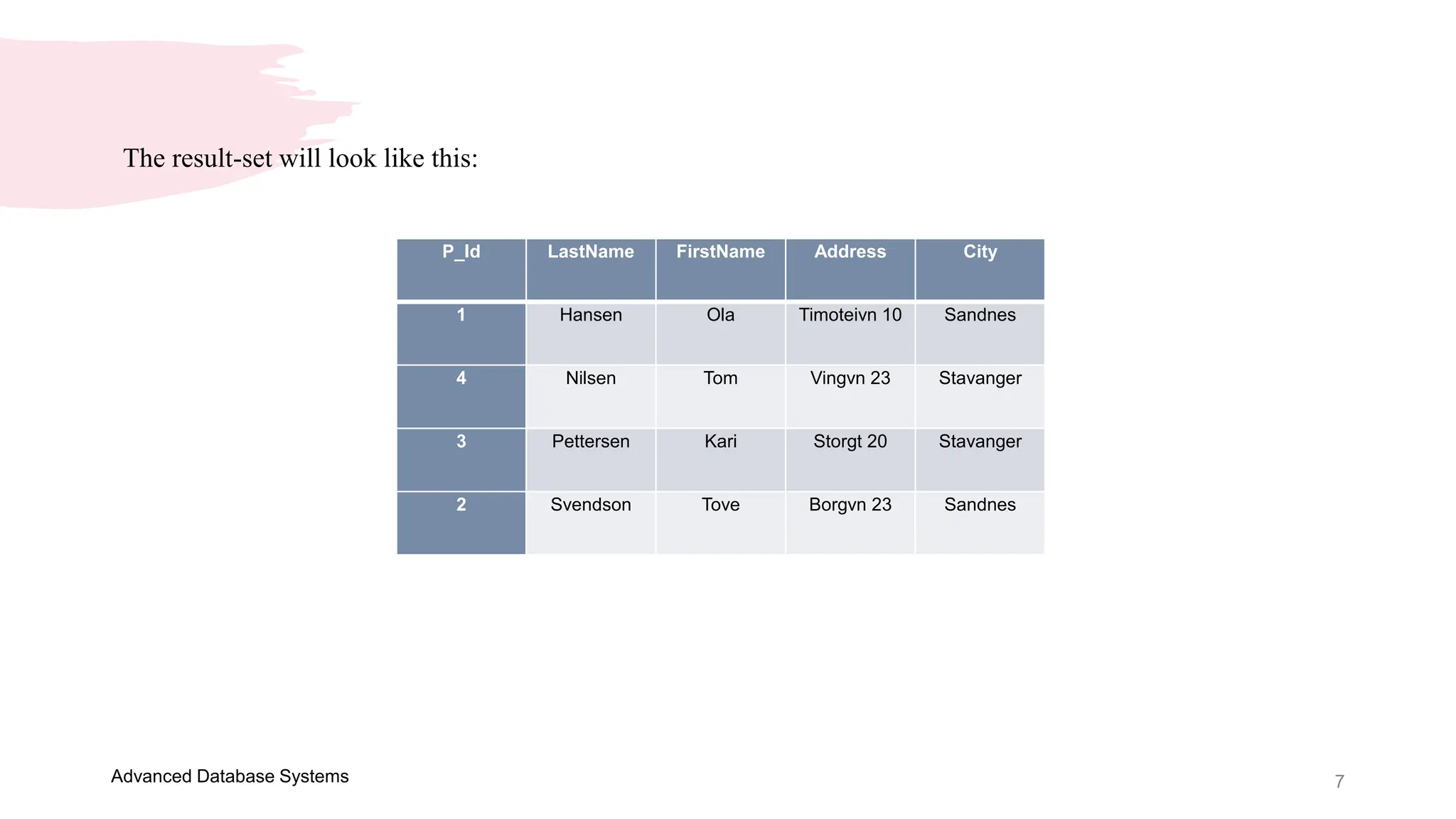
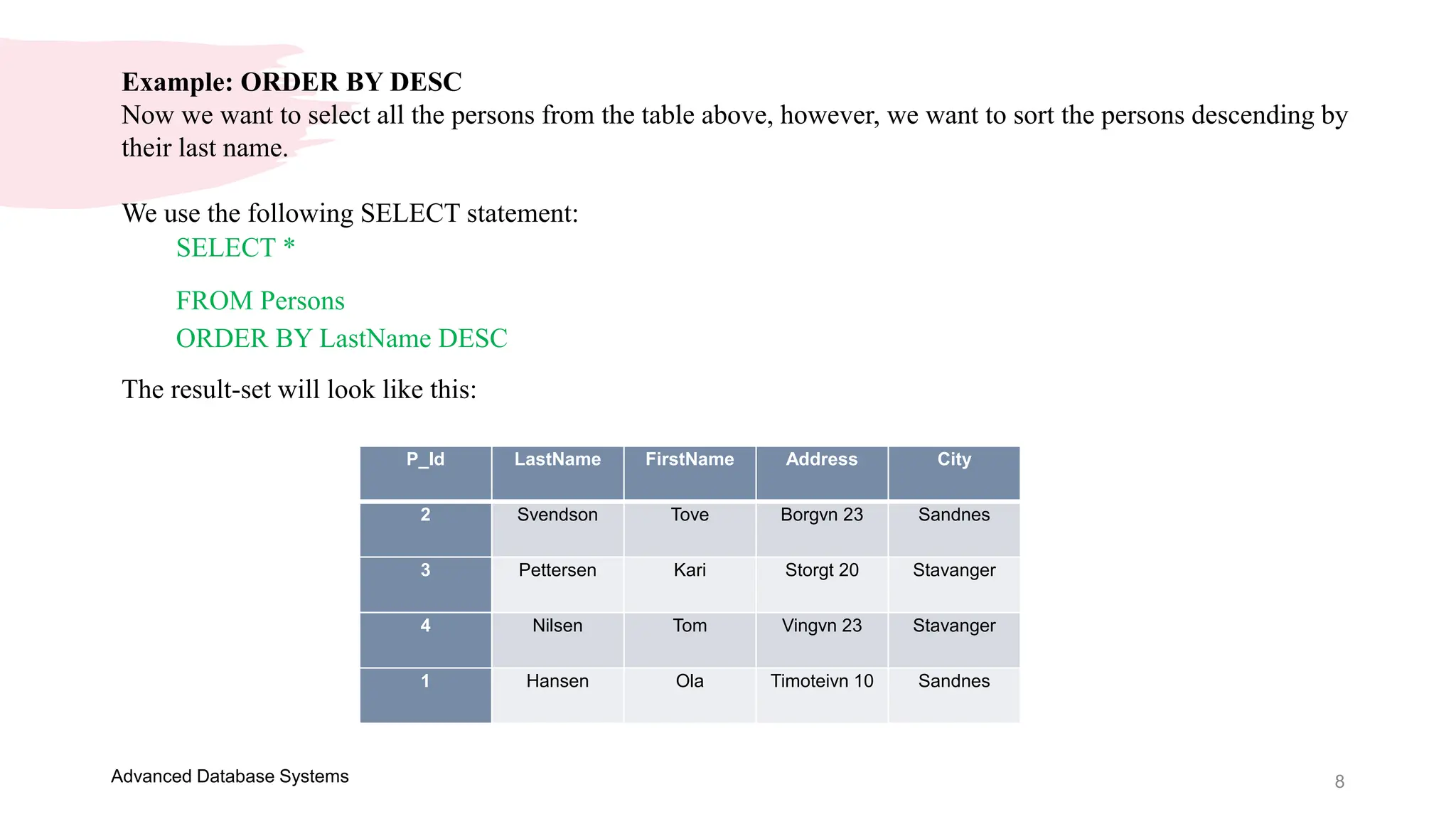
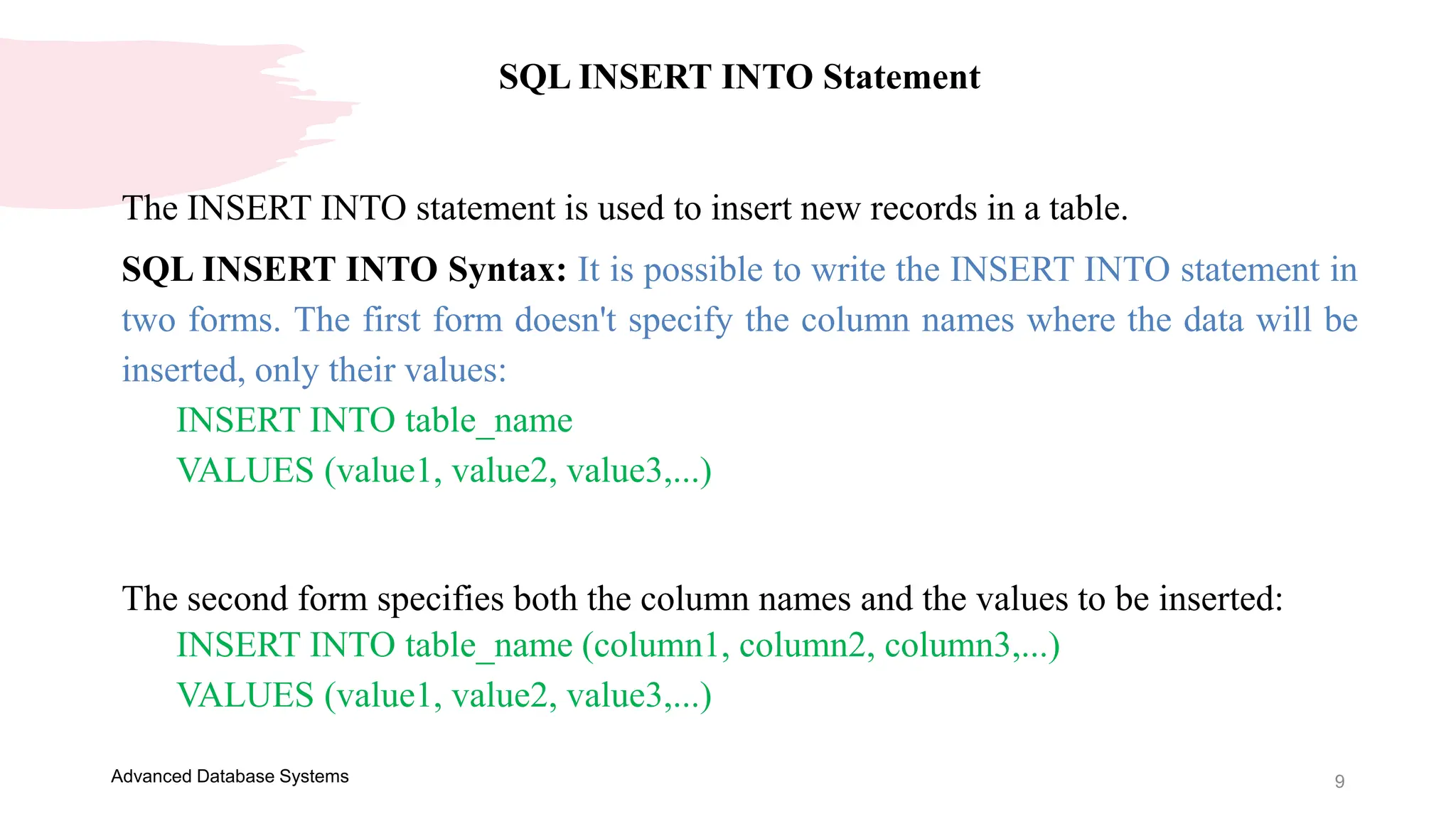
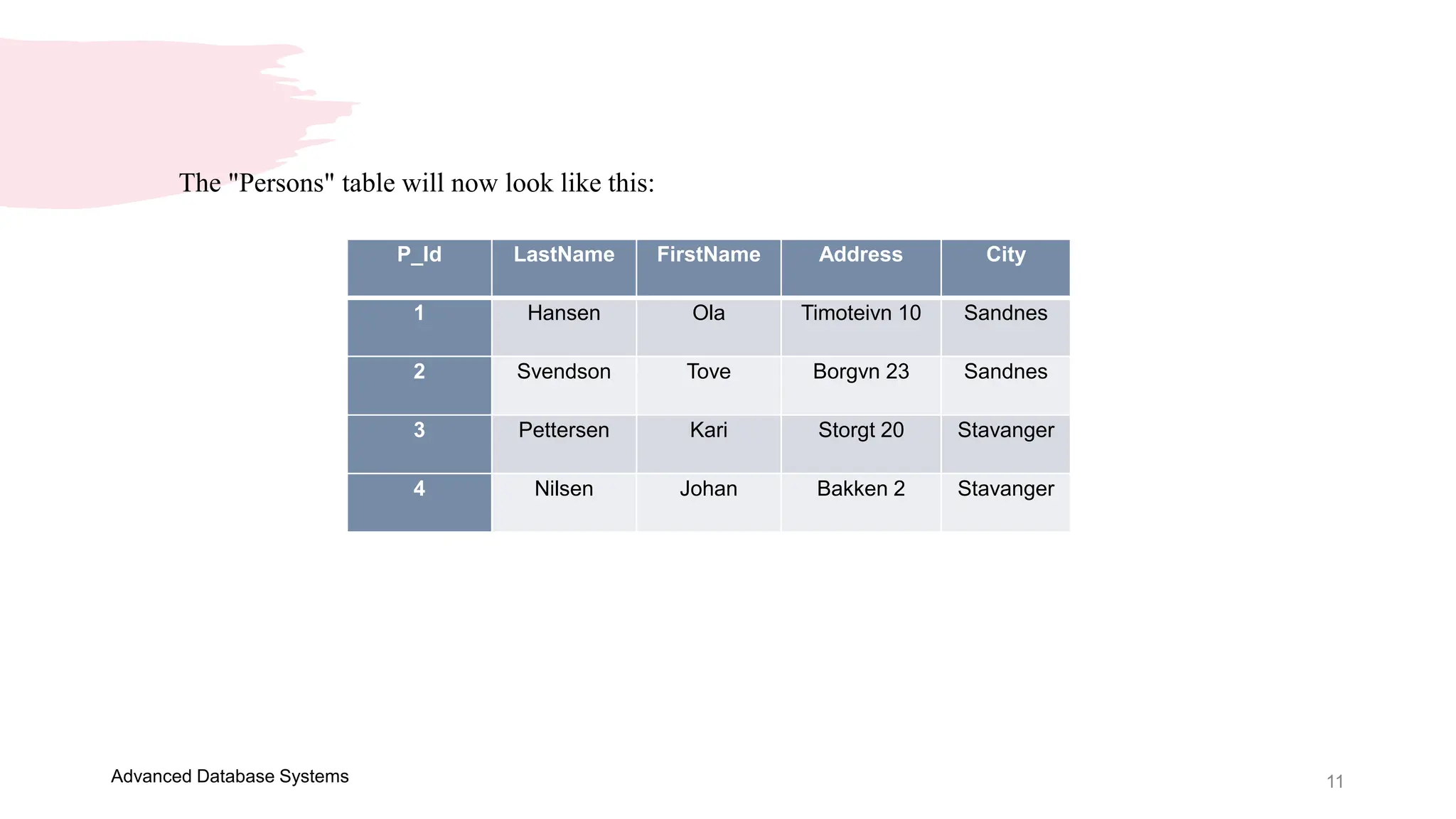
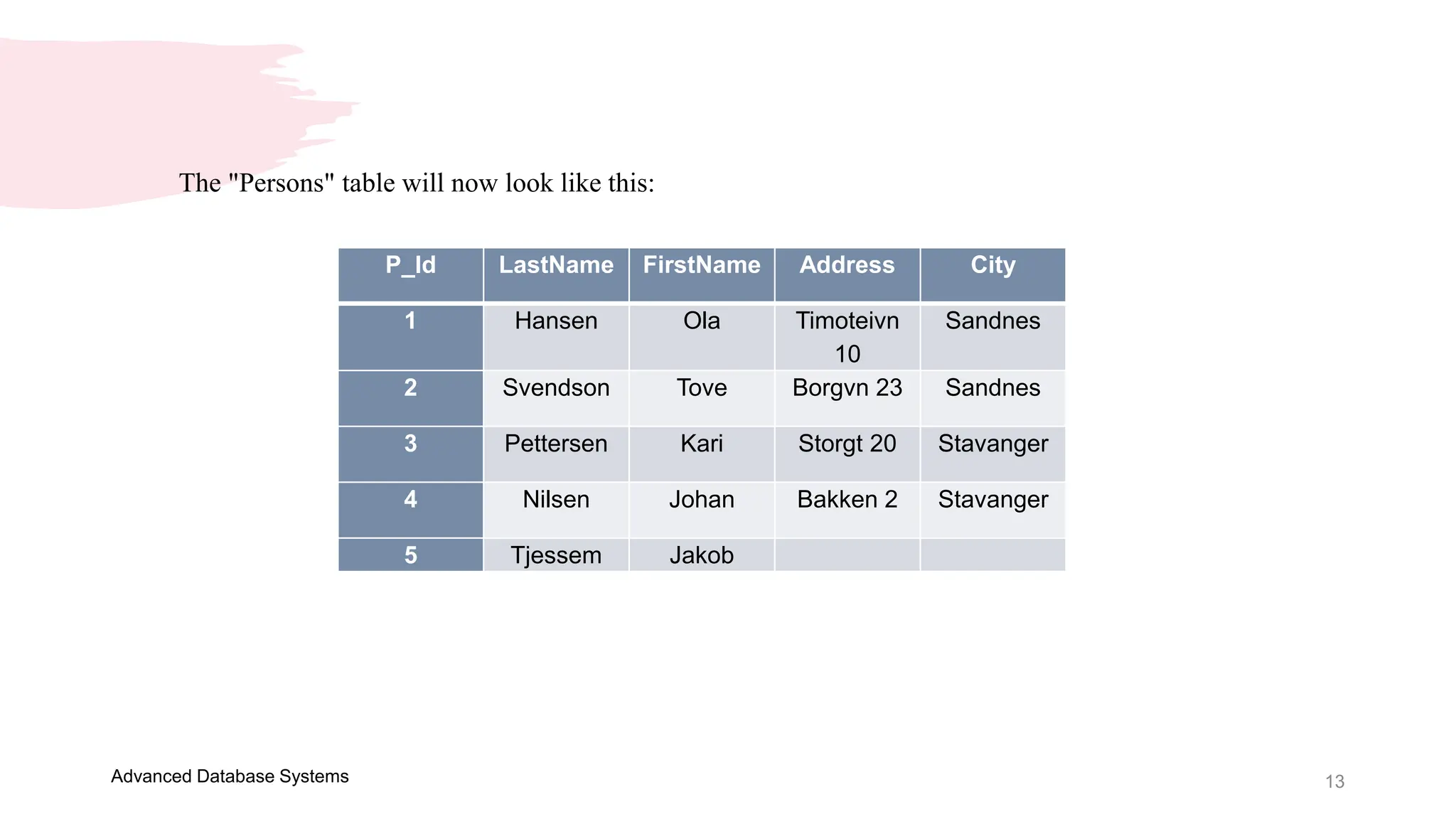
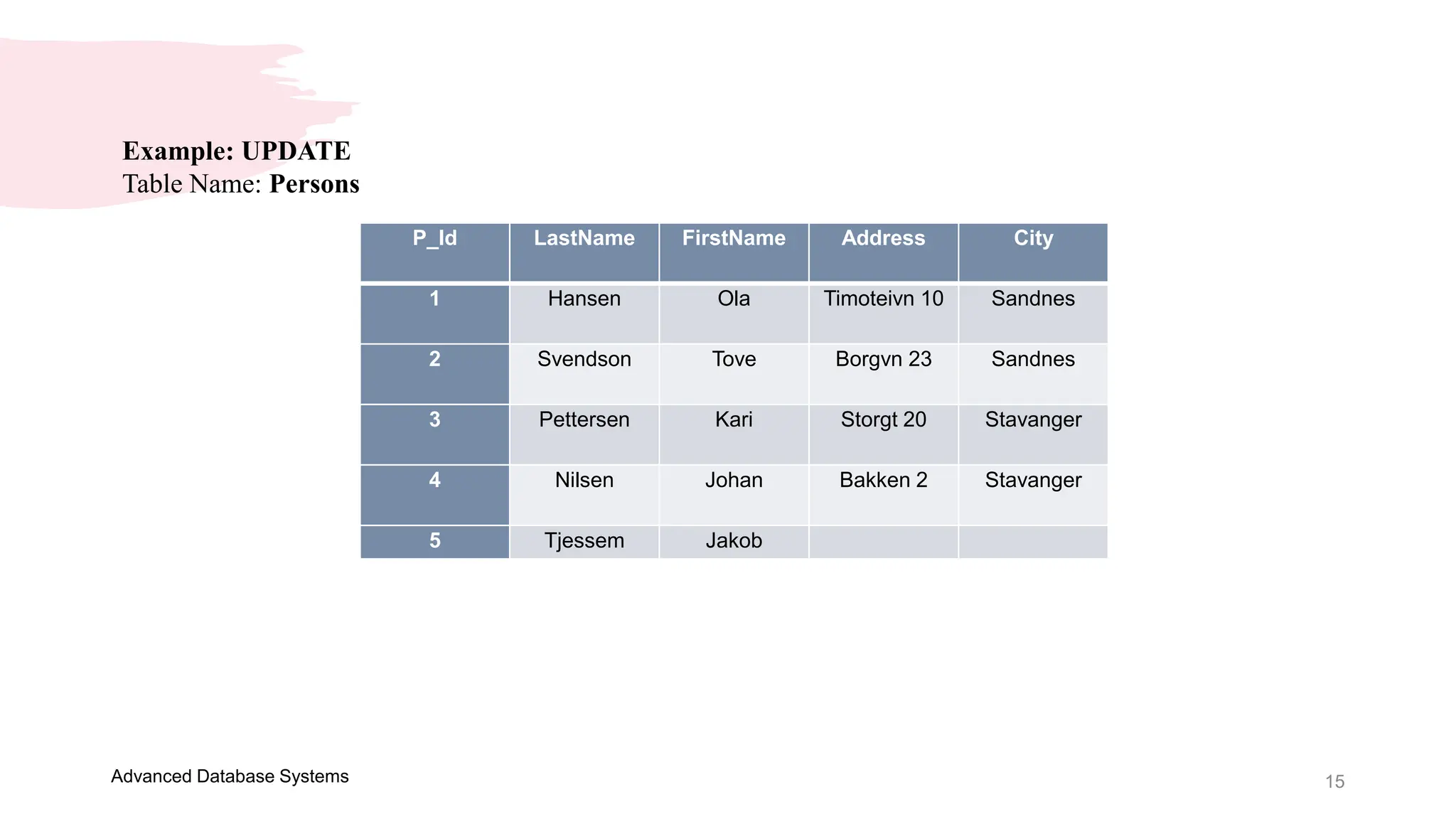
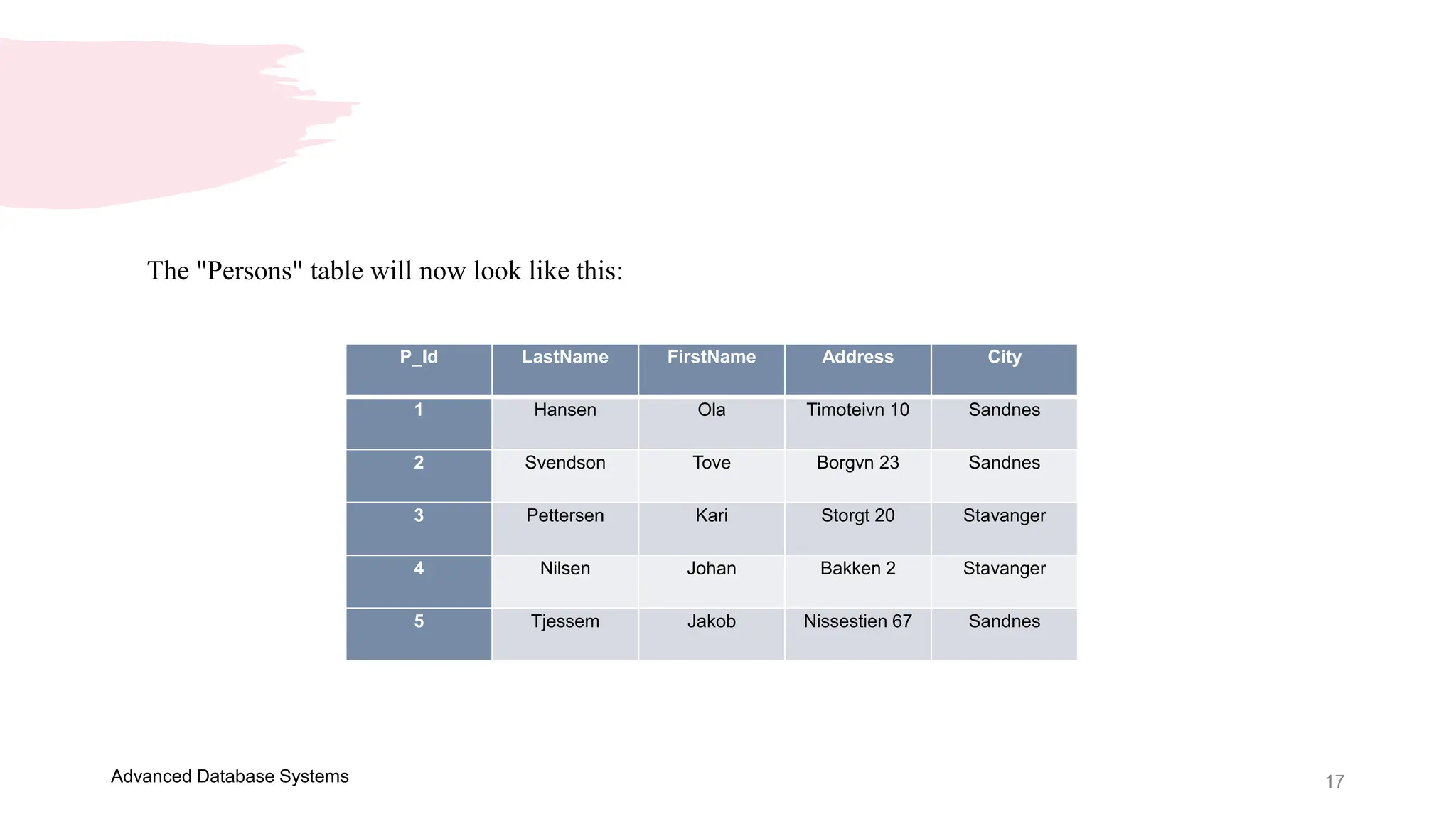
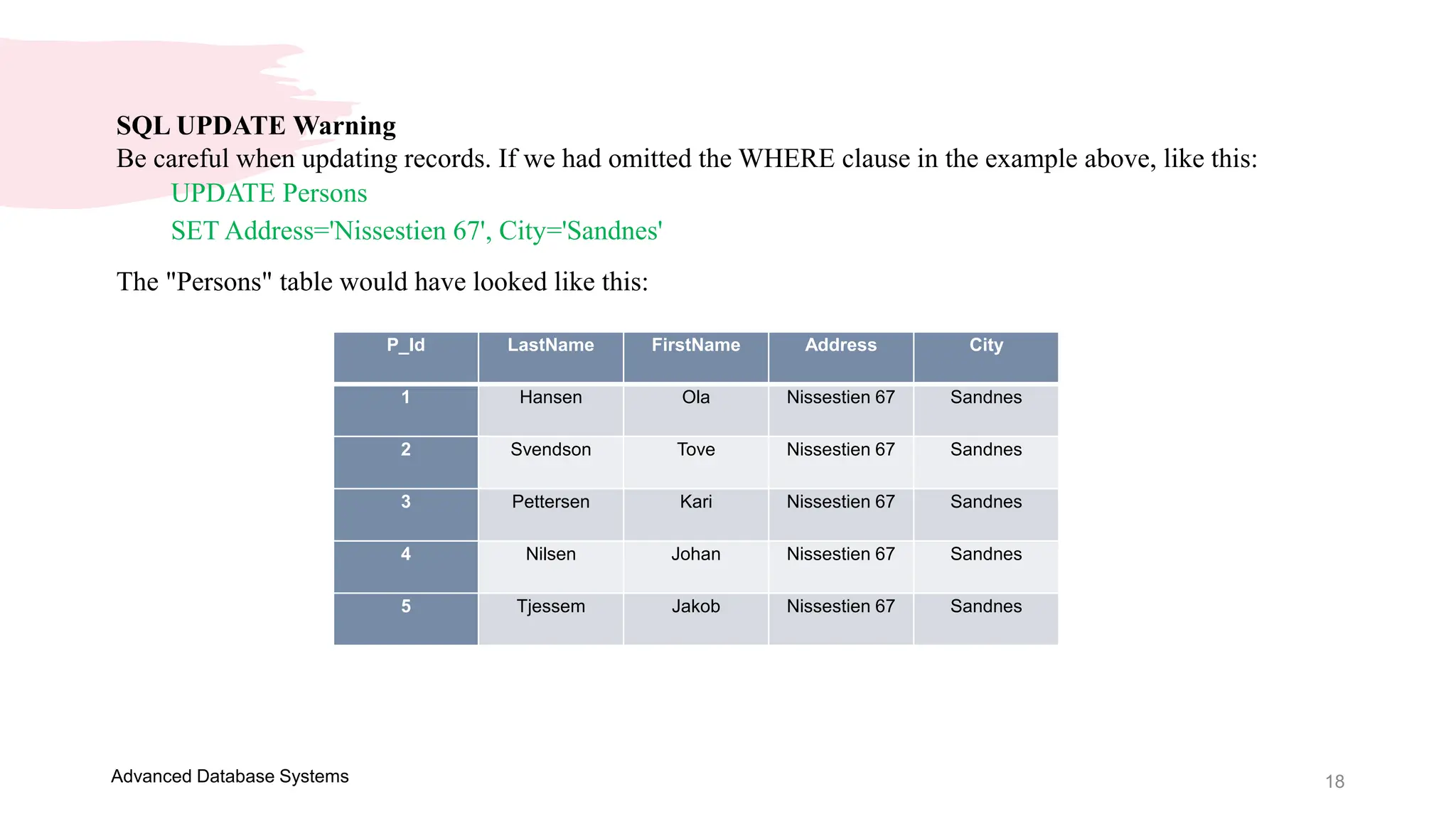
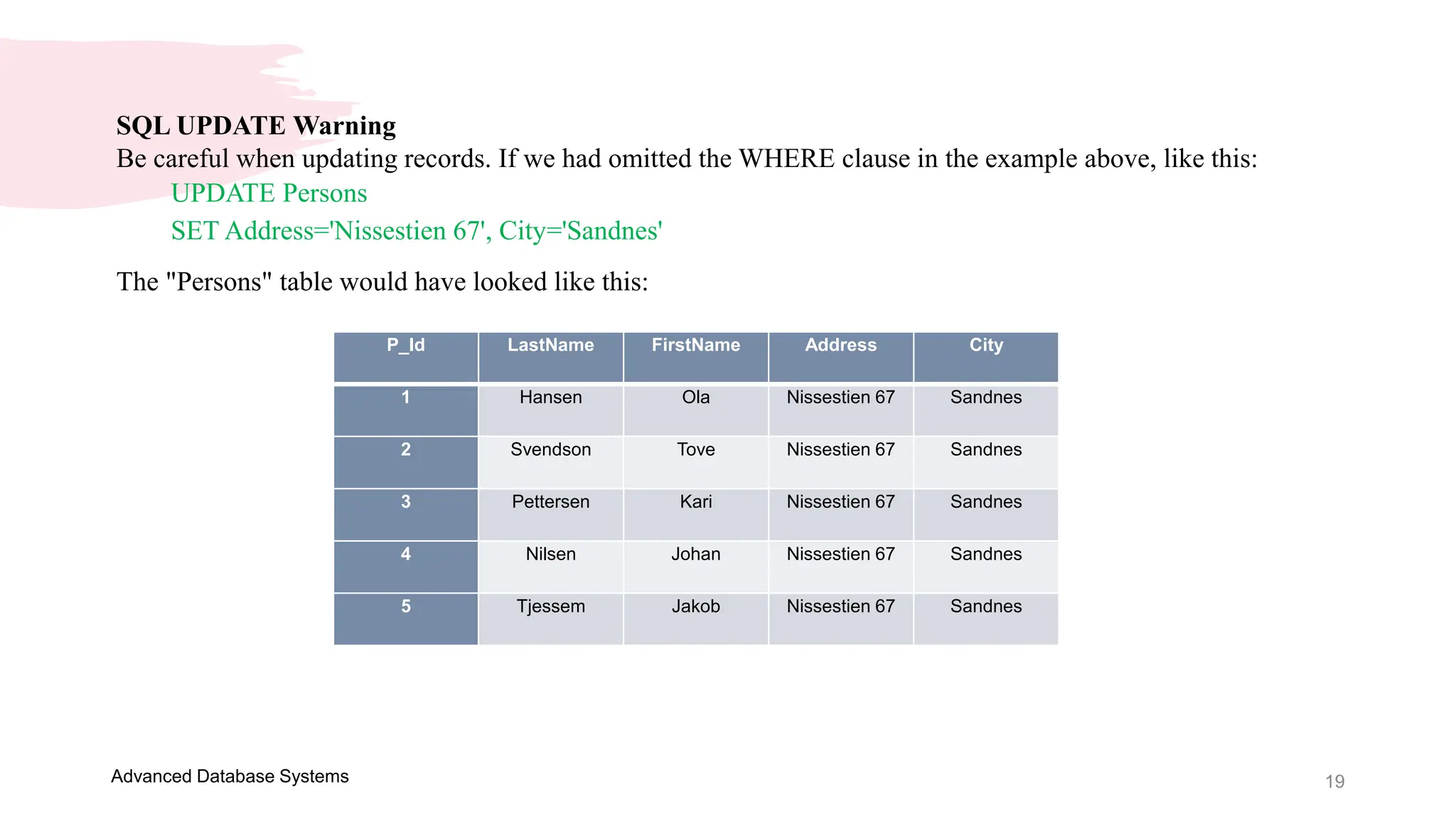
This document provides an overview of a course on Advanced Database Systems taught by Ellen Grace Porras. It covers topics like querying multiple tables using joins and subqueries, sorting result sets using ORDER BY, and modifying data using SQL statements like INSERT, UPDATE. Examples are provided on ordering results in ascending and descending order based on a column. Additional examples demonstrate inserting new records into a table, as well as updating existing records and the importance of the WHERE clause to target specific records for updating.