Here are the answers to the quiz questions:
1. A database is a structured collection of related data.
2. Data is a collection of facts made up of text, numbers and dates. Information is the meaning given to data in the way it is interpreted.
3. Examples of data: name, age, address. Examples of information: Mr. Smith is 35 years old and lives at 123 Main St.
4. SQL is Structured Query Language, which is a computer language for storing, manipulating and retrieving data stored in relational database.
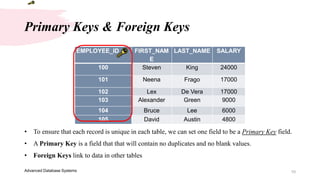
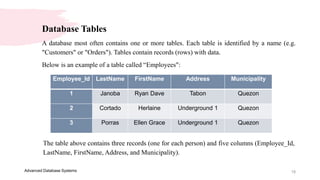
5. A Primary Key is a field that that will contain no duplicates and no blank values.
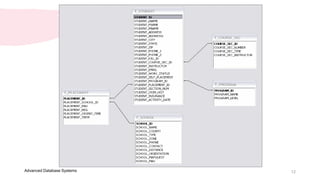
6. The 3 basic database concepts are: table